Dada una lista doblemente enlazada , la tarea es encontrar el tamaño de esa lista doblemente enlazada. Por ejemplo, el tamaño de la siguiente lista vinculada es 4.
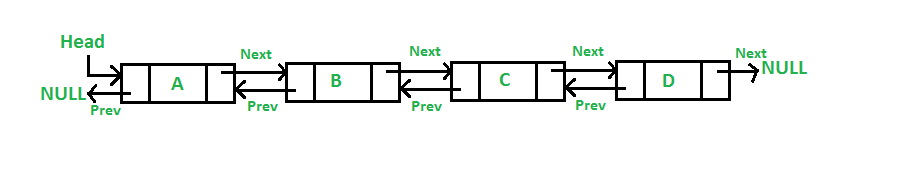
Una lista doblemente enlazada es una estructura de datos enlazados que consta de un conjunto de registros enlazados secuencialmente llamados Nodes. Cada Node contiene dos campos, llamados enlaces, que son referencias al Node anterior y al siguiente en la secuencia de Nodes.
El recorrido de una lista doblemente enlazada puede ser en cualquier dirección. De hecho, la dirección de recorrido puede cambiar muchas veces, si se desea.
Por ejemplo, la función debería devolver 3 para la lista doblemente enlazada anterior.
Algoritmo:
1) Inicialice el tamaño a 0.
2) Inicialice un puntero de Node, temp = head.
3) Haga lo siguiente mientras la temperatura no sea NULL
……a) temp = temp -> next
……b) size++;
4) Tamaño de retorno.
C++
// A complete working C++ program to
// find size of doubly linked list.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A linked list node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
/* Function to add a node to front of doubly
linked list */
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node = new Node;
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
new_node->prev = NULL;
if ((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node ;
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// This function returns size of linked list
int findSize(struct Node *node)
{
int res = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
res++;
node = node->next;
}
return res;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
cout << findSize(head);
return 0;
}
C
// C program to find size of doubly linked list.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* prev;
struct Node* next;
};
void push(struct Node** head, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = *head;
new_node->prev = NULL;
if ((*head) != NULL) {
(*head)->prev = new_node;
}
(*head) = new_node;
}
int findSize(struct Node* node)
{
int res = 0;
while (node != NULL) {
res++;
node = node->next;
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
// code
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
printf("%d", findSize(head));
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by lokeshmvs21.
Java
// A complete working Java program to
// find size of doubly linked list.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Represents a doubly linked list node
class Node
{
int data;
Node next, prev;
Node(int val)
{
data = val;
next = null;
prev = null;
}
}
class GFG
{
/* Function to add a node to front of doubly
linked list */
static Node push(Node head, int data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(data);
new_node.next = head;
new_node.prev = null;
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_node;
head = new_node;
return head;
}
// This function returns size of doubly linked list
static int findSize(Node node)
{
int res = 0;
while (node != null)
{
res++;
node = node.next;
}
return res;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node head = null;
head = push(head, 4);
head = push(head, 3);
head = push(head, 2);
head = push(head, 1);
System.out.println(findSize(head));
}
}
// This code is contributed by rachana soma
Python3
# A complete working Python3 program to # find size of doubly linked list. # A linked list node class Node: def __init__(self): self.data = None self.next = None self.prev = None # Function to add a node to front of doubly # linked list def push( head_ref, new_data): new_node = Node() new_node.data = new_data new_node.next = (head_ref) new_node.prev = None if ((head_ref) != None): (head_ref).prev = new_node (head_ref) = new_node return head_ref # This function returns size of linked list def findSize(node): res = 0 while (node != None): res = res + 1 node = node.next return res # Driver code head = None head = push(head, 4) head = push(head, 3) head = push(head, 2) head = push(head, 1) print(findSize(head)) # This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
C#
// A complete working C# program to
// find size of doubly linked list.
using System;
// Represents a doubly linked list node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next, prev;
public Node(int val)
{
data = val;
next = null;
prev = null;
}
}
class GFG
{
/* Function to add a node to front of doubly
linked list */
static Node push(Node head, int data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(data);
new_node.next = head;
new_node.prev = null;
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_node;
head = new_node;
return head;
}
// This function returns size of doubly linked list
static int findSize(Node node)
{
int res = 0;
while (node != null)
{
res++;
node = node.next;
}
return res;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Node head = null;
head = push(head, 4);
head = push(head, 3);
head = push(head, 2);
head = push(head, 1);
Console.WriteLine(findSize(head));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
Javascript
<script>
// A complete working javascript program to
// find size of doubly linked list.
// Represents a doubly linked list node
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
}
/*
* Function to add a node to front of doubly linked list
*/
function push(head , data) {
var new_node = new Node(data);
new_node.next = head;
new_node.prev = null;
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_node;
head = new_node;
return head;
}
// This function returns size of doubly linked list
function findSize(node) {
var res = 0;
while (node != null) {
res++;
node = node.next;
}
return res;
}
// Driver Code
var head = null;
head = push(head, 4);
head = push(head, 3);
head = push(head, 2);
head = push(head, 1);
document.write(findSize(head));
// This code contributed by aashish1995
</script>
4
Complejidad de tiempo: O (n), ya que estamos usando un bucle para atravesar n veces. Donde n es el número de Nodes en la lista enlazada.
Espacio auxiliar: O(1), ya que no estamos utilizando ningún espacio adicional.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por Kanishk_Verma y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA
