OpenCV-Python es una biblioteca de enlaces de Python diseñada para resolver problemas de visión por computadora. El método cv2.circle() se usa para dibujar un círculo en cualquier imagen. La sintaxis del método cv2.circle() es:
Sintaxis:
cv2.circle(image, center_coordinates, radius, color, thickness)
Parámetros:
- imagen: Es la imagen sobre la que se va a dibujar el círculo.
- center_coordinates: Son las coordenadas del centro del círculo. Las coordenadas se representan como tuplas de dos valores, es decir ( valor de la coordenada X , valor de la coordenada Y ).
- radio: Es el radio de la circunferencia.
- color: Es el color del borde de un círculo a dibujar. Para BGR , pasamos una tupla. ej.: (255, 0, 0) para el color azul.
- grosor: Es el grosor de la línea del borde del círculo en px . El grosor de -1 px llenará la forma del círculo con el color especificado.
Valor devuelto: Devuelve una imagen.
Los pasos para crear un círculo en una imagen son:
- Lee la imagen usando la función imread() .
- Pase esta imagen al método cv2.circle() junto con otros parámetros como coordenadas_centrales, radio, color y grosor.
- Muestra la imagen usando el método cv2.imshow().
Implementación:
Imagen utilizada para todos los siguientes ejemplos:

Ejemplo 1:
Python3
# Python program to explain cv2.circle() method # importing cv2 import cv2 # path path = r'C:\Users\Rajnish\Desktop\geeksforgeeks\geeks.png' # Reading an image in default mode image = cv2.imread(path) # Window name in which image is displayed window_name = 'Image' # Center coordinates center_coordinates = (120, 50) # Radius of circle radius = 20 # Blue color in BGR color = (255, 0, 0) # Line thickness of 2 px thickness = 2 # Using cv2.circle() method # Draw a circle with blue line borders of thickness of 2 px image = cv2.circle(image, center_coordinates, radius, color, thickness) # Displaying the image cv2.imshow(window_name, image)
Producción:

Ejemplo #2: Usar un grosor de -1 px para llenar el círculo con color rojo.
Python3
# Python program to explain cv2.circle() method # importing cv2 import cv2 # path path = r'C:\Users\Rajnish\Desktop\geeksforgeeks\geeks.png' # Reading an image in default mode image = cv2.imread(path) # Window name in which image is displayed window_name = 'Image' # Center coordinates center_coordinates = (120, 100) # Radius of circle radius = 30 # Red color in BGR color = (0, 0, 255) # Line thickness of -1 px thickness = -1 # Using cv2.circle() method # Draw a circle of red color of thickness -1 px image = cv2.circle(image, center_coordinates, radius, color, thickness) # Displaying the image cv2.imshow(window_name, image)
Producción:

Ejemplo # 3: para mostrar un círculo en una pantalla negra creada usando la biblioteca NumPy.
Python3
import cv2 import numpy as np # Reading an image in default mode Img = np.zeros((512, 512, 3), np.uint8) # Window name in which image is displayed window_name = 'Image' # Center coordinates center_coordinates = (220, 150) # Radius of circle radius = 100 # Red color in BGR color = (255, 133, 233) # Line thickness of -1 px thickness = -1 # Using cv2.circle() method # Draw a circle of red color of thickness -1 px image = cv2.circle(Img, center_coordinates, radius, color, thickness) # Displaying the image cv2.imshow(window_name, image) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Producción:
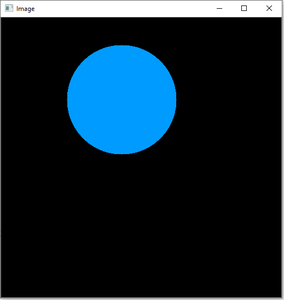
Círculo sobre fondo negro