La enumeración en Java es una de las interfaces predefinidas, cuyo objeto se utiliza para recuperar los datos de la variable del marco de las colecciones (como Stack, Vector, HashTable, etc.) solo hacia adelante y no hacia atrás.
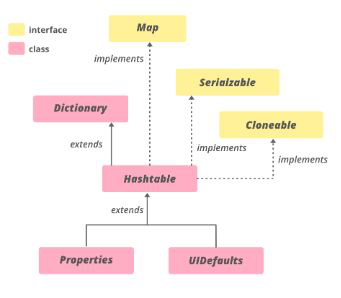
HashTable es una clase. La clase de tabla hash implementa un Mapa, que asigna claves a valores. Almacena el par clave/valor en la tabla hash. En esta estructura de datos especificamos un objeto que se utiliza como clave y el valor que queremos asociar con esa clave. A continuación, se aplica un hash a la clave y el código hash resultante se utiliza como índice en el que se almacena el valor dentro de la tabla. HashMap no proporciona ninguna enumeración, mientras que HashTable no proporciona una enumeración rápida. La jerarquía de la tabla hash es la siguiente:
Sintaxis:
public class Hashtable<K,V> extends Dictionary<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
Parámetros:
- K: Llaves insertadas.
- V: Valores asignados a las claves.
Para crear HashTable, importe hash Table desde java.util.Hashtable donde, K, V son de tipos de datos como entero, string, flotante, etc.
Sintaxis: creación de una tabla hash
Hashtable<K, V> ht = new Hashtable<K, V>();
Implementación: información de estudiantes universitarios
Ejemplo
Java
// Java Program to read elements
// using enumeration in hashtable
// Importing enumeration class
import java.util.Enumeration;
// Importing hash table
import java.util.Hashtable;
// Class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String a[])
{
// Creating hash table
Hashtable<String, String> hm
= new Hashtable<String, String>();
// Add key-value pair to Hashtable
// Custom inputs
hm.put("Name", "Bahubali");
hm.put("College", "Amarnath");
hm.put("Department", "Vedics");
// enum
Enumeration<String> keys = hm.keys();
// Condition check whether element(K,V) is present
// using hasMoreElements()
while (keys.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = keys.nextElement();
// Print corresponding key-value pair
System.out.println("Value of " + key
+ " is: " + hm.get(key));
}
System.out.println();
// Creating a new Hashtable
Hashtable<String, String> hm1
= new Hashtable<String, String>();
// Adding key-value pair to Hashtable
// Custom inputs
hm1.put("Name", "Ravaan");
hm1.put("College", "SriLanka");
hm1.put("Department", "CS");
// Enum
Enumeration<String> keys1 = hm1.keys();
// Condition check whether element(K,V) is present
// using hasMoreElements()
while (keys1.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = keys1.nextElement();
// Print corresponding key-value pair
System.out.println("Value of " + key
+ " is: " + hm1.get(key));
}
System.out.println();
// Creating a new Hashtable
Hashtable<String, String> hm2
= new Hashtable<String, String>();
// Adding key-value pair to Hashtable
// Custom inputs
hm2.put("Name", "Kattappa");
hm2.put("College", "Beardo");
hm2.put("Department", "War");
/// enum
Enumeration<String> keys2 = hm2.keys();
// Condition check whether element(K,V) is present
// using hasMoreElements()
while (keys2.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = keys2.nextElement();
// Print corresponding key-value pair
System.out.println("Value of " + key
+ " is: " + hm2.get(key));
}
}
}
Value of Name is: Bahubali Value of College is: Amarnath Value of Department is: Vedics Value of Name is: Ravaan Value of College is: SriLanka Value of Department is: CS Value of Name is: Kattappa Value of College is: Beardo Value of Department is: War
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por sravankumar8128 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA