Requisitos previos: GUI de Python: tkinter
Python ofrece múltiples opciones para desarrollar una GUI (interfaz gráfica de usuario). De todos los métodos GUI, Tkinter es el método más utilizado. Es una interfaz estándar de Python para el kit de herramientas Tk GUI que se envía con Python. Python con Tkinter genera la forma más rápida y sencilla de crear aplicaciones GUI. Crear una GUI usando Tkinter es una tarea fácil.
Pasos para crear un Tkinter:
- Importando el módulo – tkinter
- Crear la ventana principal (contenedor)
- Agregue cualquier cantidad de widgets a la ventana principal
- Aplique el evento Trigger en los widgets.
A continuación se muestra el aspecto de la GUI:
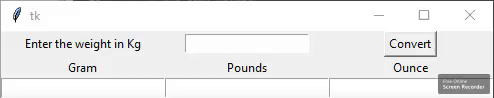
Vamos a crear un convertidor de peso basado en GUI que acepte un valor de entrada de kilogramos y convierta ese valor en gramos, libras y onzas cuando el usuario haga clic en el botón Convertir.
A continuación se muestra la implementación.
Python3
# Python program to create a simple GUI
# weight converter using Tkinter
from tkinter import *
# Create a GUI window
window = Tk()
# Function to convert weight
# given in kg to grams, pounds
# and ounces
def from_kg():
# convert kg to gram
gram = float(e2_value.get())*1000
# convert kg to pound
pound = float(e2_value.get())*2.20462
# convert kg to ounce
ounce = float(e2_value.get())*35.274
# Enters the converted weight to
# the text widget
t1.delete("1.0", END)
t1.insert(END,gram)
t2.delete("1.0", END)
t2.insert(END,pound)
t3.delete("1.0", END)
t3.insert(END,ounce)
# Create the Label widgets
e1 = Label(window, text = "Enter the weight in Kg")
e2_value = StringVar()
e2 = Entry(window, textvariable = e2_value)
e3 = Label(window, text = 'Gram')
e4 = Label(window, text = 'Pounds')
e5 = Label(window, text = 'Ounce')
# Create the Text Widgets
t1 = Text(window, height = 1, width = 20)
t2 = Text(window, height = 1, width = 20)
t3 = Text(window, height = 1, width = 20)
# Create the Button Widget
b1 = Button(window, text = "Convert", command = from_kg)
# grid method is used for placing
# the widgets at respective positions
# in table like structure
e1.grid(row = 0, column = 0)
e2.grid(row = 0, column = 1)
e3.grid(row = 1, column = 0)
e4.grid(row = 1, column = 1)
e5.grid(row = 1, column = 2)
t1.grid(row = 2, column = 0)
t2.grid(row = 2, column = 1)
t3.grid(row = 2, column = 2)
b1.grid(row = 0, column = 2)
# Start the GUI
window.mainloop()
Producción:
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por VineetLoyer y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA