Requisitos previos: Introducción a tkinter
Python ofrece múltiples opciones para desarrollar una GUI (interfaz gráfica de usuario). De todos los métodos GUI, Tkinter es el método más utilizado. Es una interfaz estándar de Python para el kit de herramientas Tk GUI que se envía con Python. Python con Tkinter genera la forma más rápida y sencilla de crear aplicaciones GUI. Ahora, depende de la imaginación o la necesidad de un desarrollador, lo que quiere desarrollar con este conjunto de herramientas.
Para crear un Tkinter:
- Importando el módulo – Tkinter
- Crear la ventana principal (contenedor)
- Agregue cualquier cantidad de widgets a la ventana principal.
- Aplique el evento Trigger en los widgets.
La GUI se vería a continuación:
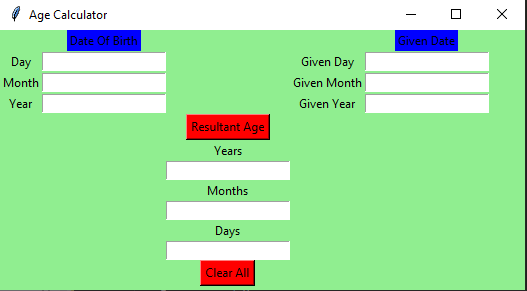
Vamos a crear una sencilla aplicación de calculadora de edad basada en GUI que pueda calcular la edad con respecto a la fecha dada y la fecha de nacimiento proporcionada por el usuario.
A continuación se muestra la implementación:
Python3
# import all functions from the tkinter
from tkinter import *
# import messagebox class from tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
# Function for clearing the
# contents of all text entry boxes
def clearAll() :
# deleting the content from the entry box
dayField.delete(0, END)
monthField.delete(0, END)
yearField.delete(0, END)
givenDayField.delete(0, END)
givenMonthField.delete(0, END)
givenYearField.delete(0, END)
rsltDayField.delete(0, END)
rsltMonthField.delete(0, END)
rsltYearField.delete(0, END)
# function for checking error
def checkError() :
# if any of the entry field is empty
# then show an error message and clear
# all the entries
if (dayField.get() == "" or monthField.get() == ""
or yearField.get() == "" or givenDayField.get() == ""
or givenMonthField.get() == "" or givenYearField.get() == "") :
# show the error message
messagebox.showerror("Input Error")
# clearAll function calling
clearAll()
return -1
# function to calculate Age
def calculateAge() :
# check for error
value = checkError()
# if error is occur then return
if value == -1 :
return
else :
# take a value from the respective entry boxes
# get method returns current text as string
birth_day = int(dayField.get())
birth_month = int(monthField.get())
birth_year = int(yearField.get())
given_day = int(givenDayField.get())
given_month = int(givenMonthField.get())
given_year = int(givenYearField.get())
# if birth date is greater then given birth_month
# then donot count this month and add 30 to the date so
# as to subtract the date and get the remaining days
month =[31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31]
if (birth_day > given_day):
given_month = given_month - 1
given_day = given_day + month[birth_month-1]
# if birth month exceeds given month, then
# donot count this year and add 12 to the
# month so that we can subtract and find out
# the difference
if (birth_month > given_month):
given_year = given_year - 1
given_month = given_month + 12
# calculate day, month, year
calculated_day = given_day - birth_day;
calculated_month = given_month - birth_month;
calculated_year = given_year - birth_year;
# calculated day, month, year write back
# to the respective entry boxes
# insert method inserting the
# value in the text entry box.
rsltDayField.insert(10, str(calculated_day))
rsltMonthField.insert(10, str(calculated_month))
rsltYearField.insert(10, str(calculated_year))
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__" :
# Create a GUI window
gui = Tk()
# Set the background colour of GUI window
gui.configure(background = "light green")
# set the name of tkinter GUI window
gui.title("Age Calculator")
# Set the configuration of GUI window
gui.geometry("525x260")
# Create a Date Of Birth : label
dob = Label(gui, text = "Date Of Birth", bg = "blue")
# Create a Given Date : label
givenDate = Label(gui, text = "Given Date", bg = "blue")
# Create a Day : label
day = Label(gui, text = "Day", bg = "light green")
# Create a Month : label
month = Label(gui, text = "Month", bg = "light green")
# Create a Year : label
year = Label(gui, text = "Year", bg = "light green")
# Create a Given Day : label
givenDay = Label(gui, text = "Given Day", bg = "light green")
# Create a Given Month : label
givenMonth = Label(gui, text = "Given Month", bg = "light green")
# Create a Given Year : label
givenYear = Label(gui, text = "Given Year", bg = "light green")
# Create a Years : label
rsltYear = Label(gui, text = "Years", bg = "light green")
# Create a Months : label
rsltMonth = Label(gui, text = "Months", bg = "light green")
# Create a Days : label
rsltDay = Label(gui, text = "Days", bg = "light green")
# Create a Resultant Age Button and attached to calculateAge function
resultantAge = Button(gui, text = "Resultant Age", fg = "Black", bg = "Red", command = calculateAge)
# Create a Clear All Button and attached to clearAll function
clearAllEntry = Button(gui, text = "Clear All", fg = "Black", bg = "Red", command = clearAll)
# Create a text entry box for filling or typing the information.
dayField = Entry(gui)
monthField = Entry(gui)
yearField = Entry(gui)
givenDayField = Entry(gui)
givenMonthField = Entry(gui)
givenYearField = Entry(gui)
rsltYearField = Entry(gui)
rsltMonthField = Entry(gui)
rsltDayField = Entry(gui)
# grid method is used for placing
# the widgets at respective positions
# in table like structure .
dob.grid(row = 0, column = 1)
day.grid(row = 1, column = 0)
dayField.grid(row = 1, column = 1)
month.grid(row = 2, column = 0)
monthField.grid(row = 2, column = 1)
year.grid(row = 3, column = 0)
yearField.grid(row = 3, column = 1)
givenDate.grid(row = 0, column = 4)
givenDay.grid(row = 1, column = 3)
givenDayField.grid(row = 1, column = 4)
givenMonth.grid(row = 2, column = 3)
givenMonthField.grid(row = 2, column = 4)
givenYear.grid(row = 3, column = 3)
givenYearField.grid(row = 3, column = 4)
resultantAge.grid(row = 4, column = 2)
rsltYear.grid(row = 5, column = 2)
rsltYearField.grid(row = 6, column = 2)
rsltMonth.grid(row = 7, column = 2)
rsltMonthField.grid(row = 8, column = 2)
rsltDay.grid(row = 9, column = 2)
rsltDayField.grid(row = 10, column = 2)
clearAllEntry.grid(row = 12, column = 2)
# Start the GUI
gui.mainloop()
Producción :