Kivy es una herramienta GUI independiente de la plataforma en Python. Como se puede ejecutar en Android, IOS, Linux y Windows, etc. Básicamente se usa para desarrollar la aplicación de Android, pero eso no significa que no se pueda usar en aplicaciones de escritorio.
Entrada de texto:
El widget TextInput proporciona un cuadro para texto sin formato editable. Se admiten las funciones Unicode, multilínea, navegación con cursor, selección y portapapeles.
Para crear un TextInput multilínea (la tecla ‘enter’ agrega una nueva línea).
Para crear una entrada de texto de una sola línea, establezca la propiedad TextInput.multiline en False.
TextInput(text='Hello world', multiline=False)
Para trabajar con Textinput, debe importarlo con el comando:
de kivy.uix.textinput importar TextInput
Basic Approach: 1) import kivy 2) import kivyApp 3) import Label 4) import Scatter 5) import Floatlayout 6) import Textinput 7) import BoxLayout 8) Set minimum version(optional) 9) create App class 10) return Layout/widget/Class(according to requirement) 11) Run an instance of the class
Ahora la implementación del Enfoque:
# Program to Show how to use textinput (UX widget) in kivy
# import kivy module
import kivy
# base Class of your App inherits from the App class.
# app:always refers to the instance of your application
from kivy.app import App
# this restrict the kivy version i.e
# below this kivy version you cannot
# use the app or software
kivy.require('1.9.0')
# The Label widget is for rendering text.
from kivy.uix.label import Label
# module consist the floatlayout
# to work with FloatLayout first
# you have to import it
from kivy.uix.floatlayout import FloatLayout
# Scatter is used to build interactive
# widgets that can be translated,
# rotated and scaled with two or more
# fingers on a multitouch system.
from kivy.uix.scatter import Scatter
# The TextInput widget provides a
# box for editable plain text
from kivy.uix.textinput import TextInput
# BoxLayout arranges widgets in either
# in vertical fashion that
# is one on top of another or in
# horizontal fashion that is one after another.
from kivy.uix.boxlayout import BoxLayout
# Create the App class
class TutorialApp(App):
def build(self):
b = BoxLayout(orientation ='vertical')
# Adding the text input
t = TextInput(font_size = 50,
size_hint_y = None,
height = 100)
f = FloatLayout()
# By this you are able to move the
# Text on the screen to anywhere you want
s = Scatter()
l = Label(text ="Hello !",
font_size = 50)
f.add_widget(s)
s.add_widget(l)
b.add_widget(t)
b.add_widget(f)
# Binding it with the label
t.bind(text = l.setter('text'))
return b
# Run the App
if __name__ == "__main__":
TutorialApp().run()
Producción:
Después de alguna entrada –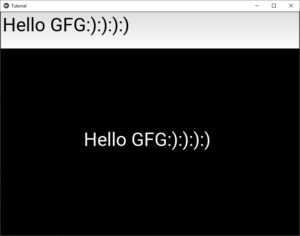
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por YashKhandelwal8 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA