Requisito previo: manejo de archivos en Python
Dado un archivo de texto fname , la tarea es contar el número total de caracteres, palabras, espacios y líneas en el archivo.
Como sabemos, Python proporciona múltiples funciones y módulos integrados para manejar archivos. Discutamos diferentes formas de calcular el número total de caracteres, palabras, espacios y líneas en un archivo usando Python.
Método #1: enfoque ingenuo
En este enfoque, la idea es resolver la tarea desarrollando nuestra propia lógica. Sin utilizar ninguna función integrada de Python, se calculará el número total de caracteres, palabras, espacios y líneas del archivo.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior.
# Python implementation to compute
# number of characters, words, spaces
# and lines in a file
# Function to count number
# of characters, words, spaces
# and lines in a file
def counter(fname):
# variable to store total word count
num_words = 0
# variable to store total line count
num_lines = 0
# variable to store total character count
num_charc = 0
# variable to store total space count
num_spaces = 0
# opening file using with() method
# so that file gets closed
# after completion of work
with open(fname, 'r') as f:
# loop to iterate file
# line by line
for line in f:
# incrementing value of
# num_lines with each
# iteration of loop to
# store total line count
num_lines += 1
# declaring a variable word
# and assigning its value as Y
# because every file is
# supposed to start with
# a word or a character
word = 'Y'
# loop to iterate every
# line letter by letter
for letter in line:
# condition to check
# that the encountered character
# is not white space and a word
if (letter != ' ' and word == 'Y'):
# incrementing the word
# count by 1
num_words += 1
# assigning value N to
# variable word because until
# space will not encounter
# a word can not be completed
word = 'N'
# condition to check
# that the encountered character
# is a white space
elif (letter == ' '):
# incrementing the space
# count by 1
num_spaces += 1
# assigning value Y to
# variable word because after
# white space a word
# is supposed to occur
word = 'Y'
# loop to iterate every
# letter character by
# character
for i in letter:
# condition to check
# that the encountered character
# is not white space and not
# a newline character
if(i !=" " and i !="\n"):
# incrementing character
# count by 1
num_charc += 1
# printing total word count
print("Number of words in text file: ", num_words)
# printing total line count
print("Number of lines in text file: ", num_lines)
# printing total character count
print('Number of characters in text file: ', num_charc)
# printing total space count
print('Number of spaces in text file: ', num_spaces)
# Driver Code:
if __name__ == '__main__':
fname = 'File1.txt'
try:
counter(fname)
except:
print('File not found')
Producción:
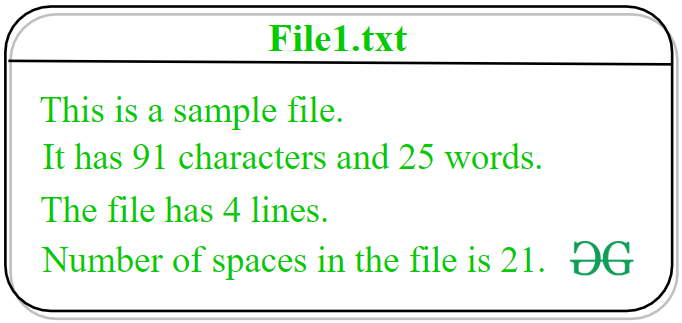
Number of words in text file: 25 Number of lines in text file: 4 Number of characters in text file: 91 Number of spaces in text file: 21
Método #2: Uso de algunas funciones integradas y funciones del módulo del sistema operativo
En este enfoque, la idea es utilizar el os.linesep()método del módulo del sistema operativo para separar las líneas en la plataforma actual. Cuando el escáner del intérprete lo encuentra os.linesep, lo reemplaza con \ncarácter. Después de eso , se usarán las funciones strip()y para llevar a cabo la tarea. Obtenga más ideas y funciones.split()strip()split()
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior.
# Python implementation to compute
# number of characters, words, spaces
# and lines in a file
# importing os module
import os
# Function to count number
# of characters, words, spaces
# and lines in a file
def counter(fname):
# variable to store total word count
num_words = 0
# variable to store total line count
num_lines = 0
# variable to store total character count
num_charc = 0
# variable to store total space count
num_spaces = 0
# opening file using with() method
# so that file gets closed
# after completion of work
with open(fname, 'r') as f:
# loop to iterate file
# line by line
for line in f:
# separating a line
# from \n character
# and storing again in line
# variable for further operations
line = line.strip(os.linesep)
# splitting the line
# to make a list of
# all the words present
# in that line and storing
# that list in
# wordlist variable
wordslist = line.split()
# incrementing value of
# num_lines with each
# iteration of loop to
# store total line count
num_lines = num_lines + 1
# incrementing value of
# num_words by the
# number of items in the
# list wordlist
num_words = num_words + len(wordslist)
# incrementing value of
# num_charc by 1 whenever
# value of variable c is other
# than white space in the separated line
num_charc = num_charc + sum(1 for c in line
if c not in (os.linesep, ' '))
# incrementing value of
# num_spaces by 1 whenever
# value of variable s is
# white space in the separated line
num_spaces = num_spaces + sum(1 for s in line
if s in (os.linesep, ' '))
# printing total word count
print("Number of words in text file: ", num_words)
# printing total line count
print("Number of lines in text file: ", num_lines)
# printing total character count
print("Number of characters in text file: ", num_charc)
# printing total space count
print("Number of spaces in text file: ", num_spaces)
# Driver Code:
if __name__ == '__main__':
fname = 'File1.txt'
try:
counter(fname)
except:
print('File not found')
Producción:
Number of words in text file: 25 Number of lines in text file: 4 Number of characters in text file: 91 Number of spaces in text file: 21
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por RISHU_MISHRA y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA