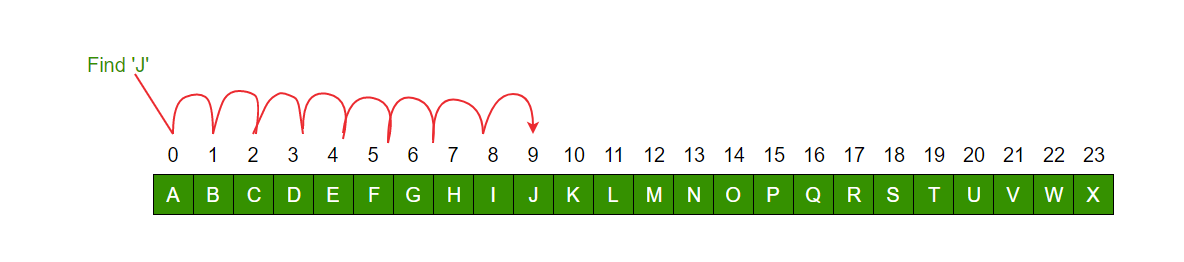
Problema: Dada una array arr[] de n elementos, escriba una función para buscar un elemento dado x en arr[].
Ejemplos:
Input : arr[] = {10, 20, 80, 30, 60, 50,
110, 100, 130, 170}
x = 110;
Output : 6
Element x is present at index 6
Input : arr[] = {10, 20, 80, 30, 60, 50,
110, 100, 130, 170}
x = 175;
Output : -1
Element x is not present in arr[].
Un enfoque simple es hacer una búsqueda lineal , es decir
- Comience desde el elemento más a la izquierda de arr[] y compare x uno por uno con cada elemento de arr[]
- Si x coincide con un elemento, devuelve el índice.
- Si x no coincide con ninguno de los elementos, devuelve -1.
Python
# Searching an element in a list/array in python # can be simply done using \'in\' operator # Example: # if x in arr: # print arr.index(x) # If you want to implement Linear Search in python # Linearly search x in arr[] # If x is present then return its location # else return -1 def search(arr, x): for i in range(len(arr)): if arr[i] == x: return i return -1
Enfoque recursivo:
Python
# This is similar to the above one, with the only difference # being that it is using the recursive approach instead of iterative. def search(arr, curr_index, key): if curr_index == -1: return -1 if arr[curr_index] == key: return curr_index return search(arr, curr_index-1, key)
La complejidad temporal del algoritmo anterior es O(n).
Espacio auxiliar: O(1) para iterativo y O(n) para recursivo.
Consulte el artículo completo sobre búsqueda lineal y diferencia entre algoritmos recursivos e iterativos para obtener más detalles.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA