QuickSort en la lista doblemente enlazada se analiza aquí . QuickSort en una lista enlazada individualmente se proporcionó como ejercicio. A continuación se muestra la implementación de C++ para el mismo. Las cosas importantes acerca de la implementación son que cambia los punteros en lugar de intercambiar datos y la complejidad del tiempo es la misma que la implementación de la lista doblemente enlazada.
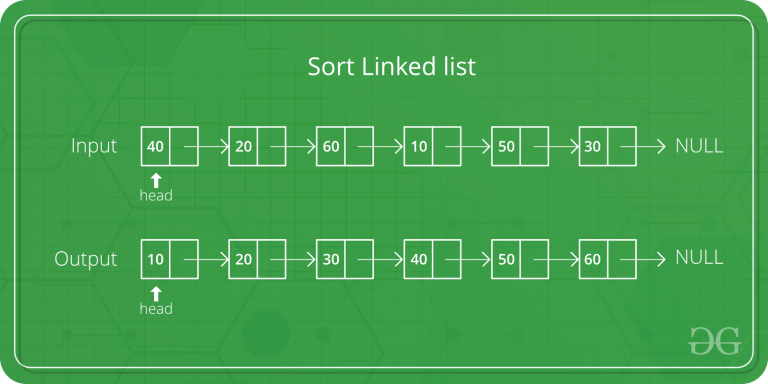
En la partición() , consideramos el último elemento como pivote. Recorremos la lista actual y si un Node tiene un valor mayor que el pivote, lo movemos después de la cola. Si el Node tiene un valor menor, lo mantenemos en su posición actual.
En QuickSortRecur() , primero llamamos a la partición() que coloca el pivote en la posición correcta y devuelve el pivote. Después de colocar el pivote en la posición correcta, encontramos el Node de cola del lado izquierdo (lista antes del pivote) y recurrimos a la lista izquierda. Finalmente, recurrimos a la lista derecha.
Implementación»:
C++
// C++ program for Quick Sort on Singly Linked List
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/* a node of the singly linked list */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* A utility function to insert a node at the beginning of
* linked list */
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct Node* new_node = new Node;
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* A utility function to print linked list */
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// Returns the last node of the list
struct Node* getTail(struct Node* cur)
{
while (cur != NULL && cur->next != NULL)
cur = cur->next;
return cur;
}
// Partitions the list taking the last element as the pivot
struct Node* partition(struct Node* head, struct Node* end,
struct Node** newHead,
struct Node** newEnd)
{
struct Node* pivot = end;
struct Node *prev = NULL, *cur = head, *tail = pivot;
// During partition, both the head and end of the list
// might change which is updated in the newHead and
// newEnd variables
while (cur != pivot) {
if (cur->data < pivot->data) {
// First node that has a value less than the
// pivot - becomes the new head
if ((*newHead) == NULL)
(*newHead) = cur;
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
else // If cur node is greater than pivot
{
// Move cur node to next of tail, and change
// tail
if (prev)
prev->next = cur->next;
struct Node* tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = NULL;
tail->next = cur;
tail = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
}
// If the pivot data is the smallest element in the
// current list, pivot becomes the head
if ((*newHead) == NULL)
(*newHead) = pivot;
// Update newEnd to the current last node
(*newEnd) = tail;
// Return the pivot node
return pivot;
}
// here the sorting happens exclusive of the end node
struct Node* quickSortRecur(struct Node* head,
struct Node* end)
{
// base condition
if (!head || head == end)
return head;
Node *newHead = NULL, *newEnd = NULL;
// Partition the list, newHead and newEnd will be
// updated by the partition function
struct Node* pivot
= partition(head, end, &newHead, &newEnd);
// If pivot is the smallest element - no need to recur
// for the left part.
if (newHead != pivot) {
// Set the node before the pivot node as NULL
struct Node* tmp = newHead;
while (tmp->next != pivot)
tmp = tmp->next;
tmp->next = NULL;
// Recur for the list before pivot
newHead = quickSortRecur(newHead, tmp);
// Change next of last node of the left half to
// pivot
tmp = getTail(newHead);
tmp->next = pivot;
}
// Recur for the list after the pivot element
pivot->next = quickSortRecur(pivot->next, newEnd);
return newHead;
}
// The main function for quick sort. This is a wrapper over
// recursive function quickSortRecur()
void quickSort(struct Node** headRef)
{
(*headRef)
= quickSortRecur(*headRef, getTail(*headRef));
return;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct Node* a = NULL;
push(&a, 5);
push(&a, 20);
push(&a, 4);
push(&a, 3);
push(&a, 30);
cout << "Linked List before sorting \n";
printList(a);
quickSort(&a);
cout << "Linked List after sorting \n";
printList(a);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for Quick Sort on Singly Linked List
/*sort a linked list using quick sort*/
public
class QuickSortLinkedList {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
this.data = d;
this.next = null;
}
}
Node head;
void addNode(int data)
{
if (head == null) {
head = new Node(data);
return;
}
Node curr = head;
while (curr.next != null)
curr = curr.next;
Node newNode = new Node(data);
curr.next = newNode;
}
void printList(Node n)
{
while (n != null) {
System.out.print(n.data);
System.out.print(" ");
n = n.next;
}
}
// takes first and last node,
// but do not break any links in
// the whole linked list
Node paritionLast(Node start, Node end)
{
if (start == end || start == null || end == null)
return start;
Node pivot_prev = start;
Node curr = start;
int pivot = end.data;
// iterate till one before the end,
// no need to iterate till the end
// because end is pivot
while (start != end) {
if (start.data < pivot) {
// keep tracks of last modified item
pivot_prev = curr;
int temp = curr.data;
curr.data = start.data;
start.data = temp;
curr = curr.next;
}
start = start.next;
}
// swap the position of curr i.e.
// next suitable index and pivot
int temp = curr.data;
curr.data = pivot;
end.data = temp;
// return one previous to current
// because current is now pointing to pivot
return pivot_prev;
}
void sort(Node start, Node end)
{
if(start == null || start == end|| start == end.next )
return;
// split list and partition recurse
Node pivot_prev = paritionLast(start, end);
sort(start, pivot_prev);
// if pivot is picked and moved to the start,
// that means start and pivot is same
// so pick from next of pivot
if (pivot_prev != null && pivot_prev == start)
sort(pivot_prev.next, end);
// if pivot is in between of the list,
// start from next of pivot,
// since we have pivot_prev, so we move two nodes
else if (pivot_prev != null
&& pivot_prev.next != null)
sort(pivot_prev.next.next, end);
}
// Driver Code
public
static void main(String[] args)
{
QuickSortLinkedList list
= new QuickSortLinkedList();
list.addNode(30);
list.addNode(3);
list.addNode(4);
list.addNode(20);
list.addNode(5);
Node n = list.head;
while (n.next != null)
n = n.next;
System.out.println("Linked List before sorting");
list.printList(list.head);
list.sort(list.head, n);
System.out.println("\nLinked List after sorting");
list.printList(list.head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by trinadumca
Python3
'''
sort a linked list using quick sort
'''
class Node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.data = val
self.next = None
class QuickSortLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head=None
def addNode(self,data):
if (self.head == None):
self.head = Node(data)
return
curr = self.head
while (curr.next != None):
curr = curr.next
newNode = Node(data)
curr.next = newNode
def printList(self,n):
while (n != None):
print(n.data, end=" ")
n = n.next
''' takes first and last node,but do not
break any links in the whole linked list'''
def paritionLast(self,start, end):
if (start == end or start == None or end == None):
return start
pivot_prev = start
curr = start
pivot = end.data
'''iterate till one before the end,
no need to iterate till the end because end is pivot'''
while (start != end):
if (start.data < pivot):
# keep tracks of last modified item
pivot_prev = curr
temp = curr.data
curr.data = start.data
start.data = temp
curr = curr.next
start = start.next
'''swap the position of curr i.e.
next suitable index and pivot'''
temp = curr.data
curr.data = pivot
end.data = temp
''' return one previous to current because
current is now pointing to pivot '''
return pivot_prev
def sort(self, start, end):
if(start == None or start == end or start == end.next):
return
# split list and partition recurse
pivot_prev = self.paritionLast(start, end)
self.sort(start, pivot_prev)
'''
if pivot is picked and moved to the start,
that means start and pivot is same
so pick from next of pivot
'''
if(pivot_prev != None and pivot_prev == start):
self.sort(pivot_prev.next, end)
# if pivot is in between of the list,start from next of pivot,
# since we have pivot_prev, so we move two nodes
elif (pivot_prev != None and pivot_prev.next != None):
self.sort(pivot_prev.next.next, end)
if __name__ == "__main__":
ll = QuickSortLinkedList()
ll.addNode(30)
ll.addNode(3)
ll.addNode(4)
ll.addNode(20)
ll.addNode(5)
n = ll.head
while (n.next != None):
n = n.next
print("\nLinked List before sorting")
ll.printList(ll.head)
ll.sort(ll.head, n)
print("\nLinked List after sorting");
ll.printList(ll.head)
# This code is contributed by humpheykibet.
C#
// C# program for Quick Sort on
// Singly Linked List
using System;
/*sort a linked list using quick sort*/
class GFG {
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
this.data = d;
this.next = null;
}
}
Node head;
void addNode(int data)
{
if (head == null) {
head = new Node(data);
return;
}
Node curr = head;
while (curr.next != null)
curr = curr.next;
Node newNode = new Node(data);
curr.next = newNode;
}
void printList(Node n)
{
while (n != null) {
Console.Write(n.data);
Console.Write(" ");
n = n.next;
}
}
// takes first and last node,
// but do not break any links in
// the whole linked list
Node paritionLast(Node start, Node end)
{
if (start == end || start == null || end == null)
return start;
Node pivot_prev = start;
Node curr = start;
int pivot = end.data;
// iterate till one before the end,
// no need to iterate till the end
// because end is pivot
int temp;
while (start != end) {
if (start.data < pivot) {
// keep tracks of last modified item
pivot_prev = curr;
temp = curr.data;
curr.data = start.data;
start.data = temp;
curr = curr.next;
}
start = start.next;
}
// swap the position of curr i.e.
// next suitable index and pivot
temp = curr.data;
curr.data = pivot;
end.data = temp;
// return one previous to current
// because current is now pointing to pivot
return pivot_prev;
}
void sort(Node start, Node end)
{
if (start == end)
return;
// split list and partition recurse
Node pivot_prev = paritionLast(start, end);
sort(start, pivot_prev);
// if pivot is picked and moved to the start,
// that means start and pivot is same
// so pick from next of pivot
if (pivot_prev != null && pivot_prev == start)
sort(pivot_prev.next, end);
// if pivot is in between of the list,
// start from next of pivot,
// since we have pivot_prev, so we move two nodes
else if (pivot_prev != null
&& pivot_prev.next != null)
sort(pivot_prev.next.next, end);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
GFG list = new GFG();
list.addNode(30);
list.addNode(3);
list.addNode(4);
list.addNode(20);
list.addNode(5);
Node n = list.head;
while (n.next != null)
n = n.next;
Console.WriteLine("Linked List before sorting");
list.printList(list.head);
list.sort(list.head, n);
Console.WriteLine("\nLinked List after sorting");
list.printList(list.head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program for Quick Sort on Singly Linked List
/*sort a linked list using quick sort*/
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
var head;
function addNode(data) {
if (head == null) {
head = new Node(data);
return;
}
var curr = head;
while (curr.next != null)
curr = curr.next;
var newNode = new Node(data);
curr.next = newNode;
}
function printList( n) {
while (n != null) {
document.write(n.data);
document.write(" ");
n = n.next;
}
}
// takes first and last node,
// but do not break any links in
// the whole linked list
function paritionLast( start, end) {
if (start == end || start == null || end == null)
return start;
var pivot_prev = start;
var curr = start;
var pivot = end.data;
// iterate till one before the end,
// no need to iterate till the end
// because end is pivot
while (start != end) {
if (start.data < pivot) {
// keep tracks of last modified item
pivot_prev = curr;
var temp = curr.data;
curr.data = start.data;
start.data = temp;
curr = curr.next;
}
start = start.next;
}
// swap the position of curr i.e.
// next suitable index and pivot
var temp = curr.data;
curr.data = pivot;
end.data = temp;
// return one previous to current
// because current is now pointing to pivot
return pivot_prev;
}
function sort( start, end) {
if (start == null || start == end || start == end.next)
return;
// split list and partition recurse
var pivot_prev = paritionLast(start, end);
sort(start, pivot_prev);
// if pivot is picked and moved to the start,
// that means start and pivot is same
// so pick from next of pivot
if (pivot_prev != null && pivot_prev == start)
sort(pivot_prev.next, end);
// if pivot is in between of the list,
// start from next of pivot,
// since we have pivot_prev, so we move two nodes
else if (pivot_prev != null && pivot_prev.next != null)
sort(pivot_prev.next.next, end);
}
// Driver Code
addNode(30);
addNode(3);
addNode(4);
addNode(20);
addNode(5);
var n = head;
while (n.next != null)
n = n.next;
document.write("Linked List before sorting<br/>");
printList(head);
sort(head, n);
document.write("<br/>Linked List after sorting<br/>");
printList(head);
// This code contributed by umadevi9616
</script>
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//Creating structure
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
//Add new node at end of linked list
void insert(struct Node **head, int value)
{
//Create dynamic node
struct Node *node = (struct Node *) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if (node == NULL)
{
//checking memory overflow
printf("Memory overflow\n");
}
else
{
node->data = value;
node->next = NULL;
if ( *head == NULL)
{
*head = node;
}
else
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
//finding last node
while (temp->next != NULL)
{
temp = temp->next;
}
//adding node at last position
temp->next = node;
}
}
}
//Displaying linked list element
void display(struct Node *head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("Empty linked list");
return;
}
struct Node *temp = head;
printf("\n Linked List :");
while (temp != NULL)
{
printf(" %d", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
}
//Finding last node of linked list
struct Node *last_node(struct Node *head)
{
struct Node *temp = head;
while (temp != NULL && temp->next != NULL)
{
temp = temp->next;
}
return temp;
}
//We are Setting the given last node position to its proper position
struct Node *parition(struct Node *first, struct Node *last)
{
//Get first node of given linked list
struct Node *pivot = first;
struct Node *front = first;
int temp = 0;
while (front != NULL && front != last)
{
if (front->data < last->data)
{
pivot = first;
//Swapping node values
temp = first->data;
first->data = front->data;
front->data = temp;
//Visiting the next node
first = first->next;
}
//Visiting the next node
front = front->next;
}
//Change last node value to current node
temp = first->data;
first->data = last->data;
last->data = temp;
return pivot;
}
//Performing quick sort in the given linked list
void quick_sort(struct Node *first, struct Node *last)
{
if (first == last)
{
return;
}
struct Node *pivot = parition(first, last);
if (pivot != NULL && pivot->next != NULL)
{
quick_sort(pivot->next, last);
}
if (pivot != NULL && first != pivot)
{
quick_sort(first, pivot);
}
}
int main()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
//Create linked list
insert( &head, 41);
insert( &head, 5);
insert( &head, 7);
insert( &head, 22);
insert( &head, 28);
insert( &head, 63);
insert( &head, 4);
insert( &head, 8);
insert( &head, 2);
insert( &head, 11);
printf("\n Before Sort ");
display(head);
quick_sort(head, last_node(head));
printf("\n After Sort ");
display(head);
return 0;
}
Linked List before sorting 30 3 4 20 5 Linked List after sorting 3 4 5 20 30
Complejidad de tiempo: O (nlogn)
Toma O (n ^ 2) en el peor de los casos y O (nlogn) en el promedio o en el mejor de los casos.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(n)
Como se usa espacio adicional en la pila de llamadas recursivas.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA
