Octal es un sistema numérico en el que un número se representa en potencias de 8. Por lo tanto, todos los números enteros se pueden representar como un número octal. Además, todos los dígitos en un número octal están entre 0 y 7. En Java, podemos almacenar números octales simplemente agregando 0 durante la inicialización. Se llaman literales octales. El tipo de datos utilizado para el almacenamiento es int.
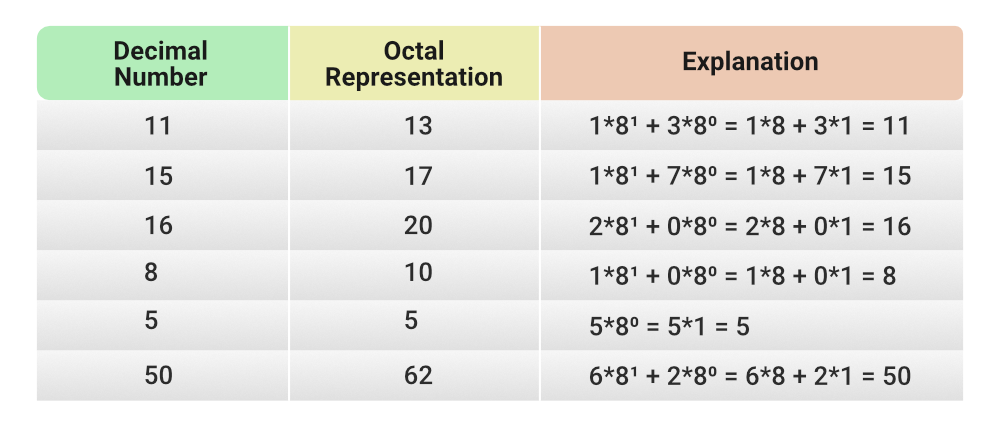
El método utilizado para convertir Decimal a Octal es Integer.toOctalString(int num)
Sintaxis:
public static String toOctalString(int num)
Parámetros: el método acepta un solo parámetro num de tipo entero que se requiere para convertirlo en una string.
Valor devuelto: la función devuelve una representación de string del argumento entero como un entero sin signo en base 8.
Ejemplo 1
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Variable Declaration
int a;
// storing normal integer value
a = 20;
System.out.println("Value of a: " + a);
// storing octal integer value
// just add 0 followed octal representation
a = 024;
System.out.println("Value of a: " + a);
// convert octal representation to integer
String s = "024";
int c = Integer.parseInt(s, 8);
System.out.println("Value of c: " + a);
// get octal representation of a number
int b = 50;
System.out.println(
"Octal Representation of the number " + b
+ " is: " + Integer.toOctalString(b));
}
}
Value of a: 20 Value of a: 20 Value of c: 20 Octal Representation of the number 50 is: 62
Ejemplo 2: Las diferentes operaciones aritméticas también se pueden realizar sobre este entero octal. La operación es la misma que se realiza en el tipo de datos int.
Java
// Arithmetic operations on Octal numbers
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a, b;
// 100
a = 0144;
// 20
b = 024;
System.out.println("Value of a: " + a);
System.out.println("Value of b: " + b);
System.out.println("Addition: " + (a + b));
System.out.println("Subtraction: " + (a - b));
System.out.println("Multiplication: " + (a * b));
System.out.println("Division: " + (a / b));
}
}
Value of a: 100 Value of b: 20 Addition: 120 Subtraction: 80 Multiplication: 2000 Division: 5