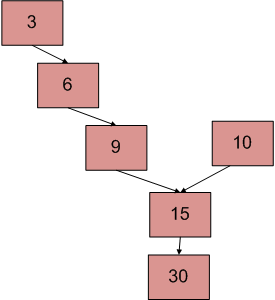
Dadas dos listas enlazadas de tamaño N y M que consisten en Nodes de valor positivo , que tienen un punto de intersección común, la tarea es encontrar el punto de intersección de las dos listas enlazadas donde se fusionan .
Ejemplos:
Entrada: L1: 3 → 6 → 9 → 15 → 30, L2: 10 → 15 → 30
Salida: 15
Explicación:De la imagen de arriba, el punto de intersección de las dos listas vinculadas es 15.
Entrada: L1: 1 → 2 → 3, L2: 4 → 5 → 1 → 2 → 3
Salida: 1
Enfoque: La idea es recorrer la primera lista enlazada y multiplicar el valor de cada Node por -1, haciéndolos así negativos. Luego, recorra la segunda lista enlazada e imprima el valor del primer Node que tiene un valor negativo. Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Recorra la primera lista enlazada L1 y multiplique el valor de cada Node por -1 .
- Ahora, recorra la segunda lista enlazada L2 y, si existe algún Node con valores negativos, imprima el valor absoluto del valor del Node como la intersección resultante de la lista enlazada y salga del bucle .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Structure of a node
// of a Linked List
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
// Constructor
Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
};
// Function to find the intersection
// point of the two Linked Lists
Node* intersectingNode(Node* headA,
Node* headB)
{
// Traverse the first linked list
// and multiply all values by -1
Node* a = headA;
while (a) {
// Update a -> data
a->data *= -1;
// Update a
a = a->next;
}
// Traverse the second Linked List
// and find the value of the first
// node having negative value
Node* b = headB;
while (b) {
// Intersection point
if (b->data < 0)
break;
// Update b
b = b->next;
}
return b;
}
// Function to create linked lists
void formLinkList(Node*& head1,
Node*& head2)
{
// Linked List L1
head1 = new Node(3);
head1->next = new Node(6);
head1->next->next = new Node(9);
head1->next->next->next = new Node(15);
head1->next->next->next->next = new Node(30);
// Linked List L2
head2 = new Node(10);
head2->next = head1->next->next->next;
return;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* head1;
Node* head2;
formLinkList(head1, head2);
cout << abs(intersectingNode(head1,
head2)
->data);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
static Node head1 = null;
static Node head2 = null;
// Structure of a node
// of a Linked List
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor
Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
// Function to find the intersection
// point of the two Linked Lists
static Node intersectingNode(Node headA, Node headB)
{
// Traverse the first linked list
// and multiply all values by -1
Node a = headA;
while (a != null)
{
// Update a -> data
a.data *= -1;
// Update a
a = a.next;
}
// Traverse the second Linked List
// and find the value of the first
// node having negative value
Node b = headB;
while (b != null)
{
// Intersection point
if (b.data < 0)
break;
// Update b
b = b.next;
}
return b;
}
// Function to create linked lists
static void formLinkList()
{
// Linked List L1
head1 = new Node(3);
head1.next = new Node(6);
head1.next.next = new Node(9);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(15);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(30);
// Linked List L2
head2 = new Node(10);
head2.next = head1.next.next.next;
return;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
formLinkList();
System.out.println(Math.abs(
intersectingNode(head1, head2).data));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Dharanendra L V.
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach # Structure of a node # of a Linked List class Node: def __init__(self, d): self.data = d self.next = None # Function to find the intersection # point of the two Linked Lists def intersectingNode(headA, headB): # Traverse the first linked list # and multiply all values by -1 a = headA while (a): # Update a . data a.data *= -1 # Update a a = a.next # Traverse the second Linked List # and find the value of the first # node having negative value b = headB while (b): # Intersection point if (b.data < 0): break # Update b b = b.next return b # Function to create linked lists def formLinkList(head1, head2): # Linked List L1 head1 = Node(3) head1.next = Node(6) head1.next.next = Node(9) head1.next.next.next = Node(15) head1.next.next.next.next = Node(30) # Linked List L2 head2 = Node(10) head2.next = head1.next.next.next return head1, head2 # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': head1, head2 = formLinkList(None, None) print(abs(intersectingNode(head1, head2).data)) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
// Constructor
public Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
public class GFG{
static Node head1 = null;
static Node head2 = null;
// Function to find the intersection
// point of the two Linked Lists
static Node intersectingNode(Node headA, Node headB)
{
// Traverse the first linked list
// and multiply all values by -1
Node a = headA;
while (a != null)
{
// Update a -> data
a.data *= -1;
// Update a
a = a.next;
}
// Traverse the second Linked List
// and find the value of the first
// node having negative value
Node b = headB;
while (b != null)
{
// Intersection point
if (b.data < 0)
break;
// Update b
b = b.next;
}
return b;
}
// Function to create linked lists
static void formLinkList()
{
// Linked List L1
head1 = new Node(3);
head1.next = new Node(6);
head1.next.next = new Node(9);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(15);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(30);
// Linked List L2
head2 = new Node(10);
head2.next = head1.next.next.next;
return;
}
// Driver Code
static public void Main ()
{
formLinkList();
Console.WriteLine(Math.Abs(
intersectingNode(head1, head2).data));
}
}
// This code is contributed by unknown2108.
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program for the above approach
let head1 = null;
let head2 = null;
// Structure of a node
// of a Linked List
class Node
{
constructor(x)
{
this.data=x;
this.next=null;
}
}
// Function to find the intersection
// point of the two Linked Lists
function intersectingNode(headA,headB)
{
// Traverse the first linked list
// and multiply all values by -1
let a = headA;
while (a != null)
{
// Update a -> data
a.data *= -1;
// Update a
a = a.next;
}
// Traverse the second Linked List
// and find the value of the first
// node having negative value
let b = headB;
while (b != null)
{
// Intersection point
if (b.data < 0)
break;
// Update b
b = b.next;
}
return b;
}
// Function to create linked lists
function formLinkList()
{
// Linked List L1
head1 = new Node(3);
head1.next = new Node(6);
head1.next.next = new Node(9);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(15);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(30);
// Linked List L2
head2 = new Node(10);
head2.next = head1.next.next.next;
return;
}
// Driver Code
formLinkList();
document.write(Math.abs(
intersectingNode(head1, head2).data));
// This code is contributed by patel2127
</script>
15
Complejidad temporal: O(N + M)
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por single__loop y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA