En este artículo, veremos cómo podemos obtener la región secundaria del objeto de vista de imagen en PyQTGraph . El gráfico PyQt es una biblioteca de gráficos e interfaz de usuario para Python que proporciona la funcionalidad comúnmente requerida en el diseño y las aplicaciones científicas. Sus objetivos principales son proporcionar gráficos rápidos e interactivos para mostrar datos (gráficos, videos, etc.), widgets utilizados para mostrar y analizar datos de imágenes, implementa muchas características como mostrar datos de imágenes en 2D y 3D. Para datos 3D, se muestra un control deslizante del eje z que permite al usuario seleccionar qué cuadro se muestra. Muestra el histograma de los datos de la imagen con una región móvil que define los niveles oscuros/claros, el degradado editable proporciona una tabla de búsqueda de colores. La vista de imagen es un grupo de widgets que contiene un objeto de vista, un botón y barras de desplazamiento, la región de niños es la región ocupada por los niños de la vista de imagen.
Podemos crear una vista de imagen con la ayuda del comando que se indica a continuación:
# creating a pyqtgraph image view object imv = pg.ImageView()
Para obtener la región secundaria de una vista de imagen, usamos el método childrenRegion() con el objeto de vista de imagen.
Sintaxis : imv.childrenRegion()
Argumento : No toma ningún argumento
Retorno : Devuelve el objeto QRion
A continuación se muestra el programa para obtener la región secundaria de una vista de imagen usando el módulo PyQTGraph :
Python3
# importing Qt widgets
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
# importing system
import sys
# importing numpy as np
import numpy as np
# importing pyqtgraph as pg
import pyqtgraph as pg
from PyQt5.QtGui import *
from PyQt5.QtCore import *
# Image View class
class ImageView(pg.ImageView):
# constructor which inherit original
# ImageView
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
pg.ImageView.__init__(self, *args, **kwargs)
class Window(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# setting title
self.setWindowTitle("PyQtGraph")
# setting geometry
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 600, 500)
# icon
icon = QIcon("skin.png")
# setting icon to the window
self.setWindowIcon(icon)
# calling method
self.UiComponents()
# showing all the widgets
self.show()
# setting fixed size of window
#self.setFixedSize(QSize(600, 500))
# method for components
def UiComponents(self):
# creating a widget object
widget = QWidget()
# creating a label
label = QLabel("Geeksforgeeks Image View")
# setting minimum width
label.setMinimumWidth(130)
# making label do word wrap
label.setWordWrap(True)
# setting configuration options
pg.setConfigOptions(antialias=True)
# creating image view object
imv = ImageView()
# Create random 3D data set with noisy signals
img = pg.gaussianFilter(np.random.normal(
size=(200, 200)), (5, 5)) * 20 + 100
# setting new axis to image
img = img[np.newaxis, :, :]
# decay data
decay = np.exp(-np.linspace(0, 0.3, 100))[:, np.newaxis, np.newaxis]
# random data
data = np.random.normal(size=(100, 200, 200))
data += img * decay
data += 2
# adding time-varying signal
sig = np.zeros(data.shape[0])
sig[30:] += np.exp(-np.linspace(1, 10, 70))
sig[40:] += np.exp(-np.linspace(1, 10, 60))
sig[70:] += np.exp(-np.linspace(1, 10, 30))
sig = sig[:, np.newaxis, np.newaxis] * 3
data[:, 50:60, 30:40] += sig
# setting image to image view
# Displaying the data and assign each frame a time value from 1.0 to 3.0
imv.setImage(data, xvals=np.linspace(1., 3., data.shape[0]))
# Set a custom color map
colors = [
(0, 0, 0),
(4, 5, 61),
(84, 42, 55),
(15, 87, 60),
(208, 17, 141),
(255, 255, 255)
]
# color map
cmap = pg.ColorMap(pos=np.linspace(0.0, 1.0, 6), color=colors)
# setting color map to the image view
imv.setColorMap(cmap)
# Creating a grid layout
layout = QGridLayout()
# minimum width value of the label
label.setFixedWidth(130)
# setting this layout to the widget
widget.setLayout(layout)
# adding label in the layout
layout.addWidget(label, 1, 0)
# plot window goes on right side, spanning 3 rows
layout.addWidget(imv, 0, 1, 3, 1)
# setting this widget as central widget of the main window
self.setCentralWidget(widget)
# getting children region of image view
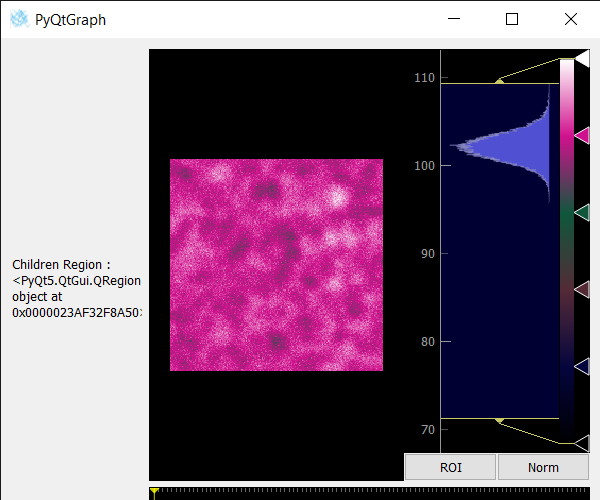
value = imv.childrenRegion()
# setting text to the label
label.setText("Children Region : " + str(value))
# create pyqt5 app
App = QApplication(sys.argv)
# create the instance of our Window
window = Window()
# start the app
sys.exit(App.exec())
Producción :
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por rakshitarora y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA