En este artículo, aprenderemos cómo podemos agregar texto a los juegos de arcade en Python.
Agregar texto simple
Podemos agregar texto en la sala de juegos usando la función draw_text().
Sintaxis: arcade.draw_text(texto, x, y, color, tamaño, ancho, alineación, nombre_fuente)
Parámetros:
- text: Texto que queremos mostrar
- x : coordenada x
- y : coordenada y
- color : color del texto
- tamaño : Tamaño de la fuente
- ancho : Ancho del texto
- align : Alineación del texto
- font_name : Nombre de la fuente
En el siguiente ejemplo, vamos a crear una clase llamada MainGame, y dentro de esta clase, crearemos una función on_draw() en la que haremos la representación y el dibujo de nuestro texto. Luego llamaremos a nuestra clase MainGame() y a la función arcade.run().
A continuación se muestra la implementación:
Python3
# Importing arcade module
import arcade
# Creating MainGame class
class MainGame(arcade.Window):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(600, 600,
title="Text in Arcade")
# Creating on_draw() function to draw on the screen
def on_draw(self):
arcade.start_render()
# Drawing the text using draw_text()
# draw_text function is used to draw
# text to the screen using Pyglet’s label.
arcade.draw_text("GeeksforGeeks",120.0,300.0,
arcade.color.GREEN,40,80,'left')
# Calling MainGame class
MainGame()
arcade.run()
Producción:

Actualización del texto
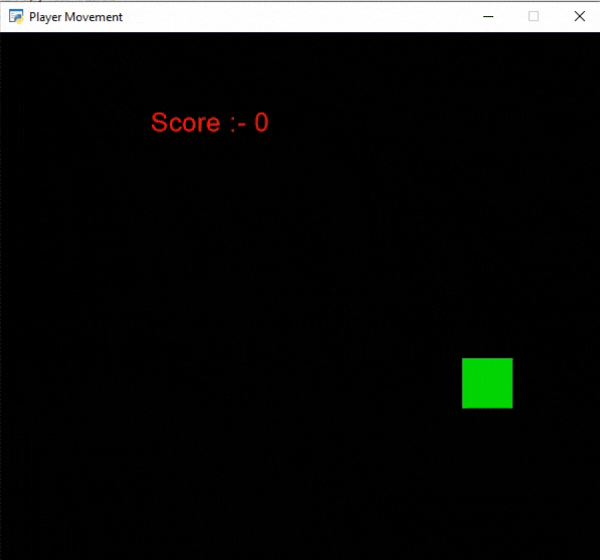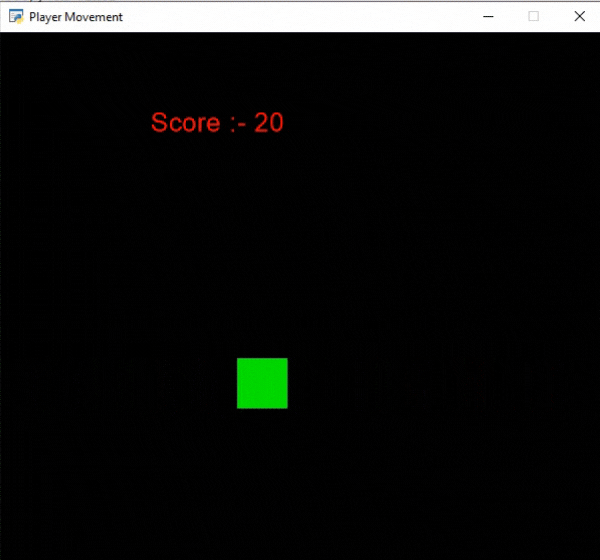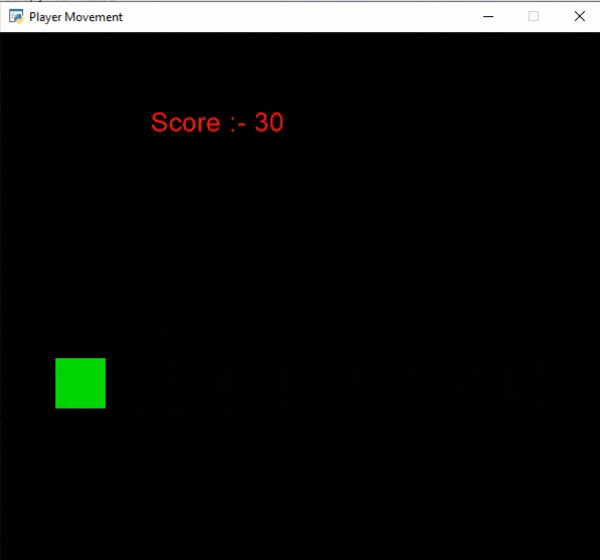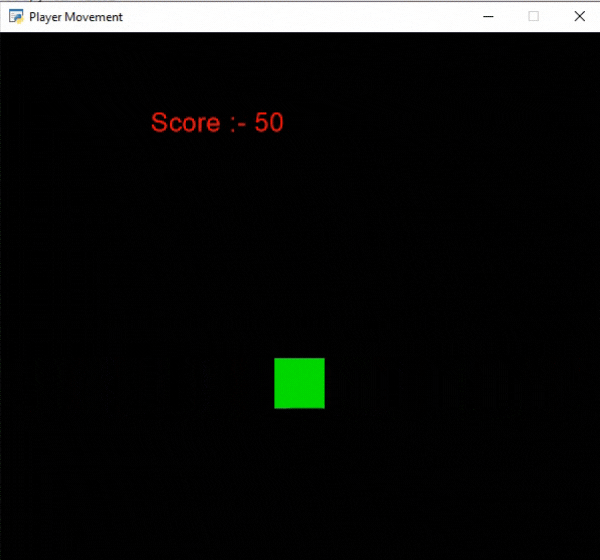
En este ejemplo, vamos a mostrar la puntuación como texto y queremos aumentar la puntuación en 10 puntos cada vez que el jugador toque el borde de la pantalla. Para ello, vamos a inicializar algunas variables para las coordenadas x e y, la puntuación y la velocidad del jugador en nuestra clase MainGame. Después de eso, crearemos 2 funciones:
- on_draw(): Dibujaremos nuestro reproductor y texto dentro de esta función.
- on_update(): Actualizaremos la coordenada x del jugador agregando velocidad. Luego cambiaremos la dirección del jugador y aumentaremos la puntuación si el jugador cruza los límites de la pantalla. Después de esto, llamaremos a nuestra clase MainGame().
A continuación se muestra la implementación:
Python3
# Importing arcade module
import arcade
# Creating MainGame class
class MainGame(arcade.Window):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(600, 600, title="Player Movement")
# Initializing the initial x and y coordinated
self.x = 250
self.y = 250
# Creating variable to store the score
self.score = 0
# Initializing a variable to store
# the velocity of the player
self.vel = 300
# Creating on_draw() function to draw on the screen
def on_draw(self):
arcade.start_render()
# Drawing the rectangle using
# draw_rectangle_filled function
arcade.draw_rectangle_filled(self.x, self.y,50, 50,
arcade.color.GREEN )
# Drawing the text
arcade.draw_text('Score :- '+str(self.score),150.0,500.0,
arcade.color.RED,20,180,'left')
# Creating on_update function to
# update the x coordinate
def on_update(self,delta_time):
self.x += self.vel * delta_time
# Changing the direction of
# movement if player crosses the screen
# and increasing the score
if self.x>=550 or self.x<=50:
self.score += 10
self.vel *= -1
# Calling MainGame class
MainGame()
arcade.run()
Producción:
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por imranalam21510 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA