En este artículo veremos cómo podemos conseguir el hilo de la caja de giro. El hilo de giro es el hilo en el que vive la caja de giro. Una interfaz puede tener varios subprocesos, lo que aumenta el rendimiento.
Para hacer esto, usamos threadel método con el objeto de cuadro de número.
Sintaxis: spin_box.thread()
Argumento: no requiere argumento
Retorno: Devuelve el objeto QThread
A continuación se muestra la implementación.
# importing libraries
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui
from PyQt5.QtGui import *
from PyQt5.QtCore import *
import sys
class Window(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# setting title
self.setWindowTitle("Python ")
# setting geometry
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 600, 400)
# calling method
self.UiComponents()
# showing all the widgets
self.show()
# method for widgets
def UiComponents(self):
# creating spin box
self.spin = QSpinBox(self)
# setting geometry to spin box
self.spin.setGeometry(100, 100, 250, 40)
# setting range to the spin box
self.spin.setRange(0, 999999)
# setting prefix to spin
self.spin.setPrefix("PREFIX ")
# setting suffix to spin
self.spin.setSuffix(" SUFFIX")
# setting status tip to the spin box
self.spin.setStatusTip("Small Value")
# creating a label
self.label = QLabel(self)
# making label multi line
self.label.setWordWrap(True)
# setting label geometry
self.label.setGeometry(100, 200, 250, 60)
# getting the thread
value = self.spin.thread()
# setting text to the label
self.label.setText("Thread : " + str(value))
# create pyqt5 app
App = QApplication(sys.argv)
# create the instance of our Window
window = Window()
# start the app
sys.exit(App.exec())
Producción :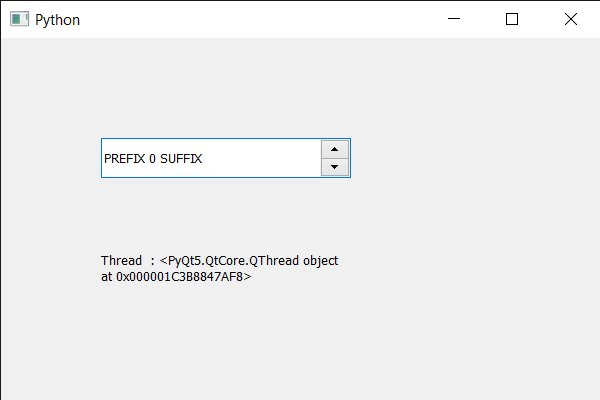
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por rakshitarora y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA