El proceso en el que una función se llama a sí misma directa o indirectamente se llama Recursión y la función correspondiente se llama función Recursiva .
Usando Recursion, ciertos problemas se pueden resolver con bastante facilidad. Ejemplos de tales problemas son Towers of Hanoi (TOH), Inorder/Preorder/Postorder Tree Traversals , DFS , etc.
Tipos de recurrencias:
La recursividad se puede clasificar en dos tipos, dependiendo de cuándo terminan:
- recursividad finita
- recursividad infinita
Recursión finita:
La recursividad finita ocurre cuando la recursión termina después de un número finito de llamadas recursivas. Una recursión termina solo cuando se cumple una condición base.
Ejemplo:
A continuación se muestra una implementación para demostrar la recursividad finita.
C++
// C++ program to demsonstrate Finite Recursion
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Recursive function
void Geek(int N)
{
// Base condition
// When this condition is met,
// the recursion terminates
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
cout << N << " ";
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N - 1);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Initial value of N
int N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
class GFG{
// Recursive function
static void Geek(int N)
{
// Base condition
// When this condition is met,
// the recursion terminates
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
System.out.println(N + " ");
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N - 1);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initial value of N
int N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by abhinavjain194
Python3
# Python program to demsonstrate Finite Recursion # Recursive function def Geek( N): # Base condition # When this condition is met, # the recursion terminates if (N == 0): return # Pr the current value of N print( N, end =" " ) # Call itself recursively Geek(N - 1) # Driver code # Initial value of N N = 5 # Call the recursive function Geek(N) # this code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Recursive function
static void Geek(int N)
{
// Base condition
// When this condition is met,
// the recursion terminates
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
Console.Write(N + " ");
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N - 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Initial value of N
int N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by target_2.
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to demsonstrate Finite Recursion
// Recursive function
function Geek(N)
{
// Base condition
// When this condition is met,
// the recursion terminates
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
document.write(N +" ");
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N - 1);
}
// Driver code
// Initial value of N
var N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
// this code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
</script>
5 4 3 2 1
El árbol de recursividad para la función recursiva anterior se ve así.
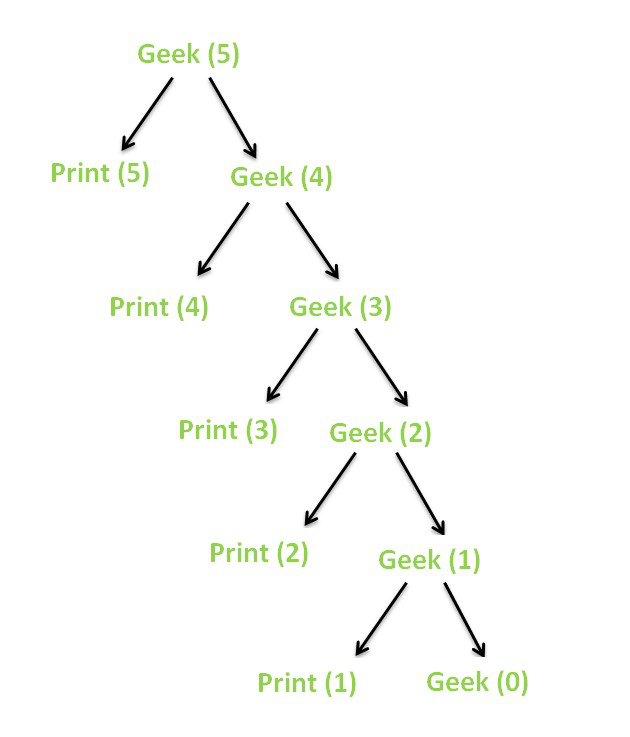
Árbol de recursión
Cuando el valor de N se convierte en 0 , debido a la condición base, la recursividad termina.
Recursividad infinita:
La recursividad infinita ocurre cuando la recursividad no termina después de un número finito de llamadas recursivas. Como nunca se cumple la condición base, la recursividad continúa infinitamente.
Ejemplo:
A continuación se muestra una implementación para demostrar la recursividad infinita.
C++
// C++ program to demsonstrate Infinite Recursion
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Recursive function
void Geek(int N)
{
// Base condition
// This condition is never met here
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
cout << N << " ";
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Initial value of N
int N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to demsonstrate Infinite Recursion
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
// Recursive function
static void Geek(int N)
{
// Base condition
// This condition is never met here
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
System.out.print( N +" ");
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initial value of N
int N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
Python3
# Python3 to demsonstrate Infinite Recursion # Recursive function def Geek(N): # Base condition # This condition is never met here if (N == 0): return # Print the current value of N print(N, end = " " ) # Call itself recursively Geek(N) # Driver code # Initial value of N N = 5 # Call the recursive function Geek(N) # This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
C#
// C# program to demsonstrate Infinite Recursion
using System;
class GFG
{
// Recursive function
static void Geek(int N)
{
// Base condition
// This condition is never met here
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
Console.Write( N +" ");
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Initial value of N
int N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to demsonstrate Infinite Recursion
// Recursive function
function Geek(N)
{
// Base condition
// This condition is never met here
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
document.write( N +" ");
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N);
}
// Driver code
// Initial value of N
var N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
</script>
El árbol de recursividad para la función recursiva anterior se ve así.
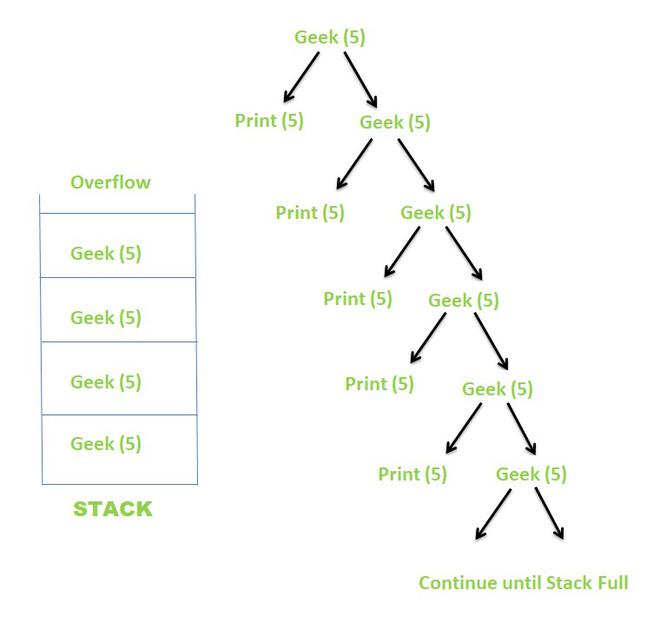
Árbol de recursión
Dado que el valor de N nunca se convierte en 0 , la recursividad nunca termina. En cambio, la recursividad continúa hasta que la pila implícita se llena, lo que da como resultado un desbordamiento de pila . Algunos compiladores dan directamente la salida como falla de segmentación (núcleo volcado) , mientras que otros pueden terminar anormalmente por algún valor y luego mostrar la falla de segmentación .
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por rishabhchakrabortygfg y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA