Requisito previo: autómatas finitos
Dada una string S de tamaño N , la tarea es diseñar un autómata finito determinista (DFA) para aceptar el lenguaje L = {a N | norte ≥ 1} . El lenguaje regular L es {a, aa, aaa, aaaaaaa…, }. Si la string dada sigue el idioma dado L , imprima «Aceptado» . De lo contrario, imprima «No aceptado» .
Ejemplos:
Entrada: S = “aaabbb”
Salida: No aceptado
Explicación: La string solo debe contener a.Entrada: S = “aa”
Salida: Aceptada
Enfoque: la idea por la cual los autómatas conducen a la aceptación de la string se establece a continuación en pasos:
- Los autómatas aceptarán todas las strings que contengan solo el carácter ‘a’ . Si el usuario intentó ingresar cualquier carácter que no sea ‘a’, la máquina lo rechazará.
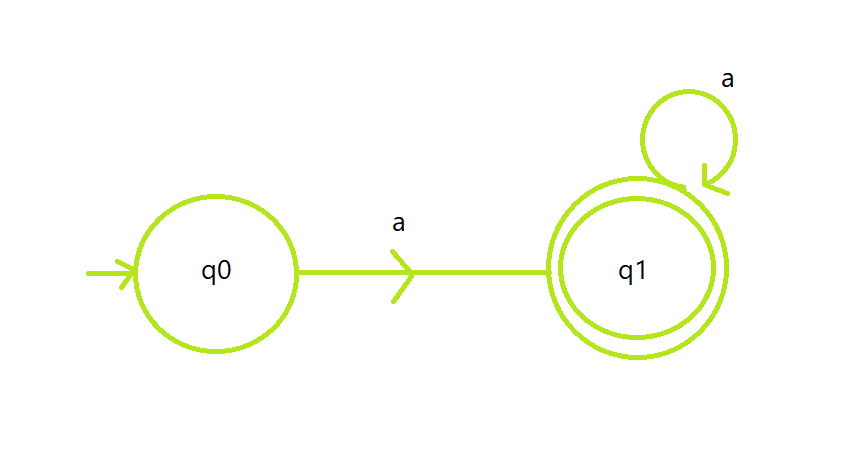
- Deje que el estado q0 es el estado inicial que representa el conjunto de todas las strings de longitud 0 , el estado q1 es el estado final que representa el conjunto de todas las strings de 1 a N.
- El estado q1 contiene un bucle propio de a que indica que se puede repetir según sea necesario.
- La lógica para el código es muy básica ya que solo tiene un bucle for que cuenta el número de a en una string dada, si el recuento de a es el mismo que N , entonces se aceptará. De lo contrario, la string será rechazada.
Diagrama de transición de estado de DFA :
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to check whether the string
// S satisfy the given DFA or not
void isAcceptedDFA(string s, int N)
{
// Stores the count of characters
int count = 0;
// Iterate over the range [0, N]
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// Count and check every
// element for 'a'
if (s[i] == 'a')
count++;
}
// If string matches with DFA
if (count == N && count != 0) {
cout << "Accepted";
}
// If not matches
else {
cout << "Not Accepted";
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
string S = "aaaaa";
// Function Call
isAcceptedDFA(S, S.size());
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
class GFG
{
// Function to check whether the String
// S satisfy the given DFA or not
static void isAcceptedDFA(String s, int N)
{
// Stores the count of characters
int count = 0;
// Iterate over the range [0, N]
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// Count and check every
// element for 'a'
if (s.charAt(i) == 'a')
count++;
}
// If String matches with DFA
if (count == N && count != 0)
{
System.out.print("Accepted");
}
// If not matches
else
{
System.out.print("Not Accepted");
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String S = "aaaaa";
// Function Call
isAcceptedDFA(S, S.length());
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Function to check whether the string
# S satisfy the given DFA or not
def isAcceptedDFA(s, N):
# Stores the count of characters
count = 0
# Iterate over the range [0, N]
for i in range(N):
# Count and check every
# element for 'a'
if (s[i] == 'a'):
count += 1
# If string matches with DFA
if (count == N and count != 0):
print ("Accepted")
# If not matches
else :
print ("Not Accepted")
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
S = "aaaaa"
# Function Call
isAcceptedDFA(S, len(S))
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to check whether the String
// S satisfy the given DFA or not
static void isAcceptedDFA(String s, int N)
{
// Stores the count of characters
int count = 0;
// Iterate over the range [0, N]
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// Count and check every
// element for 'a'
if (s[i] == 'a')
count++;
}
// If String matches with DFA
if (count == N && count != 0)
{
Console.Write("Accepted");
}
// If not matches
else
{
Console.Write("Not Accepted");
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
String S = "aaaaa";
// Function Call
isAcceptedDFA(S, S.Length);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program for the above approach
// Function to check whether the String
// S satisfy the given DFA or not
function isAcceptedDFA(s, N) {
// Stores the count of characters
var count = 0;
// Iterate over the range [0, N]
for (var i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// Count and check every
// element for 'a'
if (s[i] === "a") count++;
}
// If String matches with DFA
if (count === N && count !== 0) {
document.write("Accepted");
}
// If not matches
else {
document.write("Not Accepted");
}
}
// Driver Code
var S = "aaaaa";
// Function Call
isAcceptedDFA(S, S.length);
</script>
Accepted
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por kushwahp1234 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA