Declaración del problema: se supone que el usuario debe ingresar el número, ya sea cualquier número aleatorio que se encuentre dentro del tipo de datos primitivo que contiene el número. Primero, el número debe invertirse. Secundariamente, la suma del número se calculará con la restricción de usar un bucle do-while.
bucle do-while : ahora el usuario a veces se confunde entre un bucle while y un bucle do-while. El ciclo while primero verifica la condición y luego ejecuta la declaración, mientras que el ciclo Do-while ejecuta la declaración y luego verifica la condición. Un punto importante que surge de Do-while es que incluso si la condición falla, se ejecutará una vez.
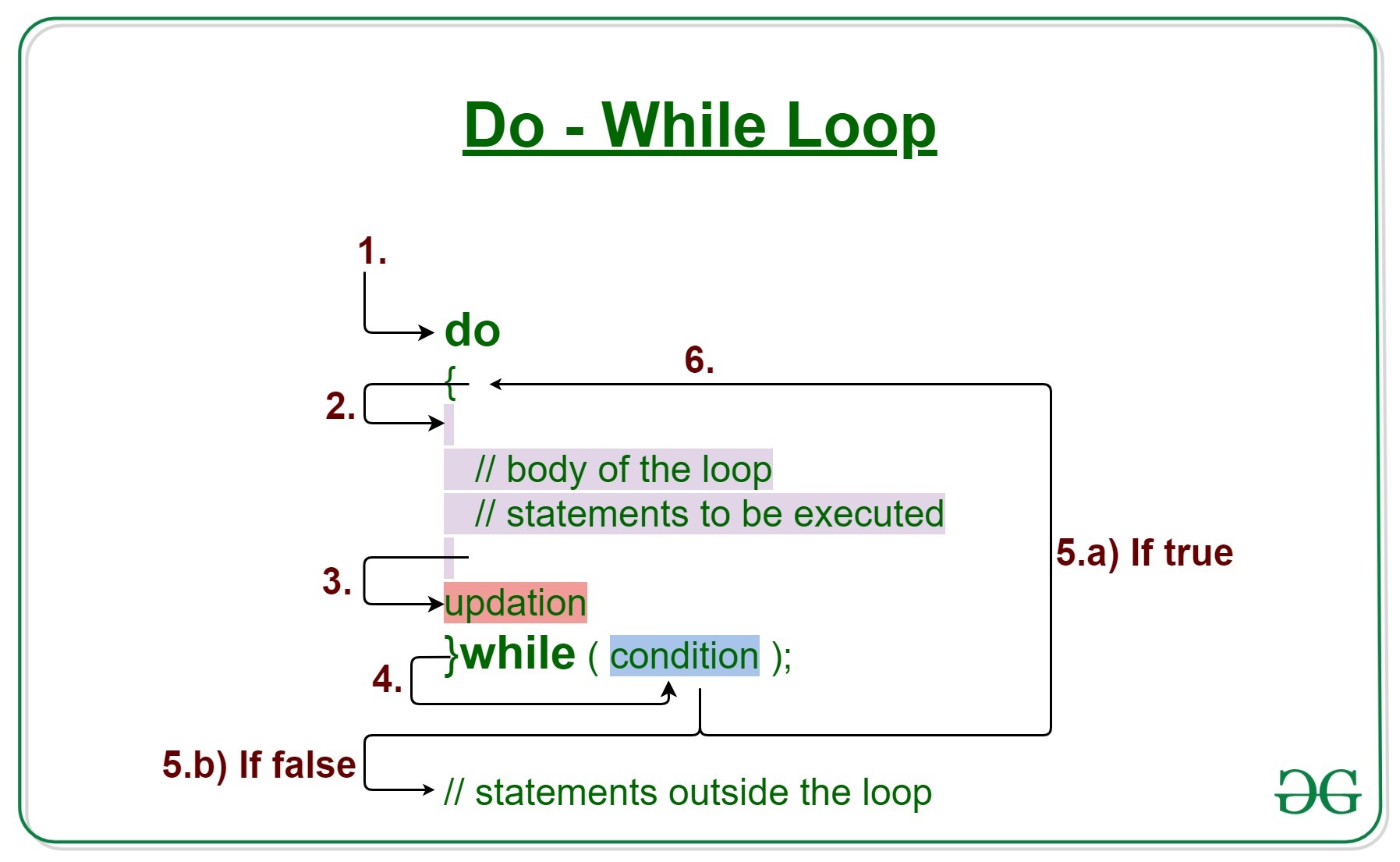
Sintaxis de do-While Loop:
do
{
// statement to be executed
}
while(condition check)
Uso del bucle Do-while:
Mostrar algún menú al usuario, en otras palabras, el juego se implementa donde el objetivo es mostrarle al usuario que presione 1 para hacer esto, 2 para hacer eso, y así sucesivamente donde haya una opción, presione Q para salir de este juego. Entonces, el ciclo do-while quiere mostrar el menú al menos una vez al usuario. Cuando el usuario ha tomado la acción, se realizan los pasos apropiados. Entonces, mientras que la condición debería ser si el usuario presiona Q para salir y el menú está dentro del ciclo do-while.
Enfoque: Usando do-while Loop, encuentra el reverso de un número así como la suma de sus dígitos. Ingrese cualquier número como entrada y luego use el módulo y la división, operadores para invertir ese número en particular y encontrar la suma de sus dígitos.
Algoritmo:
- Tomando un número del usuario
- Creando dos variables, a saber, número_inverso y suma e inicializando ambas a 0
- Invertir un número
- Impresión de número invertido
- Imprimiendo la suma final de los dígitos obtenidos de sumas más pequeñas.
Algoritmo de inversión como se explica a continuación:
- Multiplique rev por 10 y agregue el resto del número que es resto a número inverso. // rem = num%10; rev = rev*10 + rem;
- Agregue rem a la suma actual para encontrar la suma de dígitos y almacenarlos en una variable que se devolverá con la suma final. Final_sum=current_sum where current_sum=current_sum + resto
- Dividiendo el número por 10 para acceder al dígito anterior al dígito actual del número de la siguiente manera. // numero=numero/10; while(num > 0);
Ejemplo 1: programa Java para invertir y sumar dígitos del número sin hacer funciones
Java
// Java program to reverse and and sum up digits of number
// Importing generic Classes/Files
import java.io.*;
// Importing Scanner Class
import java.util.Scanner;
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// creating variables
int num, rem;
// Creating variables and initializing at same time
int rev = 0, sum = 0;
// Using scanner to take input from user
// Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// Remove comments from lineNo20
// to take dynamic user input
// Displaying message
System.out.println("Enter the number: 25 ");
// Taking input from user
// num = sc.nextInt();
// Hard coded input
num = 25;
// Do-while loop for iteration over digits of number
do {
// Step1: Modulo with 10 to get last digit
rem = num % 10;
// Step2: Reverse the number
rev = rev * 10 + rem;
// Sum of the digits of number
sum = sum + rem;
// Step3: Dividing number by 10 to loose last
// digit
num = num / 10;
}
// Condition check
// Remember: By this time 1 iteration is over even
// if conditions false
while (num > 0);
// Printing the reverse number
System.out.println("Reverse of given number: "
+ rev);
// Summing up digits of number as shown in above
// steps
System.out.println("Sum of digits of given number: "
+ sum);
}
}
Enter the number: 25 Reverse of given number: 52 Sum of digits of given number: 7
Ejemplo 2: En este ejemplo, los bucles do-while se muestran por separado como una ilustración al crear funciones de ellos y luego llamarlos en el método del controlador principal.
Java
import java.io.*;
// Importing specific Scanner Class to show menu
import java.util.Scanner;
class GFG {
// Iterative function to reverse digits of number
// static int reversDigits(int num)
// Hardcoded input where input number equals 25
static int reversDigits(int num)
{
// Making input hard coded else
num = 25;
// else do not initialize num
// creating and Initialising reverseNo with 0
// Creating remainder variable
int rev = 0, rem;
// Statements to be executed in do loop
do {
// Reversal of a number as discussed in
// algorithm
rem = num % 10;
rev = rev * 10 + rem;
num = num / 10;
}
// Condition check
while (num > 0);
// Returning reverse of the user enter number
return rev;
}
// Iterative function findingsum of the digits of number
// static int sumDigits(int num)
// Hardcoded input where input number equals 25
static int sumDigits(int num)
{
// Making input hard coded
num = 25;
// else do not initialize num
// creating and Initialising final_sum with 0
// Creating remainder variable
int sum = 0, rem;
// Statements to be executed in do loop
do {
// Retrieving steps as discussed in above 3
// steps
rem = num % 10;
sum = sum + rem;
num = num / 10;
}
// condition check
while (num > 0);
// Returning Sum of digits of a reversed number
return sum;
}
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// declaring variable to store user entered number
// int num;
// Scanner Class to read the entered number
// Commented out to hard code the input
// else remove comments
// Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// Input is hardcoded for display
// else remove comments from line no 77
// Considering hard coded input
int num = 25;
// Printing message
System.out.println(num);
// Taking input from user
// Making input hard coded else
// remove comments from line no 82
// num = sc.nextInt();
// Calling above functions to print reversed number
System.out.println("Reverse of given number: "
+ reversDigits(num));
// Calling above functions to print reversed number
System.out.println("Sum of digits of given number: "
+ sumDigits(num));
}
}
25 Reverse of given number: 52 Sum of digits of given number: 7
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por manvi_jain14 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA