PriorityBlockingQueue es una cola de bloqueo ilimitada que utiliza las mismas reglas de ordenación que la clase PriorityQueue y proporciona operaciones de recuperación de bloqueo. La parte de «bloqueo» del nombre se agrega para implicar que el hilo bloqueará la espera hasta que haya un elemento disponible en la cola. Esta clase no permite elementos nulos. Una cola de prioridad que se basa en el orden natural tampoco permite la inserción de objetos no comparables (si lo hace, se genera ClassCastException).
Implementa interfaces Serializable, Iterable<E>, Collection<E>, BlockingQueue<E>, Queue<E> y extiende la clase AbstractQueue<E>.
Declaración:
public class PriorityBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements BlockingQueue<E>, Serializable // Here, E is the type of elements held in this collection
java.lang.Object
java.util.AbstractCollection<E>
java.util.AbstractQueue<E>
java.util.concurrent.PriorityBlockingQueue<E>
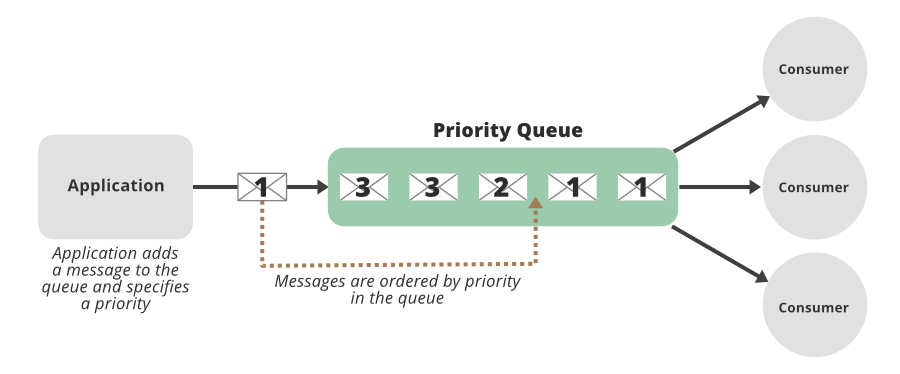
Implementación:
Ejemplo
Java
// Java Program to Implement PriorityBlockingQueue API
// Importing concurrent classes from
// java.util package
import java.util.concurrent.PriorityBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
// Class for PriorityQueue
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
throws InterruptedException
{
// Creating a new object of PriorityBlockingQueue
// Declaring Integer type object
PriorityBlockingQueue<Integer> priorityBlockingQueue
= new PriorityBlockingQueue<>();
// Creation of a thread
new Thread(() -> {
// Display message
System.out.println("Waiting to poll ...");
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Condition check
while (true) {
// Return (integer) value at head of
// queue of PriorityBlockingQueue
Integer poll
= priorityBlockingQueue.take();
// Display and print element returned in
// PriorityBlockingQueue
System.out.println("Polled : " + poll);
// Pause the execution of current thread
// for certain amount of time using
// toMills() method() to showcase
// working of PriorityBlockingQueue
Thread.sleep(
TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(1));
}
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions if any
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Print and display the line number
// where exception/s occured
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Execution of thread begins with
// use of start() method
}).start();
// Custom elememts inputs
// 1, 2, 3 to priorityBlockingQueue
// Pausing execution of first thread
Thread.sleep(TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(2));
// Insert parameter element-> 1 to method
// at the tail of priority queue
priorityBlockingQueue.add(1);
// Pausing execution of second thread
Thread.sleep(TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(2));
// Insert parameter element-> 2 to method
// at the tail of priority queue
priorityBlockingQueue.add(2);
// pausing execution of third thread
Thread.sleep(TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(2));
// Insert parameter element-> 3 to method
// at the tail of priority queue
priorityBlockingQueue.add(3);
}
}
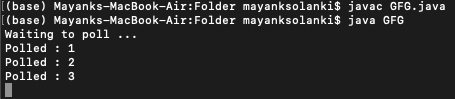
Producción:
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por mayanktyagi1709 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA