Kivy es una herramienta GUI independiente de la plataforma en Python. Como se puede ejecutar en Android, IOS, Linux y Windows, etc. Básicamente se usa para desarrollar la aplicación de Android, pero eso no significa que no se pueda usar en aplicaciones de escritorio.
Widget de imagen:
El widget Imagen se utiliza para mostrar una imagen. Para usar el widget de imagen, debe importar:
from kivy.uix.image import Image, AsyncImage
porque el módulo kivy.uix.imagetiene toda la funcionalidad relacionada con las imágenes.
Las imágenes se pueden cargar en la aplicación a través de dos tipos:
1) Del sistema:
wimg = Image(source='mylogo.png')2) Carga asíncrona:
para cargar una imagen de forma asíncrona (por ejemplo, desde un servidor web externo), use la subclase AsyncImage:aimg = AsyncImage(source='http://mywebsite.com/logo.png')
Nota: De manera predeterminada, la imagen está centrada y cabe dentro del cuadro delimitador del widget. Si no quiere eso, puede establecer allow_stretch en True y keep_ratio en False.
Basic Approach to create multiple layout in one file: 1) import kivy 2) import kivyApp 3) import image 4) set minimum version(optional) 5) create App class 6) return Image/layout/widget 7) Run an instance of the class
A continuación se muestra el código de cómo puede usar las imágenes en su código:
Código #1:
Imagen simple del sistema (debe estar en la carpeta en la que se guarda el archivo .py)
# Program to explain how to add image in kivy
# import kivy module
import kivy
# base Class of your App inherits from the App class.
# app:always refers to the instance of your application
from kivy.app import App
# this restrict the kivy version i.e
# below this kivy version you cannot
# use the app or software
kivy.require('1.9.0')
# The Image widget is used to display an image
# this module contain all features of images
from kivy.uix.image import Image
# creating the App class
class MyApp(App):
# defining build()
def build(self):
# return image
return Image(source ='download.jpg')
# run the App
MyApp().run()
Salida: 
Código #2:
¿Cómo podemos agregar AsyncImage, es decir, desde el servidor web (externo)?
# Simple program to show how we add AsyncImage in kivy App
# import kivy module
import kivy
# base Class of your App inherits from the App class.
# app:always refers to the instance of your application
from kivy.app import App
# this restrict the kivy version i.e
# below this kivy version you cannot
# use the app or software
kivy.require('1.9.0')
# The Image widget is used to display an image
# this module contains all features of images
from kivy.uix.image import AsyncImage
# creating the App class
class MyApp(App):
# defining build()
def build(self):
# return image
return AsyncImage(source ='http://kivy.org/logos/kivy-logo-black-64.png')
# run the App
MyApp().run()
Producción: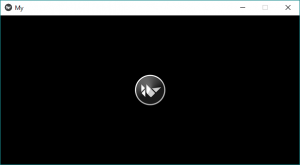
Ahora se me ocurrió una cosa: ¿cómo puede cambiar el tamaño, la posición, etc. de la imagen? El siguiente código también lo explicará:
Código #3:
# Program to Show how to use images in kivy
# import kivy module
import kivy
# base Class of your App inherits from the App class.
# app:always refers to the instance of your application
from kivy.app import App
# this restrict the kivy version i.e
# below this kivy version you cannot
# use the app or software
kivy.require('1.9.0')
# The Image widget is used to display an image
# this module contain all features of images
from kivy.uix.image import Image
# The Widget class is the base class required for creating Widgets
from kivy.uix.widget import Widget
# to change the kivy default settings we use this module config
from kivy.config import Config
# 0 being off 1 being on as in true / false
# you can use 0 or 1 && True or False
Config.set('graphics', 'resizable', True)
# creating the App class
class MyApp(App):
# defining build()
def build(self):
# loading image
self.img = Image(source ='download.jpg')
# By default, the image is centered and fits
# inside the widget bounding box.
# If you don’t want that,
# you can set allow_stretch to
# True and keep_ratio to False.
self.img.allow_stretch = True
self.img.keep_ratio = False
# Providing Size to the image
# it varies from 0 to 1
self.img.size_hint_x = 1
self.img.size_hint_y = 1
# Position set
self.img.pos = (200, 100)
# Opacity adjust the fadeness of the image if
# 0 then it is complete black
# 1 then original
# it varies from 0 to 1
self.img.opacity = 1
# adding image to widget
s = Widget()
s.add_widget(self.img)
# return widget
return s
# run the app
MyApp().run()
Producción: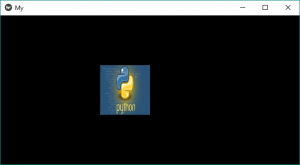
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por YashKhandelwal8 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA