A diferencia de las estructuras de datos lineales (array, lista enlazada, colas, pilas, etc.) que solo tienen una forma lógica de atravesarlos, los árboles se pueden recorrer de diferentes maneras. Las siguientes son las formas generalmente utilizadas para atravesar árboles.
C++
// C++ program for different tree traversals
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
//Utility function to create a new tree node
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node->left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node->right);
// now deal with the node
cout << node->data << " ";
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node->left);
/* then print the data of node */
cout << node->data << " ";
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node->right);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first print data of node */
cout << node->data << " ";
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node->left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node->right);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
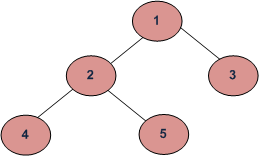
struct Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
cout << "\nPreorder traversal of binary tree is \n";
printPreorder(root);
cout << "\nInorder traversal of binary tree is \n";
printInorder(root);
cout << "\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is \n";
printPostorder(root);
return 0;
}
C
// C program for different tree traversals
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node->left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node->right);
// now deal with the node
printf("%d ", node->data);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node->left);
/* then print the data of node */
printf("%d ", node->data);
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node->right);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first print data of node */
printf("%d ", node->data);
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node->left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node->right);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
printf("\nPreorder traversal of binary tree is \n");
printPreorder(root);
printf("\nInorder traversal of binary tree is \n");
printInorder(root);
printf("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is \n");
printPostorder(root);
getchar();
return 0;
}
Python
# Python program to for tree traversals # A class that represents an individual node in a # Binary Tree class Node: def __init__(self, key): self.left = None self.right = None self.val = key # A function to do inorder tree traversal def printInorder(root): if root: # First recur on left child printInorder(root.left) # then print the data of node print(root.val), # now recur on right child printInorder(root.right) # A function to do postorder tree traversal def printPostorder(root): if root: # First recur on left child printPostorder(root.left) # the recur on right child printPostorder(root.right) # now print the data of node print(root.val), # A function to do preorder tree traversal def printPreorder(root): if root: # First print the data of node print(root.val), # Then recur on left child printPreorder(root.left) # Finally recur on right child printPreorder(root.right) # Driver code root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) print "Preorder traversal of binary tree is" printPreorder(root) print "\nInorder traversal of binary tree is" printInorder(root) print "\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is" printPostorder(root)
Java
// Java program for different tree traversals
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node {
int key;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
// Root of Binary Tree
Node root;
BinaryTree() { root = null; }
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// now deal with the node
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node.left);
/* then print the data of node */
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node.right);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first print data of node */
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node.left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node.right);
}
// Wrappers over above recursive functions
void printPostorder() { printPostorder(root); }
void printInorder() { printInorder(root); }
void printPreorder() { printPreorder(root); }
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println(
"Preorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPreorder();
System.out.println(
"\nInorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printInorder();
System.out.println(
"\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPostorder();
}
}
C#
// C# program for different
// tree traversals
using System;
/* Class containing left and
right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node {
public int key;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
// Root of Binary Tree
Node root;
BinaryTree() { root = null; }
/* Given a binary tree, print
its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// now deal with the node
Console.Write(node.key + " ");
}
/* Given a binary tree, print
its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node.left);
/* then print the data of node */
Console.Write(node.key + " ");
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node.right);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print
its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first print data of node */
Console.Write(node.key + " ");
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node.left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node.right);
}
// Wrappers over above recursive functions
void printPostorder() { printPostorder(root); }
void printInorder() { printInorder(root); }
void printPreorder() { printPreorder(root); }
// Driver Code
static public void Main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("Preorder traversal "
+ "of binary tree is ");
tree.printPreorder();
Console.WriteLine("\nInorder traversal "
+ "of binary tree is ");
tree.printInorder();
Console.WriteLine("\nPostorder traversal "
+ "of binary tree is ");
tree.printPostorder();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program for different tree traversals
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.key = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// Root of Binary Tree
var root = null;
/*
* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the "bottom-up" postorder
* traversal.
*/
function printPostorder(node) {
if (node == null)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// now deal with the node
document.write(node.key + " ");
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder */
function printInorder(node) {
if (node == null)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node.left);
/* then print the data of node */
document.write(node.key + " ");
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node.right);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder */
function printPreorder(node) {
if (node == null)
return;
/* first print data of node */
document.write(node.key + " ");
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node.left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node.right);
}
// Driver method
root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
document.write("Preorder traversal of binary tree is <br/>");
printPreorder(root);
document.write("<br/>Inorder traversal of binary tree is <br/>");
printInorder(root);
document.write("<br/>Postorder traversal of binary tree is <br/>");
printPostorder(root);
// This code is contributed by aashish1995
</script>
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA