PyQtGraph es una biblioteca Python de gráficos e interfaz de usuario para funcionalidades comúnmente requeridas en aplicaciones científicas y de diseño. Proporciona gráficos rápidos e interactivos para mostrar datos (gráficos, video, etc.). Un gráfico de líneas es un tipo de gráfico que muestra información como una serie de puntos de datos comúnmente conocidos como marcadores, conectados por segmentos de línea recta. Un diagrama de dispersión usa puntos para representar valores para dos variables numéricas diferentes. Es un tipo de gráfico, dibujado usando coordenadas cartesianas para mostrar valores de dos variables típicamente para un conjunto de datos.
Cuando creamos un gráfico de líneas o un gráfico de diagrama de dispersión, los puntos que representan algunos datos deben resaltarse con ciertos símbolos, por defecto es un círculo redondo, pero esto se puede modificar según sea necesario. Pyqtgraph ofrece un total de 12 símbolos que se pueden usar para cambiar el símbolo según sea necesario.
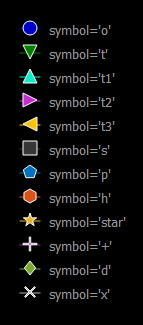
A continuación se muestra la lista de los símbolos disponibles en este módulo:
- o : Símbolo predeterminado, símbolo de círculo redondo
- t : Triángulo apuntando hacia abajo símbolo
- t1 : Triángulo apuntando hacia arriba símbolo
- t2 : Triángulo que señala el símbolo del lado derecho
- t3 : Triángulo que señala el símbolo del lado izquierdo
- s : Símbolo cuadrado
- p : símbolo del Pentágono
- h : símbolo hexagonal
- estrella : símbolo de estrella
- + : símbolo más
- d : símbolo del prisma
- x : Símbolo de cruz
Así es como aparecen en la pantalla de salida:
Podemos crear una ventana de trazado con la ayuda de los comandos que se indican a continuación:
plt = pg.plot()
Para implementar el concepto explicado anteriormente, se pueden seguir los siguientes pasos:
- Importar módulos pyqtgraph, pyqt5 y numpy
- Crear clase de ventana principal
- Crear un objeto de ventana de trazado
- Agregar leyenda a la ventana de trazado
- Cree 12 líneas que tengan diferentes puntos para que no se crucen entre sí y dividan diferentes símbolos y colores.
- Agregue la ventana de trazado y otro widget como etiqueta al diseño de cuadrícula
- Establecer el widget de diseño de cuadrícula como el widget central de la ventana principal
Ejemplo:
Python3
# importing Qt widgets
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
# importing system
import sys
# importing numpy as np
import numpy as np
# importing pyqtgraph as pg
import pyqtgraph as pg
from PyQt5.QtGui import * from PyQt5.QtCore import * from collections import namedtuple
class Window(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# setting title
self.setWindowTitle("PyQtGraph")
# setting geometry
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 500)
# icon
icon = QIcon("skin.png")
# setting icon to the window
self.setWindowIcon(icon)
# calling method
self.UiComponents()
# showing all the widgets
self.show()
# method for components
def UiComponents(self):
# creating a widget object
widget = QWidget()
# text
text = "Geeksforgeeks Different Symbols"
# creating a label
label = QLabel(text)
# setting minimum width
label.setMinimumWidth(130)
# making label do word wrap
label.setWordWrap(True)
# setting pyqtgraph configuration
pg.setConfigOptions(antialias = True)
# creating a plot window
plot = pg.plot()
# adding legend to the plot window
plot.addLegend()
# plot the line1 with symbol o
# having color blue
line1 = plot.plot([1, 1, 1, 1, 1], pen =(0, 0, 200), symbolBrush =(0, 0, 200),
symbolPen ='w', symbol ='o', symbolSize = 14, name ="symbol ='o'")
# plot the line2 with symbol t
# having color green
line2 = plot.plot([2, 2, 2, 2, 2], pen =(0, 128, 0), symbolBrush =(0, 128, 0),
symbolPen ='w', symbol ='t', symbolSize = 14, name ="symbol ='t'")
# plot the line3 with symbol t1
# having color bluegreen
line3 = plot.plot([3, 3, 3, 3, 3], pen =(19, 234, 201), symbolBrush =(19, 234, 201),
symbolPen ='w', symbol ='t1', symbolSize = 14, name ="symbol ='t1'")
# plot the line4 with symbol t2
# having color purple
line4 = plot.plot([4, 4, 4, 4, 4], pen =(195, 46, 212), symbolBrush =(195, 46, 212),
symbolPen ='w', symbol ='t2', symbolSize = 14, name ="symbol ='t2'")
# plot the line5 with symbol t3
# having color brownish
line5 = plot.plot([5, 5, 5, 5, 5], pen =(250, 194, 5), symbolBrush =(250, 194, 5),
symbolPen ='w', symbol ='t3', symbolSize = 14, name ="symbol ='t3'")
# plot the line6 with symbol s
# having color grey
line6 = plot.plot([6, 6, 6, 6, 6], pen =(54, 55, 55), symbolBrush =(55, 55, 55), symbolPen ='w', symbol ='s', symbolSize = 14,
name ="symbol ='s'")
# plot the line7 with symbol p
# having color sky blue
line7 = plot.plot([7, 7, 7, 7, 7], pen =(0, 114, 189), symbolBrush =(0, 114, 189),
symbolPen ='w', symbol ='p', symbolSize = 14, name ="symbol ='p'")
# plot the line8 with symbol h
# having color orange
line8 = plot.plot([8, 8, 8, 8, 8], pen =(217, 83, 25), symbolBrush =(217, 83, 25),
symbolPen ='w', symbol ='h', symbolSize = 14, name ="symbol ='h'")
# plot the line9 with symbol star
# having yellow color
line9 = plot.plot([9, 9, 9, 9, 9], pen =(237, 177, 32), symbolBrush =(237, 177, 32),
symbolPen ='w', symbol ='star', symbolSize = 14, name ="symbol ='star'")
# plot the line10 with symbol +
# having bluish color
line10 = plot.plot([10, 10, 10, 10, 10], pen =(126, 47, 142), symbolBrush =(126, 47, 142),
symbolPen ='w', symbol ='+', symbolSize = 14, name ="symbol ='+'")
# plot the line11 with symbol d
# having greenish color
line11 = plot.plot([11, 11, 11, 11, 11], pen =(119, 172, 48), symbolBrush =(119, 172, 48),
symbolPen ='w', symbol ='d', symbolSize = 14, name ="symbol ='d'")
# plot the line12 with symbol x
# having off white color
line12 = plot.plot([12, 12, 12, 12, 12], pen =(180, 180, 180), symbolBrush =(180, 180, 180),
symbolPen ='w', symbol ='x', symbolSize = 14, name ="symbol ='x'")
# setting x-axis range
plot.setXRange(-3, 4)
# Creating a grid layout
layout = QGridLayout()
# minimum width value of the label
label.setMinimumWidth(130)
# setting this layout to the widget
widget.setLayout(layout)
# adding label in the layout
layout.addWidget(label, 1, 0)
# plot window goes on right side, spanning 3 rows
layout.addWidget(plot, 0, 1, 3, 1)
# setting this widget as central widget of the main window
self.setCentralWidget(widget)
# create pyqt5 app
App = QApplication(sys.argv)
# create the instance of our Window
window = Window()
# start the app
sys.exit(App.exec())
Producción :
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por rakshitarora y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA