Dada una lista enlazada individualmente, gire la lista enlazada en sentido contrario a las agujas del reloj por k Nodes. Donde k es un entero positivo dado. Por ejemplo, si la lista enlazada dada es 10->20->30->40->50->60 y k es 4, la lista debe modificarse a 50->60->10->20->30- >40. Suponga que k es menor que el número de Nodes en una lista enlazada.
Método 1:
para rotar la lista enlazada, necesitamos cambiar el siguiente Node k-ésimo a NULL, el siguiente del último Node al Node principal anterior y, finalmente, cambiar el Node principal a (k+1) Node. Así que necesitamos conseguir tres Nodes: k-ésimo Node, (k+1)-ésimo Node y último Node.
Recorra la lista desde el principio y deténgase en el k-ésimo Node. Almacene el puntero al k-ésimo Node. Podemos obtener (k+1) Node usando kthNode->next. Continúe recorriendo hasta el final y almacene un puntero al último Node también. Finalmente, cambie los punteros como se indicó anteriormente.
La imagen a continuación muestra cómo funciona la función de rotación en el código:
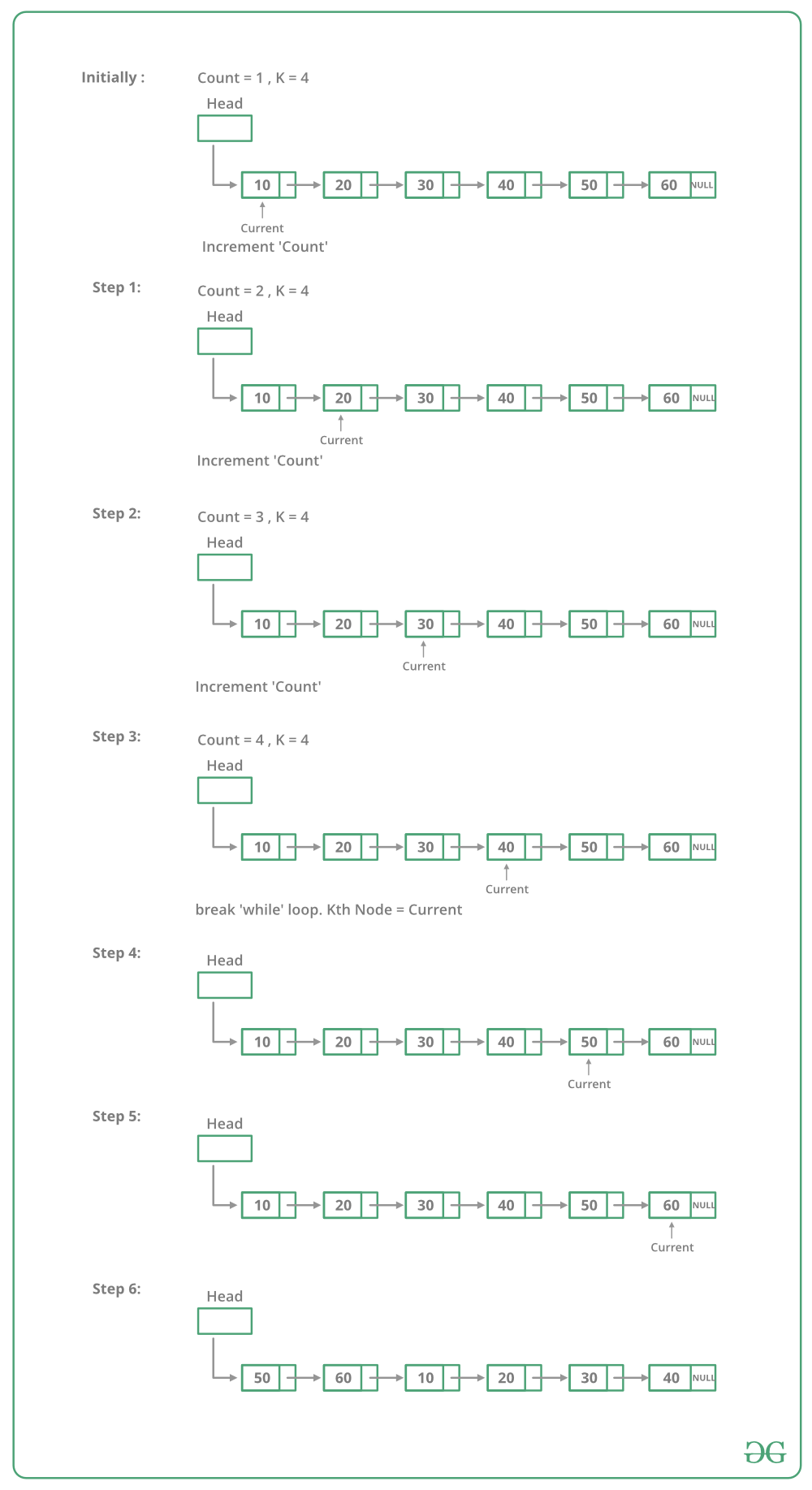
Python
# Python program to rotate # a linked list # Node class class Node: # Constructor to initialize # the node object def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None class LinkedList: # Function to initialize head def __init__(self): self.head = None # Function to insert a new node # at the beginning def push(self, new_data): # allocate node and put the data new_node = Node(new_data) # Make next of new node as head new_node.next = self.head # Move the head to point to the # new Node self.head = new_node # Utility function to print it the # linked LinkedList def printList(self): temp = self.head while(temp): print temp.data, temp = temp.next # This function rotates a linked list # counter-clockwise and updates the # head. The function assumes that k # is smaller than size of linked list. # It doesn't modify the list if k is # greater than of equal to size def rotate(self, k): if k == 0: return # Let us understand the below code # for example k = 4 and list = # 10->20->30->40->50->60 current = self.head # current will either point to kth # or NULL after this loop current # will point to node 40 in the above # example count = 1 while(count <k and current is not None): current = current.next count += 1 # If current is None, k is greater # than or equal to count of nodes # in linked list. Don't change # the list in this case if current is None: return # current points to kth node. Store # it in a variable kth node points # to node 40 in the above example kthNode = current # current will point to last node # after this loop current will point # to node 60 in above example while(current.next is not None): current = current.next # Change next of last node to previous # head Next of 60 is now changed to # node 10 current.next = self.head # Change head to (k + 1)th node # head is not changed to node 50 self.head = kthNode.next # change next of kth node to NULL # next of 40 is not NULL kthNode.next = None # Driver code llist = LinkedList() # Create a list # 10->20->30->40->50->60 for i in range(60, 0, -10): llist.push(i) print "Given linked list" llist.printList() llist.rotate(4) print "Rotated Linked list" llist.printList() # This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)
pag>
Producción:
Given linked list 10 20 30 40 50 60 Rotated Linked list 50 60 10 20 30 40
Complejidad de tiempo: O(n) donde n es el número de Nodes en la lista enlazada. El código atraviesa la lista enlazada solo una vez.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Método 2:
para rotar una lista enlazada por k, primero podemos hacer que la lista enlazada sea circular y luego mover k-1 pasos hacia adelante desde el Node principal, haciendo que el (k-1)-ésimo Node esté junto a nulo y hacer que el k-ésimo Node sea la cabeza.
Python3
# Python3 program to rotate a
# linked list counter clock wise
# Link list node
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.data = 0
self.next = None
# This function rotates a linked list
# counter-clockwise and updates the
# head. The function assumes that k is
# smaller than size of linked list.
def rotate(head_ref, k):
if (k == 0):
return
# Let us understand the below
# code for example k = 4 and
# list = 10.20.30.40.50.60.
current = head_ref
# Traverse till the end.
while (current.next != None):
current = current.next
current.next = head_ref
current = head_ref
# Traverse the linked list to k-1
# position which will be last
# element for rotated array.
for i in range(k - 1):
current = current.next
# Update the head_ref and last
# element pointer to None
head_ref = current.next
current.next = None
return head_ref
# UTILITY FUNCTIONS
# Function to push a node
def push(head_ref, new_data):
# Allocate node
new_node = Node()
# Put in the data
new_node.data = new_data
# Link the old list off
# the new node
new_node.next = (head_ref)
# Move the head to point
# to the new node
(head_ref) = new_node
return head_ref
# Function to print linked list
def printList(node):
while (node != None):
print(node.data, end = ' ')
node = node.next
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
# Start with the empty list
head = None
# Create a list
# 10.20.30.40.50.60
for i in range(60, 0, -10):
head = push(head, i)
print("Given linked list ")
printList(head)
head = rotate(head, 4)
print("\nRotated Linked list ")
printList(head)
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56
¿Escribir código en un comentario? Utilice ide.geeksforgeeks.org , genere un enlace y compártalo aquí.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA