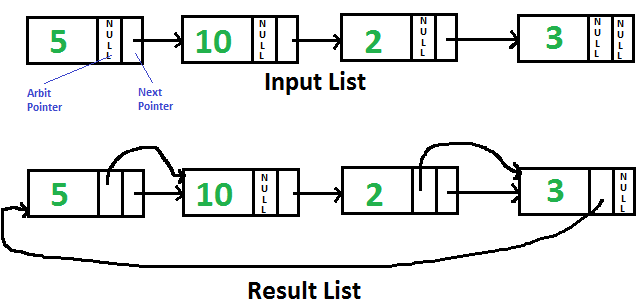
Dada una lista enlazada individualmente con cada Node que tiene un puntero «arbitrario» adicional que actualmente apunta a NULL. Necesita hacer que el puntero «arbitrario» apunte al siguiente Node de mayor valor.
Recomendamos encarecidamente minimizar su navegador e intentarlo usted mismo primero.
Una solución simple es atravesar todos los Nodes uno por uno, para cada Node, encontrar el Node que tiene el siguiente valor mayor del Node actual y cambiar el puntero siguiente. La complejidad temporal de esta solución es O(n 2 ).
Una solución eficiente funciona en tiempo O(nLogn). La idea es usar Merge Sort para lista enlazada .
1) Atraviese la lista de entrada y copie el siguiente puntero en el puntero de arbitraje para cada Node.
2) Haga Merge Sort para la lista enlazada formada por punteros arbitrales.
A continuación se muestra la implementación de la idea anterior. Todas las funciones de clasificación de fusión se toman de aquí . Las funciones tomadas se modifican aquí para que funcionen en punteros de arbitraje en lugar de punteros siguientes.
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to populate
// arbit pointers to next higher
// value using merge sort
var head;
// Link list node
class Node
{
constructor(val)
{
this.data = val;
this.arbit = null;
this.next = null;
}
}
// Utility function to print
// result linked list
function printList(node, anode)
{
document.write(
"Traversal using Next Pointer<br/>");
while (node != null)
{
document.write(node.data + ", ");
node = node.next;
}
document.write(
"<br/>Traversal using Arbit Pointer<br/>");
while (anode != null)
{
document.write(anode.data + ", ");
anode = anode.arbit;
}
}
// This function populates arbit pointer
// in every node to the next higher value.
// And returns pointer to the node with
// minimum value
function populateArbit(start)
{
var temp = start;
// Copy next pointers to arbit
// pointers
while (temp != null)
{
temp.arbit = temp.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
// Do merge sort for arbitrary pointers
// and return head of arbitrary pointer
// linked list
return MergeSort(start);
}
/* Sorts the linked list formed by arbit
pointers (does not change next pointer
or data) */
function MergeSort(start)
{
// Base case -- length 0 or 1
if (start == null ||
start.arbit == null)
{
return start;
}
/* Split head into 'middle' and
'nextofmiddle' sublists */
var middle = getMiddle(start);
var nextofmiddle = middle.arbit;
middle.arbit = null;
// Recursively sort the sublists
var left = MergeSort(start);
var right = MergeSort(nextofmiddle);
/* answer = merge the two sorted lists
together */
var sortedlist = SortedMerge(left,
right);
return sortedlist;
}
// Utility function to get the
// middle of the linked list
function getMiddle(source)
{
// Base case
if (source == null)
return source;
var fastptr = source.arbit;
var slowptr = source;
// Move fastptr by two and slow ptr
// by one. Finally slowptr will point
// to middle node
while (fastptr != null)
{
fastptr = fastptr.arbit;
if (fastptr != null)
{
slowptr = slowptr.arbit;
fastptr = fastptr.arbit;
}
}
return slowptr;
}
function SortedMerge(a, b)
{
var result = null;
// Base cases
if (a == null)
return b;
else if (b == null)
return a;
// Pick either a or b, and recur
if (a.data <= b.data)
{
result = a;
result.arbit =
SortedMerge(a.arbit, b);
}
else
{
result = b;
result.arbit = SortedMerge(a, b.arbit);
}
return result;
}
// Driver code
/* Let us create the list shown above */
head = new Node(5);
head.next = new Node(10);
head.next.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next.next = new Node(3);
// Sort the above created Linked List
var ahead = populateArbit(head);
document.write(
"Result Linked List is:<br/>");
printList(head, ahead);
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
Producción:
Result Linked List is: Traversal using Next Pointer 5, 10, 2, 3, Traversal using Arbit Pointer 2, 3, 5, 10,
Consulte el artículo completo sobre Apuntar al siguiente Node de mayor valor en una lista vinculada con un puntero arbitrario para obtener más detalles.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA