PyTorch es una biblioteca de aprendizaje automático de código abierto desarrollada por Facebook. Se utiliza para fines de procesamiento de lenguaje natural y redes neuronales profundas.
La función torch.cos() brinda soporte para la función coseno en PyTorch. Espera la entrada en forma de radianes y la salida está en el rango [-1, 1]. El tipo de entrada es tensor y si la entrada contiene más de un elemento, se calcula el coseno por elemento.
Sintaxis : torch.cos(x, out=None)
Parámetros :
x :
Nombre del tensor de entrada (opcional): Tensor de salida
Tipo de retorno : Un tensor con el mismo tipo que el de x.
Código #1:
Python3
# Importing the PyTorch library import torch # A constant tensor of size 6 a = torch.FloatTensor([1.0, -0.5, 3.4, -2.1, 0.0, -6.5]) print(a) # Applying the cos function and # storing the result in 'b' b = torch.cos(a) print(b)
Producción:
1.0000 -0.5000 3.4000 -2.1000 0.0000 -6.5000 [torch.FloatTensor of size 6] 0.5403 0.8776 -0.9668 -0.5048 1.0000 0.9766 [torch.FloatTensor of size 6]
Código #2: Visualización
Python3
# Importing the PyTorch library
import torch
# Importing the NumPy library
import numpy as np
# Importing the matplotlib.pyplot function
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# A vector of size 15 with values from -5 to 5
a = np.linspace(-5, 5, 15)
# Applying the cosine function and
# storing the result in 'b'
b = torch.cos(torch.FloatTensor(a))
print(b)
# Plotting
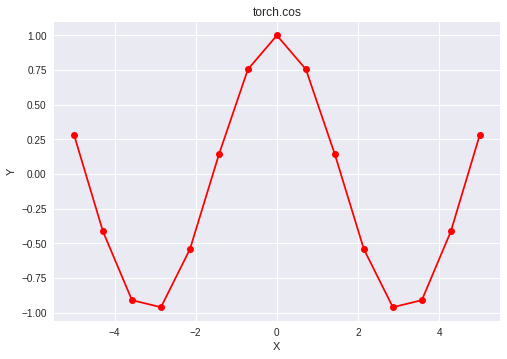
plt.plot(a, b.numpy(), color = 'red', marker = "o")
plt.title("torch.cos")
plt.xlabel("X")
plt.ylabel("Y")
plt.show()
Producción:
0.2837 -0.4138 -0.9090 -0.9598 -0.5414 0.1417 0.7556 1.0000 0.7556 0.1417 -0.5414 -0.9598 -0.9090 -0.4138 0.2837 [torch.FloatTensor of size 15]
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por vaibhav29498 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA