Requisito previo: crear y escribir en una hoja de Excel
XlsxWriter es una biblioteca de Python con la que se pueden realizar múltiples operaciones en archivos de Excel, como crear, escribir, operaciones aritméticas y trazar gráficos. Veamos cómo trazar un gráfico con rellenos de patrón, utilizando datos en tiempo real.
Los gráficos se componen de al menos una serie de uno o más puntos de datos. Las series en sí mismas se componen de referencias a rangos de celdas. Para trazar los gráficos en una hoja de Excel, en primer lugar, cree un objeto de gráfico de un tipo de gráfico específico (es decir, gráfico de columnas, etc.). Después de crear objetos de gráfico, inserte datos en él y, por último, agregue ese objeto de gráfico en el objeto de hoja.
Código: trazar un gráfico con rellenos de patrón.
Para trazar este tipo de gráfico en una hoja de Excel, use el método add_series() con el argumento de palabra clave ‘patrón’ del objeto del gráfico.
Python3
# import xlsxwriter module
import xlsxwriter
# Workbook() takes one, non-optional, argument
# which is the filename that we want to create.
workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook('chart_pattern.xlsx')
# The workbook object is then used to add new
# worksheet via the add_worksheet() method.
worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet()
# Create a new Format object to formats cells
# in worksheets using add_format() method .
# here we create bold format object .
bold = workbook.add_format({'bold': 1})
# Add the worksheet data that the charts will refer to.
headings = ['Shingle', 'Brick']
data = [
[105, 150, 130, 90 ],
[50, 120, 100, 110],
]
# Write a row of data starting from 'A1'
# with bold format .
worksheet.write_row('A1', headings, bold)
# Write a column of data starting from
# 'A2', 'B2' respectively .
worksheet.write_column('A2', data[0])
worksheet.write_column('B2', data[1])
# Create a chart object that can be added
# to a worksheet using add_chart() method.
# here we create a column chart object
chart = workbook.add_chart({'type': 'column'})
# Add a data series with pattern to a chart
# using add_series method. The gap is used
# to make the patterns more visible.
# Configure the first series.
# = Sheet1 !$A$1 is equivalent to ['Sheet1', 0, 0].
# note : spaces is not inserted in b / w
# = and Sheet1, Sheet1 and !
# if space is inserted it throws warning.
chart.add_series({
'name': '= Sheet1 !$A$1',
'values': '= Sheet1 !$A$2:$A$5',
'pattern': {
'pattern': 'shingle',
'fg_color': '# 804000',
'bg_color': '# c68c53'
},
'border': {'color': '# 804000'},
'gap': 70,
})
# Configure a second series.
chart.add_series({
'name': '= Sheet1 !$B$1',
'values': '= Sheet1 !$B$2:$B$5',
'pattern': {
'pattern': 'horizontal_brick',
'fg_color': '# b30000',
'bg_color': '# ff6666'
},
'border': {'color': '# b30000'},
})
# Add a chart title
chart.set_title ({'name': 'Cladding types'})
# Add x-axis label
chart.set_x_axis({'name': 'Region'})
# Add y-axis label
chart.set_y_axis({'name': 'Number of houses'})
# add chart to the worksheet with given
# offset values at the top-left corner of
# a chart is anchored to cell D2 .
worksheet.insert_chart('D2', chart, {'x_offset': 25, 'y_offset': 10})
# Finally, close the Excel file
# via the close() method.
workbook.close()
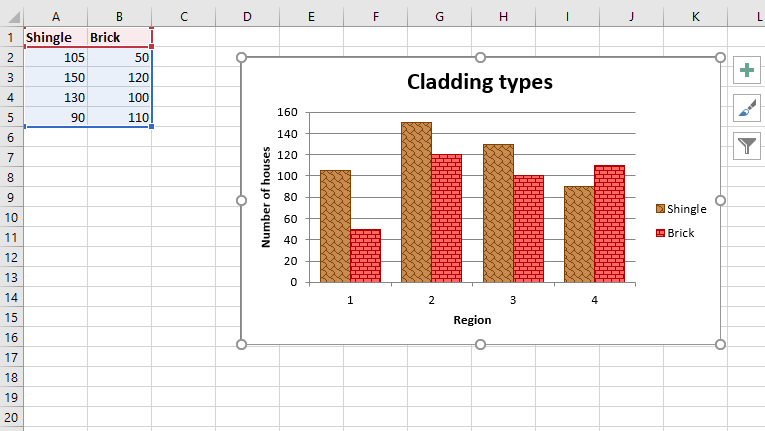
Producción :