En este artículo, veremos cómo podemos cargar un archivo de texto sin formato en el módulo PYGLET en python. Pyglet es una biblioteca fácil de usar pero poderosa para desarrollar aplicaciones GUI visualmente ricas como juegos, multimedia, etc. Una ventana es un objeto «pesado» que ocupa los recursos del sistema operativo. Las ventanas pueden aparecer como regiones flotantes o pueden configurarse para llenar una pantalla completa (pantalla completa). Para cargar un archivo, es decir, un recurso, usamos el módulo de recursos de pyglet. Este módulo permite que las aplicaciones especifiquen una ruta de búsqueda de recursos. Las rutas relativas se consideran relativas al módulo __principal__ de la aplicación. Texto sin formato o Texto sin formato es cualquier texto, archivo de texto o documento que contiene solo texto. A diferencia de un documento de texto enriquecido, un archivo de texto sin formato no puede tener texto en negrita, fuentes, tamaños de fuente más grandes ni ningún otro formato de texto especial.
Podemos crear un objeto de ventana con la ayuda del comando dado a continuación
# creating a window window = pyglet.window.Window(width, height, title)
Para hacer esto, usamos el método de texto con la
sintaxis de pyglet.resource: resource.text (file_name)
Argument: toma una string, es decir, el nombre del archivo como argumento
Return: devuelve el objeto UnformattedDocument
A continuación se muestra la implementación.
Python3
# importing pyglet module
import pyglet
import pyglet.window.key as key
# width of window
width = 500
# height of window
height = 500
# caption i.e title of the window
title = "Geeksforgeeks"
# creating a window
window = pyglet.window.Window(width, height, title)
# text
text = "Welcome to GeeksforGeeks"
# creating label with following properties
# font = cooper
# position = 250, 150
# anchor position = center
label = pyglet.text.Label(text,
font_name ='Cooper',
font_size = 16,
x = 250,
y = 150,
anchor_x ='center',
anchor_y ='center')
# creating a batch
batch = pyglet.graphics.Batch()
# loading geeksforgeeks image
image = pyglet.image.load('gfg.png')
# creating sprite object
# it is instance of an image displayed on-screen
sprite = pyglet.sprite.Sprite(image, x = 200, y = 230)
# on draw event
@window.event
def on_draw():
# clear the window
window.clear()
# draw the label
label.draw()
# draw the image on screen
sprite.draw()
# key press event
@window.event
def on_key_press(symbol, modifier):
# key "C" get press
if symbol == key.C:
# printing the message
print("Key : C is pressed")
# image for icon
img = image = pyglet.resource.image("gfg.png")
# setting image as icon
window.set_icon(img)
# loading a plain text file
value = pyglet.resource.text("plain.txt")
# setting text of label
label.text = str(value)
# start running the application
pyglet.app.run()
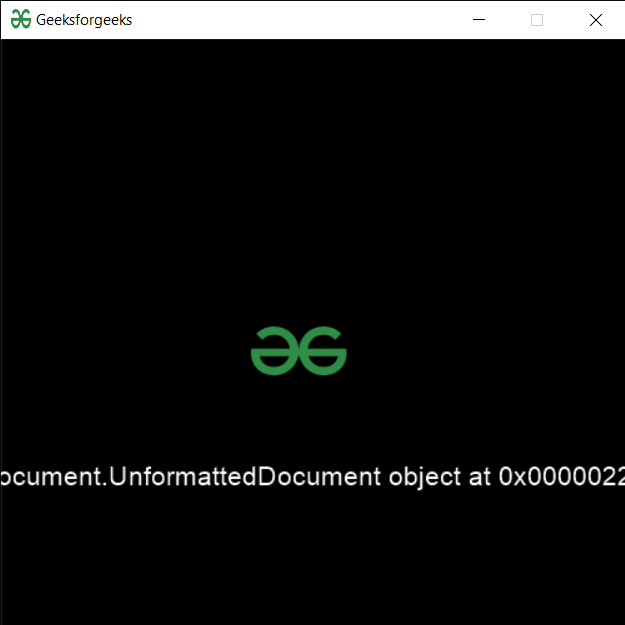
Producción :
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por rakshitarora y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA