Los microservicios son más populares hoy en día. Se pueden escribir en cualquier idioma. En este artículo, veamos los microservicios Spring Boot . En este artículo, veamos un proyecto base «servicio de muestra de cambio de moneda» que tiene una lógica comercial y que se puede invocar en otro proyecto » servicio de muestra de conversión de moneda «. Ambos son proyectos de Maven y vamos a verlos uno por uno.
Microservicio 1: servicio de muestra de cambio de moneda
Estructura del proyecto
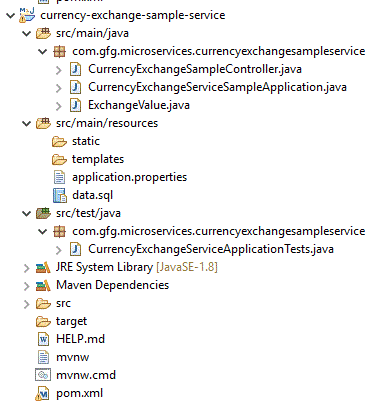
pom.xml
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.gfg.microservices</groupId>
<artifactId>currency-exchange-sample-service</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>currency-exchange-sample-service</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Hoxton.RC2</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Starter for building web, including RESTful,
applications using Spring MVC. -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- The spring-boot-devtools module can be included in any
project to provide additional development-time features -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!-- H2 is an open-source lightweight Java database -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- starter for using Spring Data JPA with Hibernate. -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- provides secured endpoints for monitoring
and managing your Spring Boot application -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
</project>
Veamos los archivos importantes
CurrencyExchangeServiceSampleApplication.java
Java
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
// It is equivalent to using @Configuration,
// @EnableAutoConfiguration and @ComponentScan with their
// default attributes:
public class CurrencyExchangeServiceSampleApplication {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SpringApplication.run(
CurrencyExchangeServiceSampleApplication.class,
args);
}
}
MonedaExchangeSampleController.java
@GetMapping("/currency-exchange-sample/fromCurrency/{fromCurrency}/toCurrency/{toCurrency}")
// where {fromCurrency} and {toCurrency} are path variable
// fromCurrency can be USD,EUR,AUD,INR and toCurrency can be the opposite of any fromCurrency
Java
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
// The @RestController annotation in Spring is essentially
// just a combination of
// @Controller and @ResponseBody. This annotation was added
// during Spring 4.0 to remove the redundancy of declaring
// the @ResponseBody annotation in your controller
public class CurrencyExchangeSampleController {
@Autowired private Environment environment;
@GetMapping(
"/currency-exchange-sample/fromCurrency/{fromCurrency}/toCurrency/{toCurrency}")
// where {fromCurrency} and {toCurrency} are path
// variable
// fromCurrency can be USD,EUR,AUD,INR and toCurrency
// can be the opposite of any fromCurrency
public ExchangeValue
retrieveExchangeValue(@PathVariable String fromCurrency,
@PathVariable String toCurrency)
{
// Here we need to write all of our business logic
BigDecimal conversionMultiple = null;
ExchangeValue exchangeValue = new ExchangeValue();
if (fromCurrency != null && toCurrency != null) {
if (fromCurrency.equalsIgnoreCase("USD")
&& toCurrency.equalsIgnoreCase("INR")) {
conversionMultiple = BigDecimal.valueOf(78);
}
if (fromCurrency.equalsIgnoreCase("INR")
&& toCurrency.equalsIgnoreCase("USD")) {
conversionMultiple
= BigDecimal.valueOf(0.013);
}
if (fromCurrency.equalsIgnoreCase("EUR")
&& toCurrency.equalsIgnoreCase("INR")) {
conversionMultiple = BigDecimal.valueOf(82);
}
if (fromCurrency.equalsIgnoreCase("AUD")
&& toCurrency.equalsIgnoreCase("INR")) {
conversionMultiple = BigDecimal.valueOf(54);
}
}
// setting the port
exchangeValue = new ExchangeValue(
1000L, fromCurrency, toCurrency,
conversionMultiple);
exchangeValue.setPort(Integer.parseInt(
environment.getProperty("local.server.port")));
return exchangeValue;
}
}
ExchangeValue.java
Java
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
// @Entity annotation defines that a class can be mapped to
// a table
@Entity
// Representation of the table name
@Table(name = "Exchange_Value")
public class ExchangeValue {
// The @Id annotation is inherited from
// javax.persistence.Id, indicating the member field
// below is the primary key of the current entity
@Id @Column(name = "id") private Long id;
@Column(name = "currency_from")
private String fromCurrency;
@Column(name = "currency_to") private String toCurrency;
@Column(name = "conversion_multiple")
private BigDecimal conversionMultiple;
@Column(name = "port") private int port;
public ExchangeValue() {}
// generating constructor using fields
public ExchangeValue(Long id, String fromCurrency,
String toCurrency,
BigDecimal conversionMultiple)
{
super();
this.id = id;
this.fromCurrency = fromCurrency;
this.toCurrency = toCurrency;
this.conversionMultiple = conversionMultiple;
}
// generating getters
public int getPort() { return port; }
public void setPort(int port) { this.port = port; }
public Long getId() { return id; }
public String getFrom() { return fromCurrency; }
public String getTo() { return toCurrency; }
public BigDecimal getConversionMultiple()
{
return conversionMultiple;
}
}
aplicación.propiedades
spring.application.name=currency-exchange-sample-service server.port=8000 #Representation of the port number . We can set different port number in run configuration also spring.jpa.show-sql=true #To display the SQL spring.h2.console.enabled=true spring.datasource.platform=h2 #As we are using h2 datasource spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:gfg
datos.sql
insert into exchange_value(id,currency_from,currency_to,conversion_multiple,port) values(10001,'USD', 'INR' ,65,0); insert into exchange_value(id,currency_from,currency_to,conversion_multiple,port) values(10002,'EUR', 'INR' ,82,0); insert into exchange_value(id,currency_from,currency_to,conversion_multiple,port) values(10003,'AUD', 'INR' ,53,0);
De forma predeterminada, se ha configurado para ejecutarse en el puerto 8000. Podemos crear otra instancia y hacer que el proyecto se ejecute en el puerto 8001 de las siguientes maneras
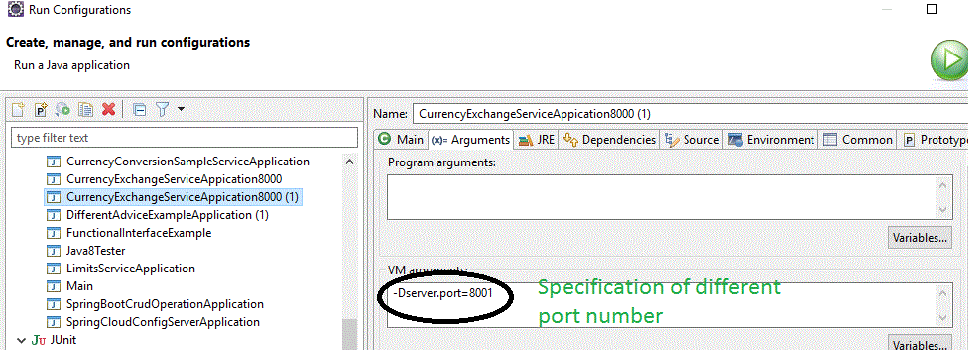
Como esta es la aplicación Spring Boot, normalmente se puede ejecutar como una aplicación Java
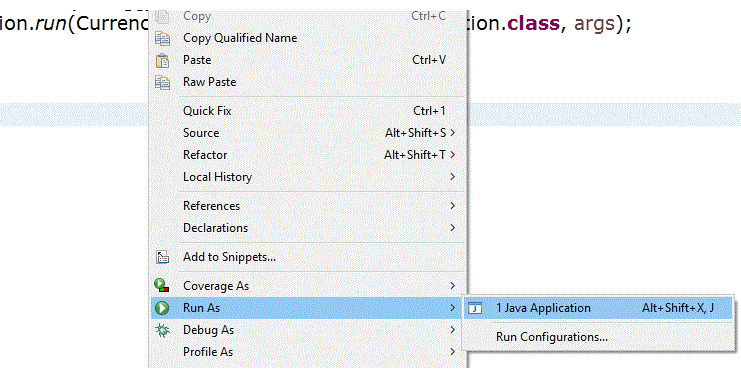
Si configuramos para ejecutar la aplicación en dos puertos diferentes, obtendremos las siguientes opciones
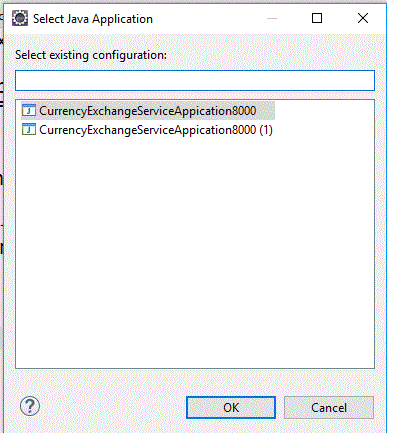
Seleccionemos la primera. Al ejecutar la aplicación, en la consola, vemos como
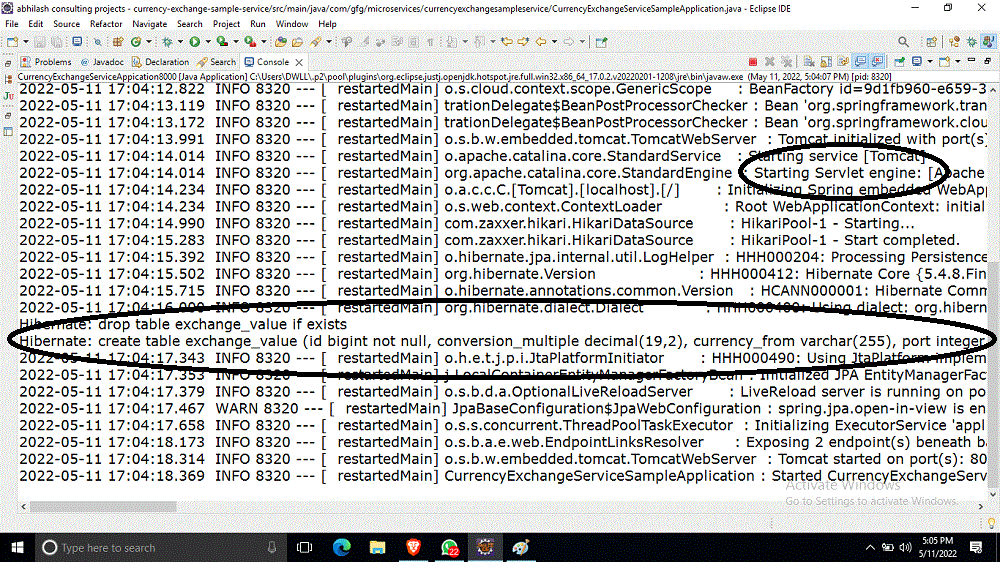
Desde la consola, podemos ver que usó Tomcat predeterminado y que el proyecto se está ejecutando en el puerto 8080. Como hemos usado 3 scripts de inserción, automáticamente se crea la tabla y se insertan los datos. Podemos hacer lo siguiente
http://localhost:8000/currency-exchange-sample/fromCurrency/USD/toCurrency/INR
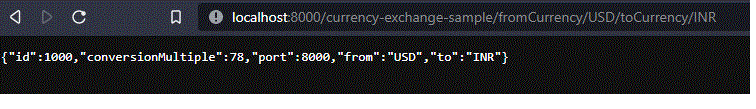
Cuando se accede a esta URL, se redirigirá al controlador, y fromCurrency se toma como «USD» y toCurrency se toma como «INR»
Debido a esto,
// Below set of code is executed and hence we are seeing the result like above
if (fromCurrency != null && toCurrency != null) {
if (fromCurrency.equalsIgnoreCase("USD") && toCurrency.equalsIgnoreCase("INR")) {
conversionMultiple = BigDecimal.valueOf(78);
}
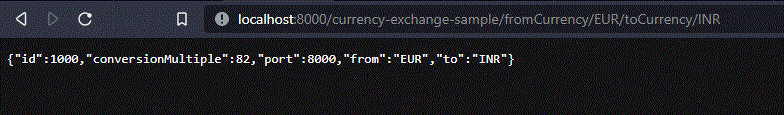
Del mismo modo, podemos ejecutar las siguientes URL a continuación
http://localhost:8000/currency-exchange-sample/fromCurrency/EUR/toCurrency/INR
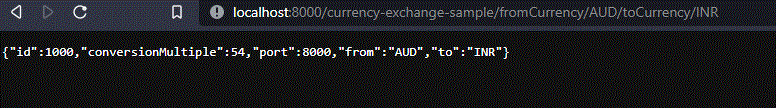
http://localhost:8000/currency-exchange-sample/fromCurrency/AUD/toCurrency/INR
Por lo tanto, de acuerdo con nuestras necesidades comerciales, podemos agregar lógica comercial al archivo del controlador. Veamos cómo se llama al servicio anterior en el proyecto de conversión de moneda
Microservicio 2: servicio de muestra de conversión de moneda
Este también es un proyecto experto.
pom.xml
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>com.gfg.microservices</groupId>
<artifactId>currency-conversion-sample-service</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>currency-conversion-servicce</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Hoxton.RC2</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
</project>
Principales archivos java importantes
CurrencyConversionSampleServiceApplication.java
Java
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class CurrencyConversionSampleServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CurrencyConversionSampleServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}
MonedaConversiónSampleBean.java
Java
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class CurrencyConversionSampleBean {
// We need to set all the fields that is going to
// received in response
private Long id;
private String from;
private String to;
private BigDecimal ConversionMultiple;
private BigDecimal quantity;
private BigDecimal totalCalculatedAmount;
private int port;
// default constructor
public CurrencyConversionSampleBean() {}
// creating constructor
public CurrencyConversionSampleBean(
Long id, String from, String to,
BigDecimal conversionMultiple, BigDecimal quantity,
BigDecimal totalCalculatedAmount, int port)
{
super();
this.id = id;
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
ConversionMultiple = conversionMultiple;
this.quantity = quantity;
this.totalCalculatedAmount = totalCalculatedAmount;
this.port = port;
}
// creating setters and getters
public Long getId() { return id; }
public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; }
public String getFrom() { return from; }
public void setFrom(String from) { this.from = from; }
public String getTo() { return to; }
public void setTo(String to) { this.to = to; }
public BigDecimal getConversionMultiple()
{
return ConversionMultiple;
}
public void
setConversionMultiple(BigDecimal conversionMultiple)
{
ConversionMultiple = conversionMultiple;
}
public BigDecimal getQuantity() { return quantity; }
public void setQuantity(BigDecimal quantity)
{
this.quantity = quantity;
}
public BigDecimal getTotalCalculatedAmount()
{
return totalCalculatedAmount;
}
public void setTotalCalculatedAmount(
BigDecimal totalCalculatedAmount)
{
this.totalCalculatedAmount = totalCalculatedAmount;
}
public int getPort() { return port; }
public void setPort(int port) { this.port = port; }
}
CurrencyConversionSampleController.java
@GetMapping("/currency-converter-sample/fromCurrency/{fromCurrency}/toCurrency/{toCurrency}/quantity/{quantity}")
Java
package com.gfg.microservices.currencyconversionservice;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
// To invoke an external service, RestTemplate() constructor
// is used
@RestController
public class CurrencyConversionSampleController {
@GetMapping(
"/currency-converter-sample/fromCurrency/{fromCurrency}/toCurrency/{toCurrency}/quantity/{quantity}")
// where {from} and {to} represents the
// column
// returns a bean back
public CurrencyConversionSampleBean
convertCurrency(@PathVariable String fromCurrency,
@PathVariable String toCurrency,
@PathVariable BigDecimal quantity)
{
// setting variables to currency exchange service
Map<String, String> uriVariables = new HashMap<>();
// urlParams should match properly
uriVariables.put("fromCurrency", fromCurrency);
uriVariables.put("toCurrency", toCurrency);
// calling the currency-exchange-sample-service
// http://localhost:8000/currency-exchange-sample/fromCurrency/{fromCurrency}/toCurrency/{toCurrency}
// is the service that got called from part 1. Its
// response is received and via
// CurrencyConversionSampleBean we are getting the
// results back
ResponseEntity<CurrencyConversionSampleBean>
responseEntity
= new RestTemplate().getForEntity(
"http://localhost:8000/currency-exchange-sample/fromCurrency/{fromCurrency}/toCurrency/{toCurrency}",
CurrencyConversionSampleBean.class,
uriVariables);
CurrencyConversionSampleBean response
= responseEntity.getBody();
// creating a new response bean and getting the
// response back and taking it into Bean Hence the
// output bean should have all the fields that is
// received from the response
return new CurrencyConversionSampleBean(
response.getId(), fromCurrency, toCurrency,
response.getConversionMultiple(), quantity,
quantity.multiply(
response.getConversionMultiple()),
response.getPort());
}
}
Es decir, este proyecto se inicia en el puerto 8100. Ahora podemos ejecutar las siguientes URLS
http://localhost:8100/currency-converter-sample/fromCurrency/USD/toCurrency/INR/quantity/1000
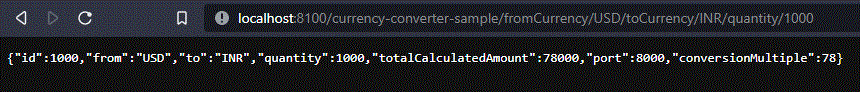
Cuando se llama a este servicio, a su vez se invocará.
Suposición: muestra de cambio de moneda se está ejecutando en el puerto 8000 y produce la respuesta requerida
http://localhost:8000/currency-exchange-sample/fromCurrency/USD/toCurrency/INR
Y luego como la lógica se escribe como
ResponseEntity<CurrencyConversionSampleBean>responseEntity=new RestTemplate().getForEntity("http://localhost:8000/currency-exchange-sample/fromCurrency/{fromCurrency}/toCurrency/{toCurrency}",CurrencyConversionSampleBean.class, uriVariables);
CurrencyConversionSampleBean response=responseEntity.getBody();
// creating a new response bean and getting the response back and taking it into Bean
// Hence the output bean should have all the fields that is received from the response
return new CurrencyConversionSampleBean(response.getId(), fromCurrency,toCurrency,response.getConversionMultiple(), quantity,quantity.multiply(response.getConversionMultiple()),response.getPort());
Estamos viendo el totalCalculatedAmount como 78 * 1000, es decir, 78000. Obtenemos «conversionMultiple» de la primera URL y se multiplica con el valor de cantidad aquí. Es muy ideal que no necesitemos llevar la lógica del servicio de intercambio a esta aplicación, es decir, el proyecto de la parte 1 puede estar separado y el proyecto de la parte 2 puede invocar las URL de la parte 1 aquí. Por lo tanto, los microservicios pueden ejecutarse por separado y otros servicios pueden usarlos. Resto de URLs que se pueden consultar
Ejemplo
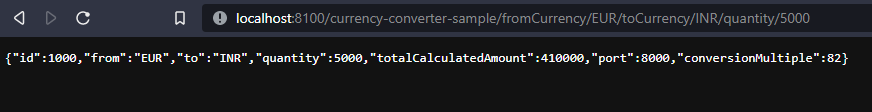
http://localhost:8100/currency-converter-sample/fromCurrency/EUR/toCurrency/INR/quantity/5000
Esto llamará a su vez
http://localhost:8000/currency-exchange-sample/fromCurrency/EUR/toCurrency/INR
Y la salida será
Ejemplo
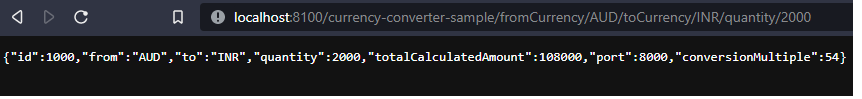
http://localhost:8100/currency-converter-sample/fromCurrency/AUD/toCurrency/INR/quantity/2000
Esto llamará a su vez
http://localhost:8000/currency-exchange-sample/fromCurrency/AUD/toCurrency/INR
Y la salida será
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por priyarajtt y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA