Consulte primero los conjuntos anteriores del artículo Proto Van Emde Boas Tree . Es muy recomendable.
Procedimiento para borrar:
- Caso base: si llegamos a Proto VEB con tamaño 2, verificaremos si la clave está presente o no, en caso afirmativo, asignamos el puntero a nullptr, que configurará falso para su presencia.
- Recursividad:
- Llamamos recursivamente a la función de eliminación sobre el grupo de claves, es decir, alto (clave) y su posición baja (clave).
- Después de eliminar la clave del clúster (después de llegar al caso base), verificamos si hay otras claves presentes en el clúster. Si hay alguna clave presente, no podemos establecer el resumen en nullptr; de lo contrario, estableceremos el resumen en nullptr llamando a eliminar sobre resumen.
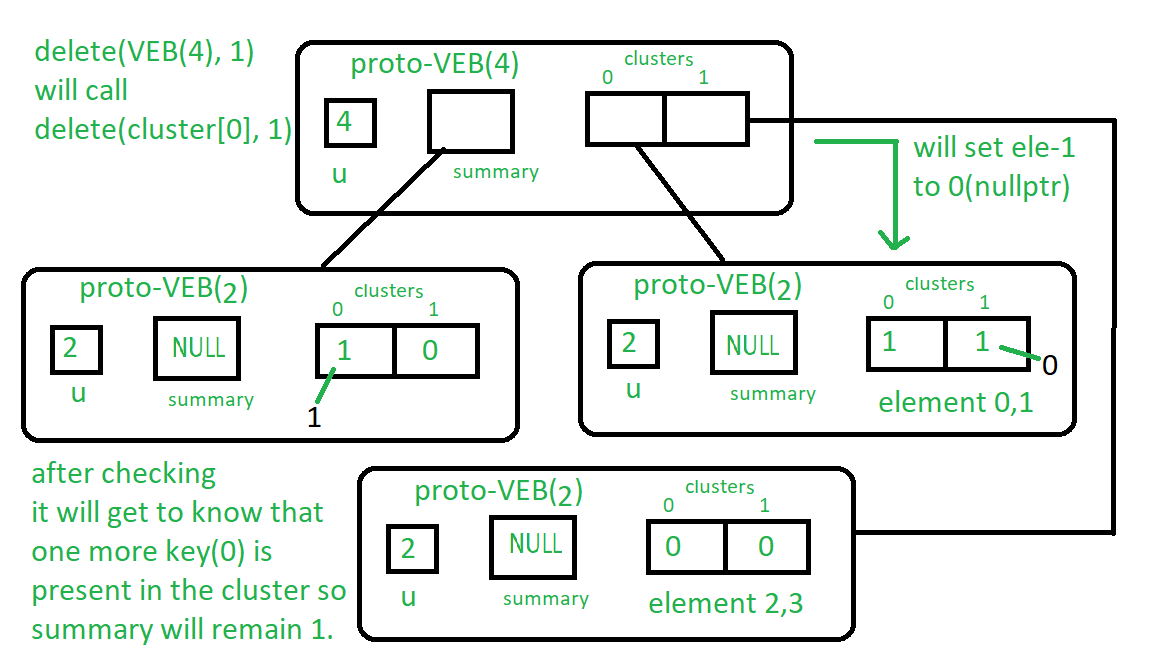
Entendamos 1 eliminación en Proto-VEB de tamaño 4:
Primero llamará recursivamente a eliminar (cluster [0], 1).
Entonces, ahora el caso base está satisfecho, por lo que irá a la posición 1 en el clúster [0] Proto-VEB y lo establecerá en nullptr si está presente.
Ahora verificaremos si hay más claves presentes en el clúster [0] (vea el bucle for en eliminar), 0 está presente, por lo que la llamada eliminar (resumen, 0) no se ejecutará y el resumen permanecerá igual.
Vea la imagen a continuación para entenderlo:
Siga las instrucciones escritas cerca de los cuadros de arriba a abajo.
A continuación se muestra la implementación:
CPP
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Proto_Van_Emde_Boas {
public:
// Total number of keys
int universe_size;
// Summary
Proto_Van_Emde_Boas* summary;
// Clusters array of Proto-VEB pointers
vector<Proto_Van_Emde_Boas*> clusters;
int root(int u)
{
return int(sqrt(u));
}
// Function to return cluster numbers
// in which key is present
int high(int x)
{
return x / root(universe_size);
}
// Function to return position of x in cluster
int low(int x)
{
return x % root(universe_size);
}
// Function to return the index from
// cluster number and position
int generate_index(int cluster, int position)
{
return cluster * root(universe_size) + position;
}
// Constructor
Proto_Van_Emde_Boas(int size)
{
universe_size = size;
// Base case
if (size <= 2) {
// Set summary to nullptr as there is no
// more summary for size 2
summary = nullptr;
// Vector of two pointers
// nullptr in starting
clusters = vector<Proto_Van_Emde_Boas*>(size, nullptr);
}
else {
// Assigning Proto-VEB(sqrt(u)) to summary
summary = new Proto_Van_Emde_Boas(root(size));
// Creating array of Proto-VEB Tree pointers of size sqrt(u)
// first all nullptrs are going to assign
clusters = vector<Proto_Van_Emde_Boas*>(root(size), nullptr);
// Assigning Proto-VEB(sqrt(u)) to all its clusters
for (int i = 0; i < root(size); i++) {
clusters[i] = new Proto_Van_Emde_Boas(root(size));
}
}
}
};
// Function that returns true if the
// key is present in the tree
bool isMember(Proto_Van_Emde_Boas* helper, int key)
{
// If key is greater then universe_size then
// returns false
if (key >= helper->universe_size)
return false;
// If we reach at base case
// the just return whether
// pointer is nullptr then false
// else return true
if (helper->universe_size == 2) {
return helper->clusters[key];
}
else {
// Recursively go deep into the
// level of Proto-VEB tree using its
// cluster index and its position
return isMember(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)],
helper->low(key));
}
}
// Function to insert a key in the tree
void insert(Proto_Van_Emde_Boas*& helper, int key)
{
// If we reach at base case
// then assign Proto-VEB(1) in place
// of nullptr
if (helper->universe_size == 2) {
helper->clusters[key] = new Proto_Van_Emde_Boas(1);
}
else {
// Recursively using index of cluster and its
// position in cluster
insert(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)],
helper->low(key));
// Also do the same recursion in summary VEB
insert(helper->summary, helper->high(key));
}
}
// Function to delete a key from the tree
void pveb_delete(Proto_Van_Emde_Boas*& helper, int key)
{
// Base case: If the key is present
// then make it nullptr
if (helper->universe_size == 2) {
if (helper->clusters[key]) {
delete helper->clusters[key];
helper->clusters[key] = nullptr;
}
}
else {
// Recursive delete to reach at the base case
pveb_delete(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)], helper->low(key));
bool isanyinCluster = false;
// Iterate over the cluster of keys to check whether
// any other key is present within that cluster
// If yes then we should not update summary to 0
// else update summary to 0
for (int i = helper->high(key) * helper->root(helper->universe_size);
i < (helper->high(key) + 1) * helper->root(helper->universe_size);
i++) {
// If member is present then break the loop
if (isMember(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)], i)) {
isanyinCluster = true;
break;
}
}
// If no member is present then
// update summary to zero
if (isanyinCluster == false) {
pveb_delete(helper->summary, helper->high(key));
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Proto_Van_Emde_Boas* hello = new Proto_Van_Emde_Boas(4);
cout << isMember(hello, 2);
insert(hello, 2);
insert(hello, 3);
cout << isMember(hello, 2);
pveb_delete(hello, 2);
cout << isMember(hello, 2);
}
Relación de recurrencia para eliminar:
T(u) = T(u) = 2T()) + O(log2(
))
Complejidad del tiempo : O(log2(u)*log2(log2(u)))
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por Aakash_Panchal y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA