En este artículo, vamos a explorar el efecto de desvanecimiento en jQuery . El desvanecimiento básicamente trabaja con la opacidad de ciertos elementos. En jQuery, podemos desvanecer y desvanecer elementos con respecto a la opacidad. En jQuery tenemos varios métodos que nos ayudarán a lograr el efecto de desvanecimiento. Buscaremos cada método con ejemplos adecuados.
Métodos de desvanecimiento:
Método jQuery fadeIn(): con la ayuda de este método, podemos desvanecer un elemento que básicamente está oculto en la página web.
Sintaxis:
$(selector).fadeIn(<duration>,
<easing>, <callback function>);
Ejemplo:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<!-- jQuery CDN link -->
<script src=
"https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.0/jquery.min.js">
</script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.main {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
background-color: rgb(41, 41, 41);
flex-direction: column;
height: 100vh;
}
h1 {
color: white;
display: none;
}
#fadein {
position: absolute;
top: 550px;
height: 50px;
width: 130px;
background-color: rgb(0, 141, 19);
outline: none;
border: none;
border-radius: 60px;
color: black;
font-size: 1rem;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="main">
<button id="fadein">Fade In</button>
<h1 id="text">Text in now visible</h1>
</div>
<!-- jQuery code -->
<script>
// Initially text is invisible.
$("#fadein").click(function () {
$("#text").fadeIn(2000, function () {
alert("Animation is completed");
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Producción:
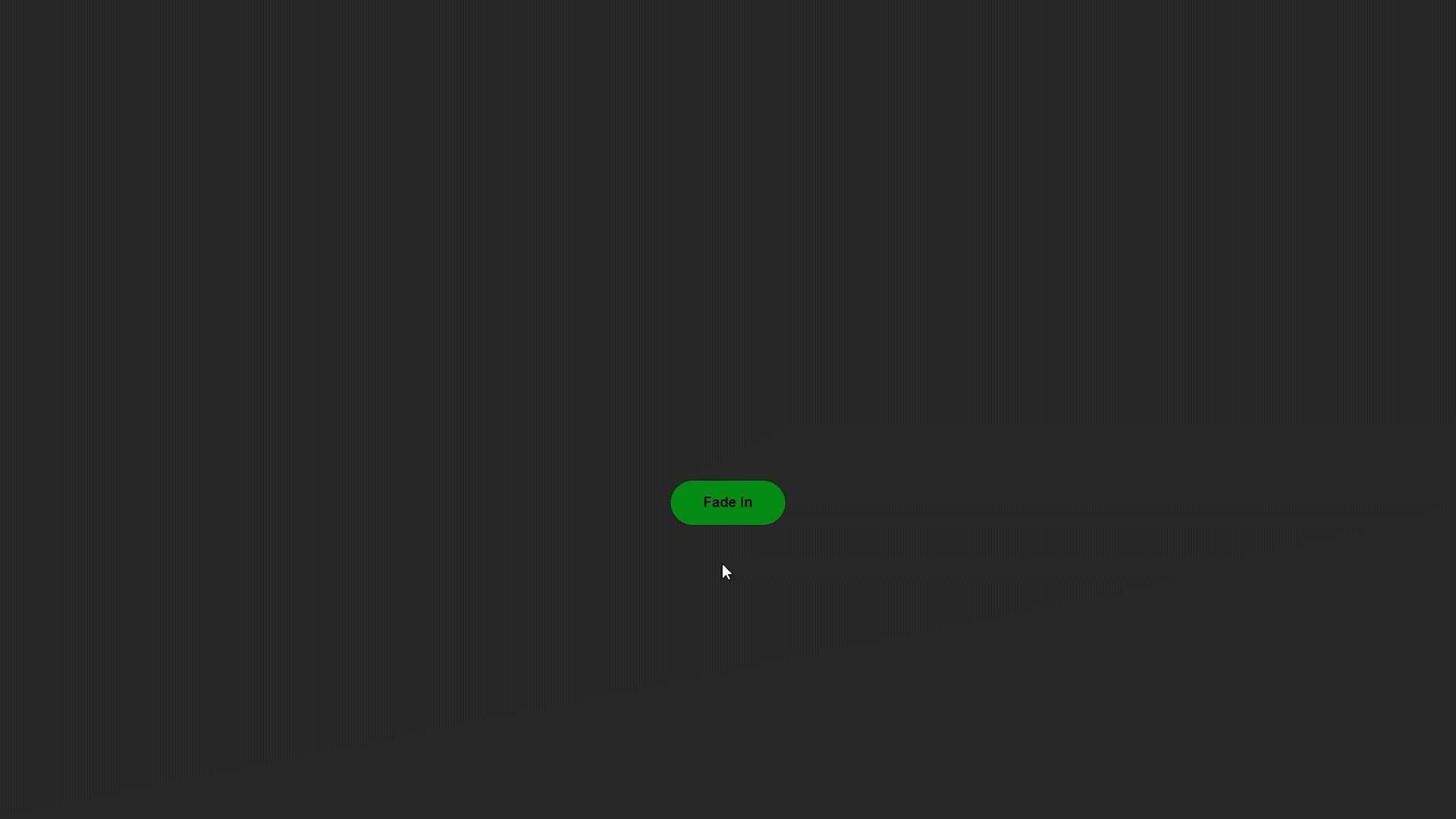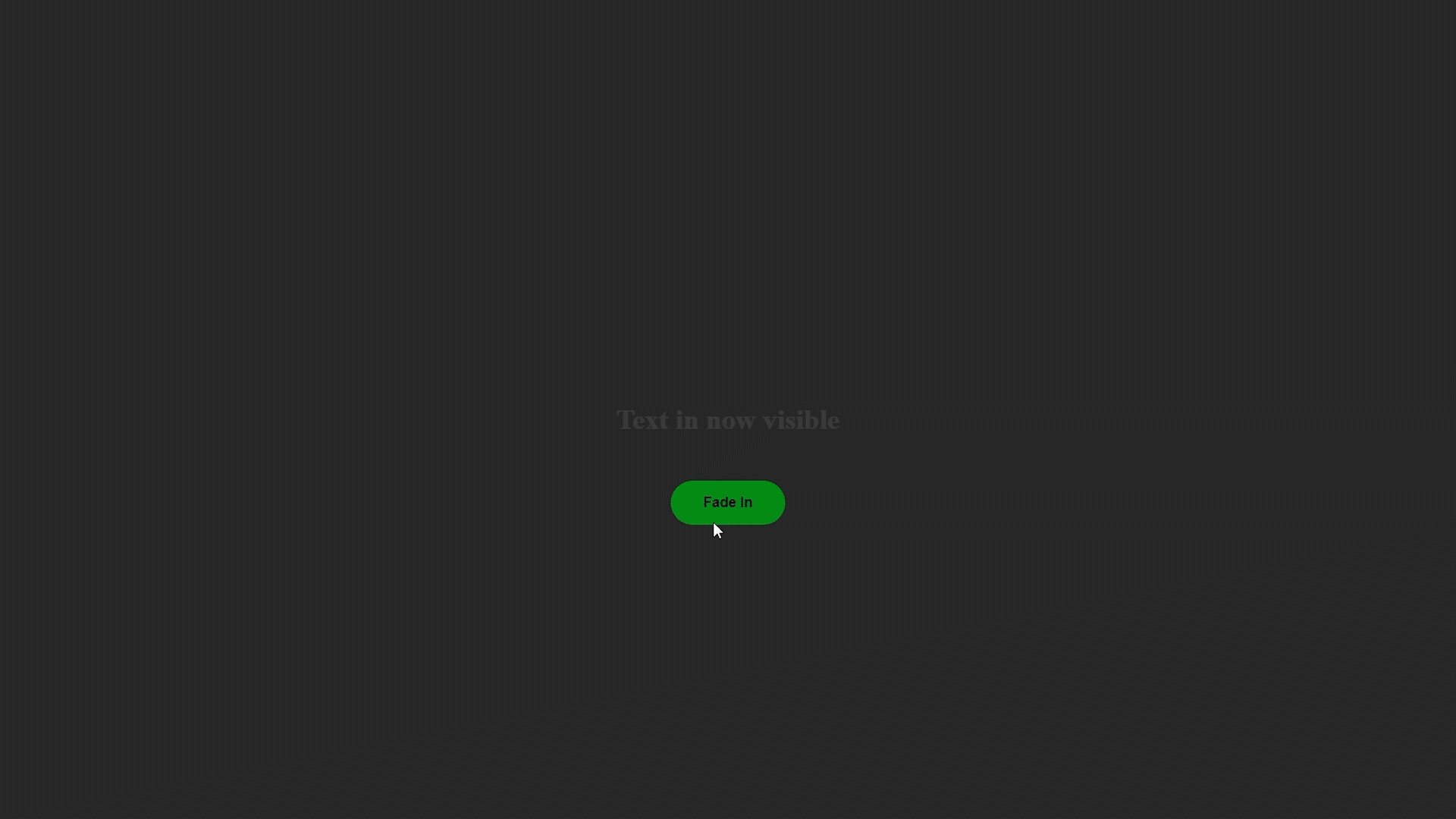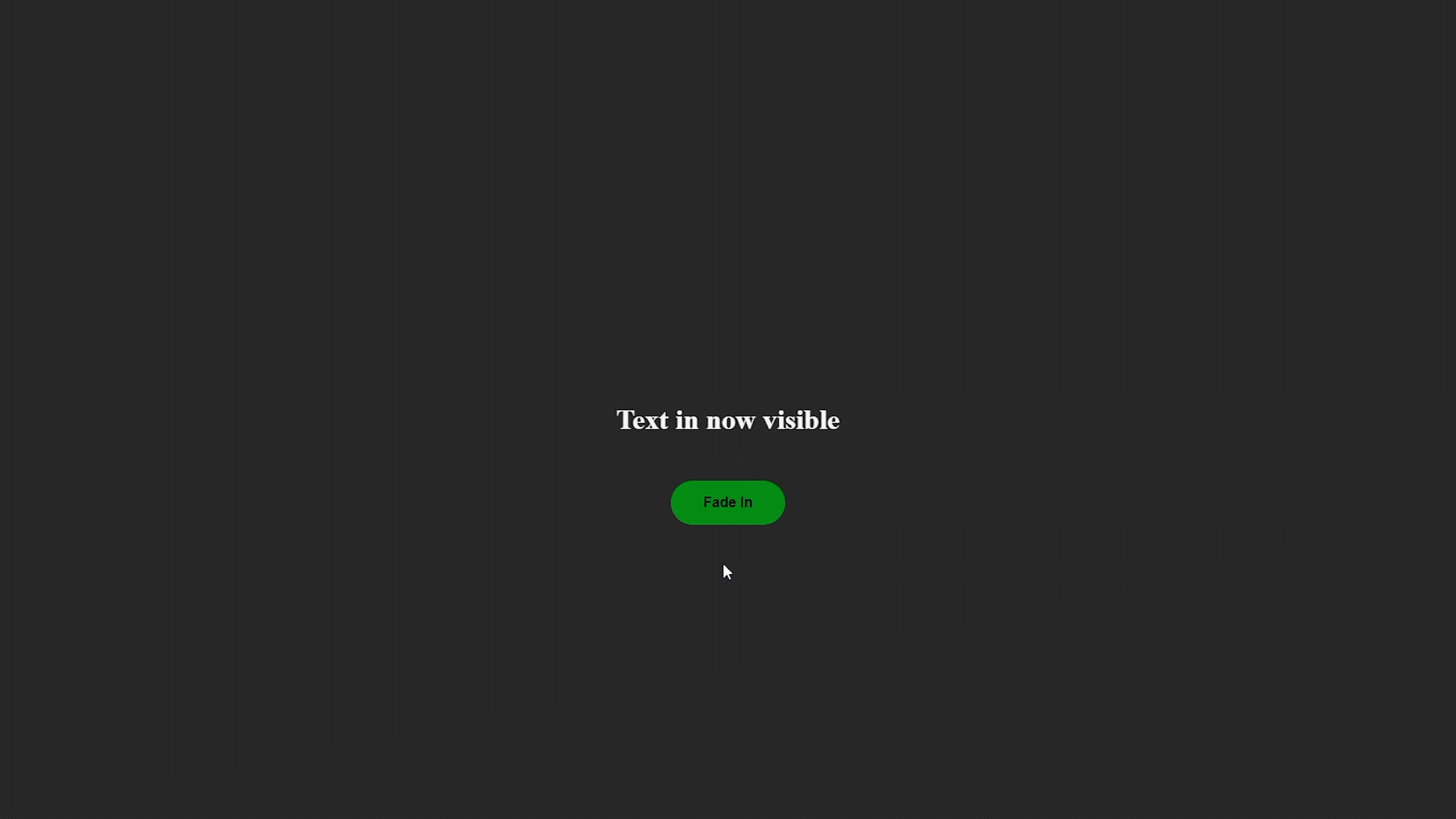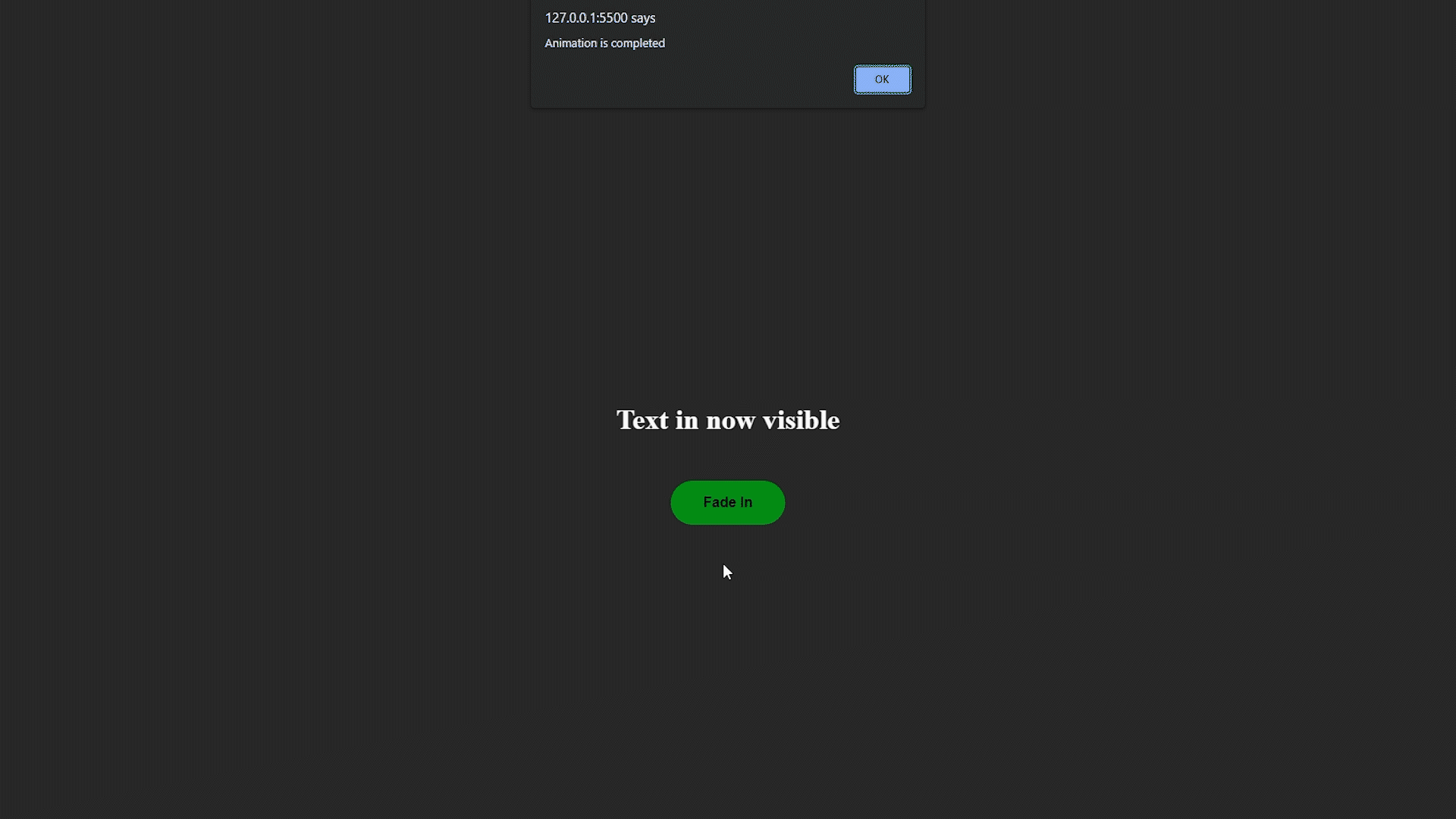
Ejemplo de Fade in
Método jQuery fadeOut() : este método funciona justo al contrario que el método fadeIn() , hará que un elemento sea invisible.
Sintaxis:
$(selector).fadeOut(<duration>,
<easing>, <callback function>);
Ejemplo:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<!-- jQuery CDN link -->
<script src=
"https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.0/jquery.min.js">
</script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.main {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
background-color: rgb(41, 41, 41);
flex-direction: column;
height: 100vh;
}
h1 {
color: white;
}
#fadeout {
position: absolute;
top: 550px;
height: 50px;
width: 130px;
background-color: rgb(0, 141, 19);
outline: none;
border: none;
border-radius: 60px;
color: black;
font-size: 1rem;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="main">
<button id="fadeout">Fade Out</button>
<h1 id="text">Click button to hide text.</h1>
</div>
<!-- jQuery code -->
<script>
$("#fadeout").click(function () {
$("#text").fadeOut(2000, function () {
alert("Animation is completed");
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
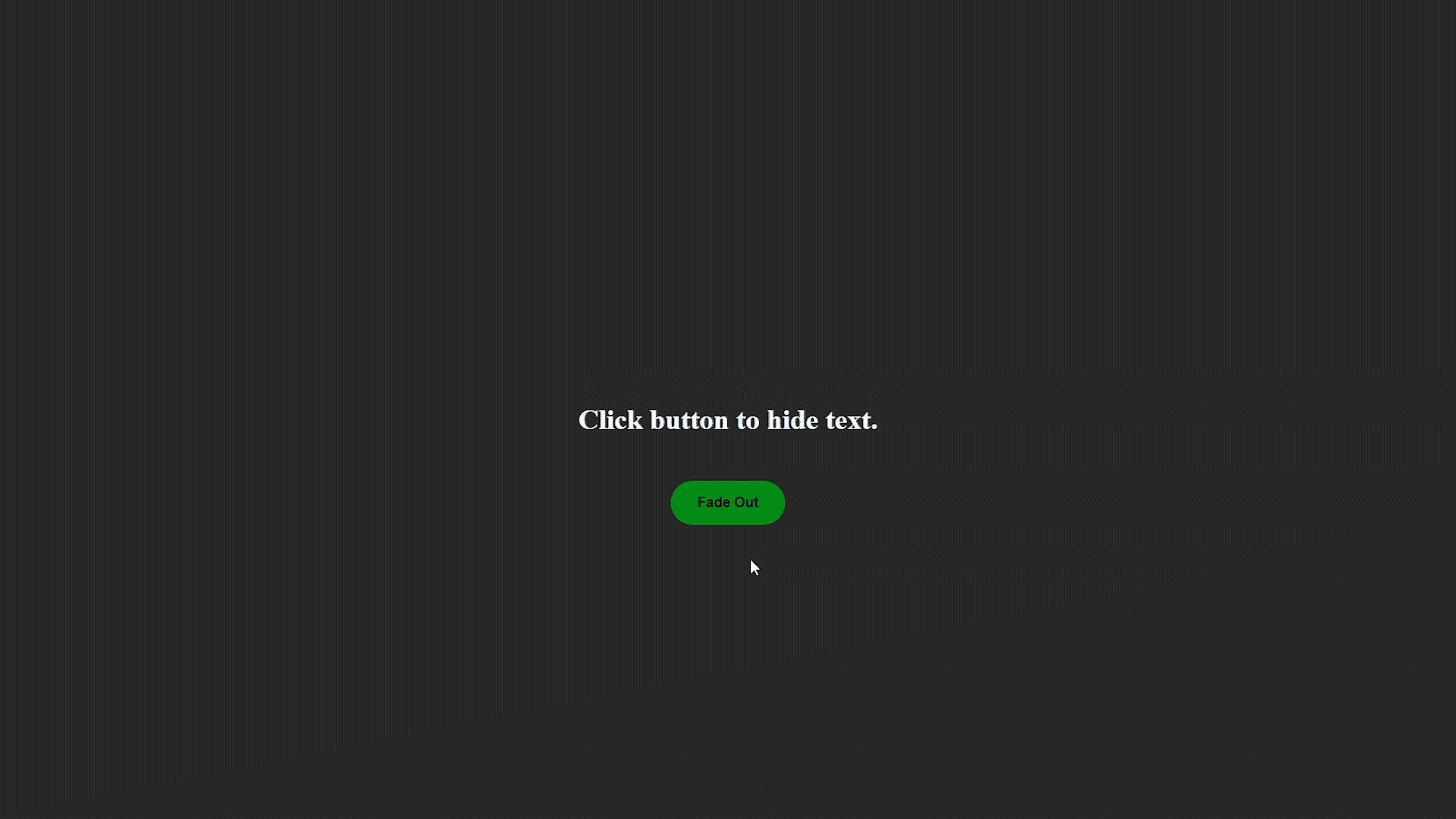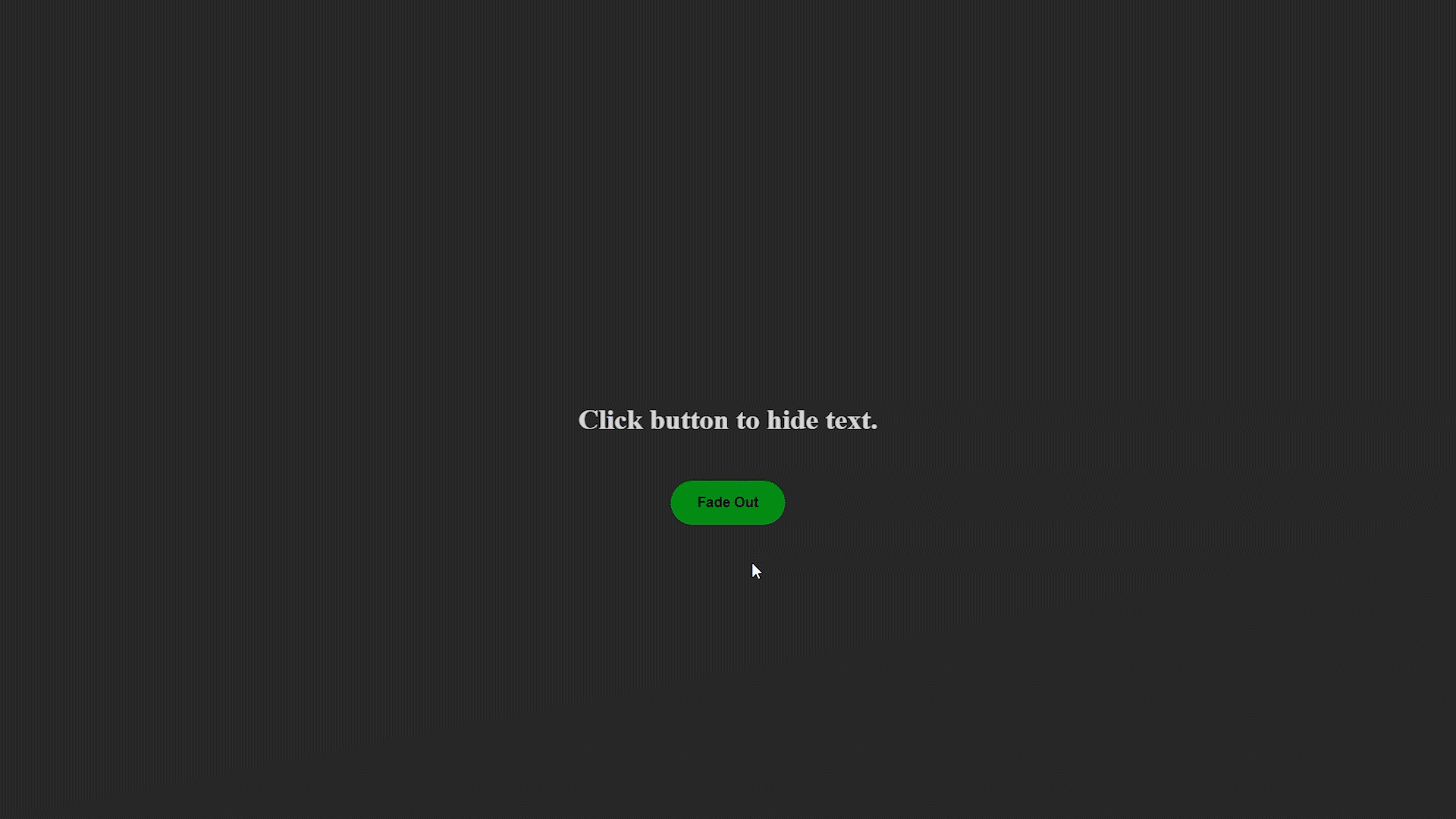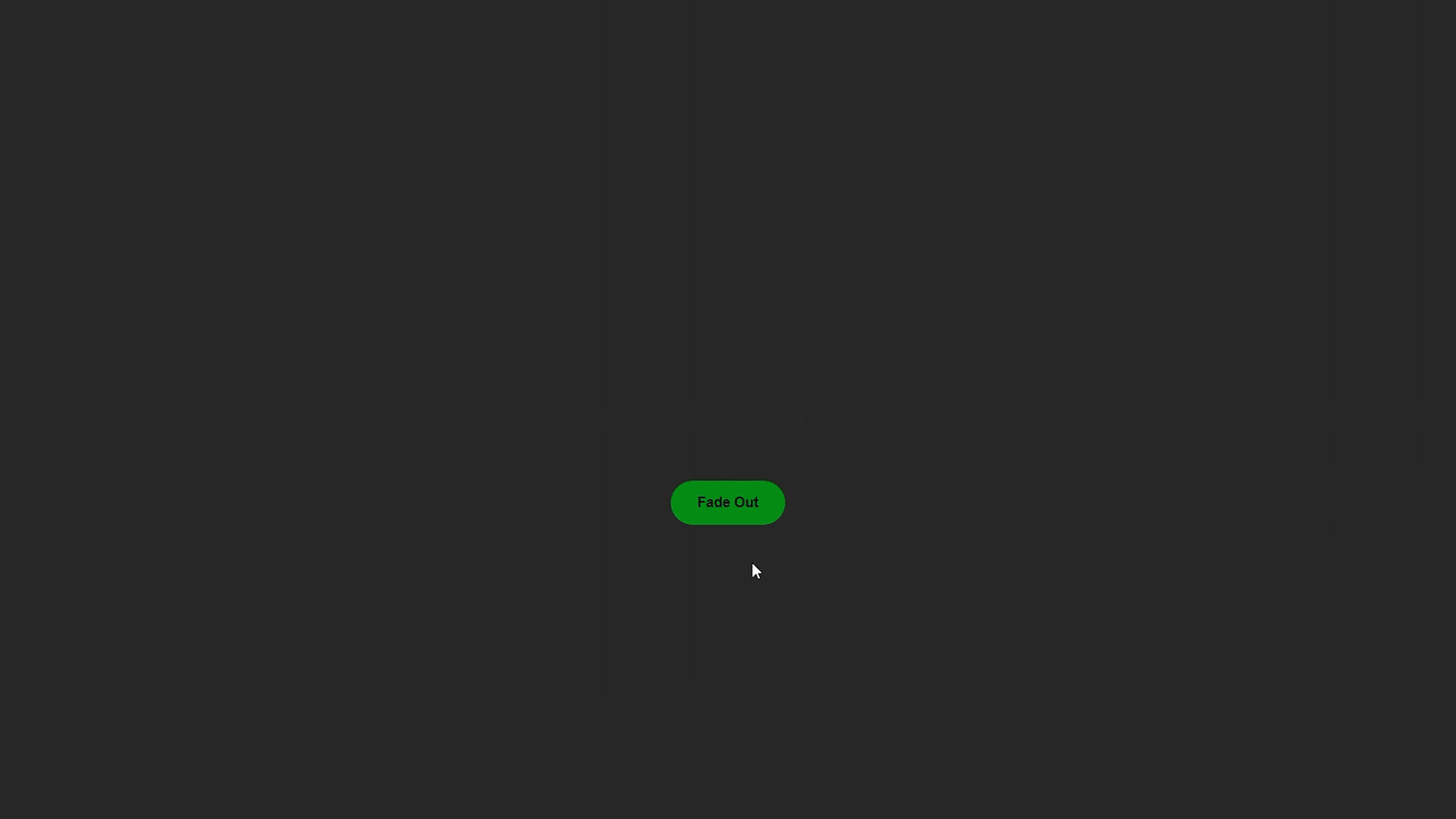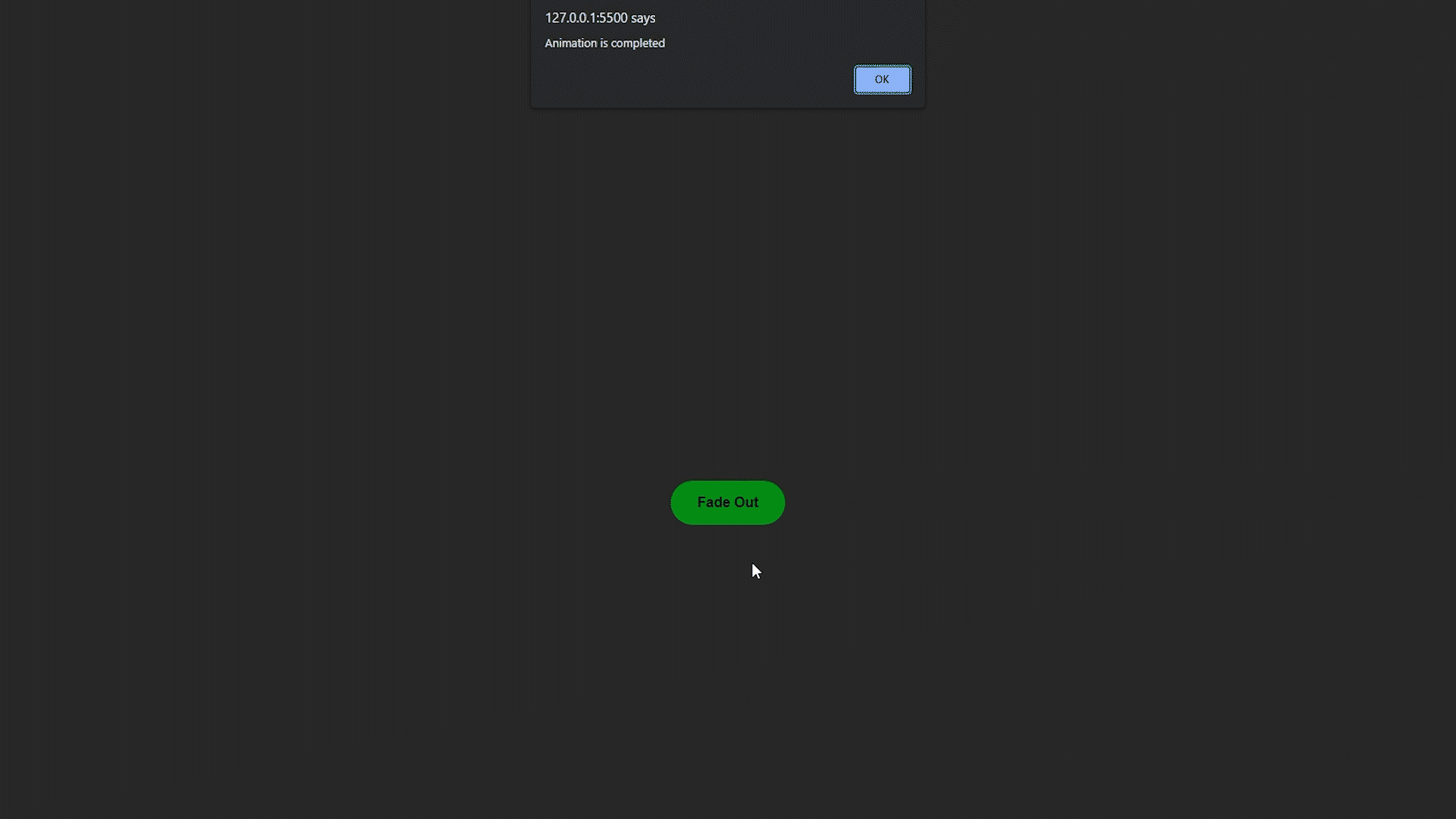
Ejemplo de desvanecimiento
Método jQuery fadeToggle(): este método alternará entre los métodos fadeIn() y fadeOut() con un solo clic de botón.
Sintaxis:
$(selector).fadeToggle(<duration>,
<easing>, <callback function>);
Ejemplo:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<!-- jQuery CDN link -->
<script src=
"https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.0/jquery.min.js">
</script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.main {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
background-color: rgb(41, 41, 41);
flex-direction: column;
height: 100vh;
}
h1 {
color: white;
display: none;
}
.Toggle {
position: absolute;
top: 550px;
height: 50px;
width: 130px;
background-color: rgb(0, 141, 19);
border-radius: 60px;
border: none;
color: black;
font-size: 1rem;
font-weight: bold;
}
.Toggle:hover {
background-color: rgb(1, 122, 17);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="main">
<button class="Toggle">Fade Toggle</button>
<h1 id="text">Text in now visible</h1>
</div>
<!-- jQuery code -->
<script>
$(".Toggle").click(function () {
$("#text").fadeToggle("fast");
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Producción:

Método jQuery fadeTo(): en este método, no se desvanecerá el elemento por valor predeterminado, en realidad, pasaremos el valor de opacidad deseado para que se desvanezca o desaparezca.
Sintaxis:
$(selector).fadeTo(<duration>, <opacity>,
<easing>, <callback function>);
Ejemplo: En este ejemplo, desvaneceremos un elemento a los tres valores diferentes.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<!-- jQuery CDN link -->
<script src=
"https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.0/jquery.min.js">
</script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.main {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
background-color: rgb(41, 41, 41);
flex-direction: row;
height: 100vh;
}
#text2 {
margin: 170px;
color: white;
}
h1 {
color: white;
}
#fadeto1 {
position: absolute;
top: 550px;
left: 500px;
height: 50px;
width: 130px;
background-color: rgb(0, 141, 19);
outline: none;
border: none;
border-radius: 60px;
color: black;
font-size: 1rem;
font-weight: bold;
}
#fadeto2 {
position: absolute;
top: 550px;
height: 50px;
width: 130px;
background-color: rgb(0, 141, 19);
outline: none;
border: none;
border-radius: 60px;
color: black;
font-size: 1rem;
font-weight: bold;
}
#fadeto3 {
position: absolute;
top: 550px;
right: 500px;
height: 50px;
width: 130px;
background-color: rgb(0, 141, 19);
outline: none;
border: none;
border-radius: 60px;
color: black;
font-size: 1rem;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="main">
<button id="fadeto1">Fade To 0.5 opacity</button>
<button id="fadeto2">Fade To 0.2 opacity</button>
<button id="fadeto3">Fade To 0 opacity</button>
<h1 id="text1">GeeksforGeeks</h1>
<h1 id="text2">GeeksforGeeks</h1>
<h1 id="text3">GeeksforGeeks</h1>
</div>
<!-- jQuery code -->
<script>
$("#fadeto1").click(function () {
$("#text1").fadeTo("slow", 0.5);
});
$("#fadeto2").click(function () {
$("#text2").fadeTo("slow", 0.2);
});
$("#fadeto3").click(function () {
$("#text3").fadeTo("slow", 0);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Producción:

Ejemplo de Fundido a