S , t Autómatas finitos deterministas (DFA) L = {a N b M | N ≥ 0, M ≥ 0, N+M ≥ 1} L la ocurrencia L “Aceptado” “No aceptado”
Ejemplos
Entrada: S = “aabbb”
Salida: Aceptada
Explicación: Todas las ‘a’ vienen antes de las ‘b’.Entrada: S = “ba”
Salida: No aceptada
Explicación: ‘b’ viene antes de ‘a’.Entrada: S = “aaa”
Salida: Aceptada
Explicación: Tenga en cuenta que ‘b’ no necesita aparecer en SEntrada: S = “b”
Salida: Aceptada
Explicación: Tenga en cuenta que ‘a’ no necesita aparecer en S
Planteamiento : El problema puede aceptarse solo cuando se cumplen los siguientes casos:
- Todos los caracteres pueden ser ‘a’.
- Todos los caracteres pueden ser ‘b’.
- Todas las ‘b’ vienen después de todas las ‘a’.
- Hay al menos un carácter en la string.
Esto se puede visualizar mejor con la ayuda del diagrama de transición de estado del DFA
Diagrama de transición de estado:
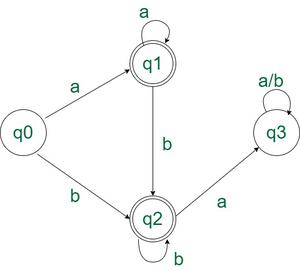
Diagrama de transición de estado del DFA anterior
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ Program to implement
// the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function for state zero Q0
int startStateQ0(char s) {
int state;
if (s == 'a')
state = 1;
else if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for first state Q1
int firstStateQ1(char s) {
int state;
if (s == 'a')
state = 1;
else if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for second state Q2
int secondStateQ2(char s) {
int state;
if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else if (s == 'a')
state = 3;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for third state Q3
int thirdStateQ3(char s) {
int state = 3;
return state;
}
// Function to check
// if the string is accepted or not
int isAcceptedString(string String) {
int l = String.length();
// dfa tells the number associated
// with the present dfa = state
int state = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) {
if (state == 0)
state = startStateQ0(String[i]);
else if (state == 1)
state = firstStateQ1(String[i]);
else if (state == 2)
state = secondStateQ2(String[i]);
else if (state == 3)
state = thirdStateQ3(String[i]);
else
return 0;
}
if (state == 1 || state == 2)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int main() {
string String = "ba";
if (isAcceptedString(String))
cout << "ACCEPTED";
else
cout << "NOT ACCEPTED";
}
// This code is contributed by Samim Hossain Mondal.
Java
// Java Program to implement
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
// Function for state zero Q0
static int startStateQ0(char s)
{
int state;
if (s == 'a')
state = 1;
else if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for first state Q1
static int firstStateQ1(char s)
{
int state;
if (s == 'a')
state = 1;
else if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for second state Q2
static int secondStateQ2(char s)
{
int state;
if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else if (s == 'a')
state = 3;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for third state Q3
static int thirdStateQ3(char s)
{
int state = 3;
return state;
}
// Function to check
// if the string is accepted or not
static int isAcceptedString(String Str)
{
int l = Str.length();
// dfa tells the number associated
// with the present dfa = state
int state = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) {
if (state == 0)
state = startStateQ0(Str.charAt(i));
else if (state == 1)
state = firstStateQ1(Str.charAt(i));
else if (state == 2)
state = secondStateQ2(Str.charAt(i));
else if (state == 3)
state = thirdStateQ3(Str.charAt(i));
else
return 0;
}
if (state == 1 || state == 2)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
String Str = "ba";
if (isAcceptedString(Str) != 0)
System.out.println("ACCEPTED");
else
System.out.println("NOT ACCEPTED");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Samim Hossain Mondal.
Python3
# Function for state zero Q0
def startStateQ0(s):
if (s == 'a'):
state = 1
elif (s == 'b'):
state = 2
else:
state = -1
return state
# Function for first state Q1
def firstStateQ1(s):
if (s == 'a'):
state = 1
elif (s == 'b'):
state = 2
else:
state = -1
return state
# Function for second state Q2
def secondStateQ2(s):
if (s == 'b'):
state = 2
elif (s == 'a'):
state = 3
else:
state = -1
return state
# Function for third state Q3
def thirdStateQ3(s):
state = 3
return state
#Function to check
#if the string is accepted or not
def isAcceptedString(String):
l = len(String)
# dfa tells the number associated
# with the present dfa = state
state = 0
for i in range(l):
if (state == 0):
state = startStateQ0(String[i])
elif (state == 1):
state = firstStateQ1(String[i])
elif (state == 2):
state = secondStateQ2(String[i])
elif (state == 3):
state = thirdStateQ3(String[i])
else:
return 0
if(state == 1 or state == 2):
return 1
else:
return 0
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
String = "ba"
if (isAcceptedString(String)):
print("ACCEPTED")
else:
print("NOT ACCEPTED")
C#
// C# Program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
class GFG {
// Function for state zero Q0
static int startStateQ0(char s)
{
int state;
if (s == 'a')
state = 1;
else if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for first state Q1
static int firstStateQ1(char s)
{
int state;
if (s == 'a')
state = 1;
else if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for second state Q2
static int secondStateQ2(char s)
{
int state;
if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else if (s == 'a')
state = 3;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for third state Q3
static int thirdStateQ3(char s)
{
int state = 3;
return state;
}
// Function to check
// if the string is accepted or not
static int isAcceptedString(string Str)
{
int l = Str.Length;
// dfa tells the number associated
// with the present dfa = state
int state = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) {
if (state == 0)
state = startStateQ0(Str[i]);
else if (state == 1)
state = firstStateQ1(Str[i]);
else if (state == 2)
state = secondStateQ2(Str[i]);
else if (state == 3)
state = thirdStateQ3(Str[i]);
else
return 0;
}
if (state == 1 || state == 2)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
public static void Main()
{
string Str = "ba";
if (isAcceptedString(Str) != 0)
Console.Write("ACCEPTED");
else
Console.Write("NOT ACCEPTED");
}
}
// This code is contributed by ukasp.
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript Program to implement
// the above approach
// Function for state zero Q0
function startStateQ0(s) {
if (s == 'a')
state = 1
else if (s == 'b')
state = 2
else
state = -1
return state
}
// Function for first state Q1
function firstStateQ1(s) {
if (s == 'a')
state = 1
else if (s == 'b')
state = 2
else
state = -1
return state
}
// Function for second state Q2
function secondStateQ2(s) {
if (s == 'b')
state = 2
else if (s == 'a')
state = 3
else
state = -1
return state
}
// Function for third state Q3
function thirdStateQ3(s) {
state = 3
return state
}
// Function to check
// if the string is accepted or not
function isAcceptedString(String) {
l = String.length;
// dfa tells the number associated
// with the present dfa = state
state = 0
for (let i = 0; i < l; i++) {
if (state == 0)
state = startStateQ0(String[i])
else if (state == 1)
state = firstStateQ1(String[i])
else if (state == 2)
state = secondStateQ2(String[i])
else if (state == 3)
state = thirdStateQ3(String[i])
else
return 0
}
if (state == 1 || state == 2)
return 1
else
return 0
}
let String = "ba"
if (isAcceptedString(String))
document.write("ACCEPTED")
else
document.write("NOT ACCEPTED")
// This code is contributed by Potta Lokesh
</script>
NOT ACCEPTED
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N) donde N es la longitud de la string
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por ashutosh deshwal y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA