Dada una array arr[] que representa un árbol genérico (N-ario) . La tarea es reemplazar los datos del Node con la profundidad (nivel) del Node. Suponga que el nivel de la raíz es 0.
Representación de array : el árbol N-ario se serializa en la array arr[] utilizando un recorrido de orden de nivel como se describe a continuación:
- La entrada se proporciona como un recorrido de orden de nivel de N-ary Tree .
- El primer elemento de la array arr[] es el Node raíz.
- Luego, seguido de un número N, que denota el número de hijos del Node anterior. El valor cero indica un Node nulo.
Ejemplos:
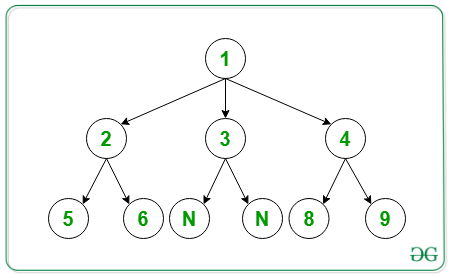
Entrada: arr[] = { 10, 3, 20, 30, 40, 2, 40, 50, 0, 0, 0, 0 }
A continuación se muestra el árbol N-ario del recorrido de orden de nivel de array anterior:
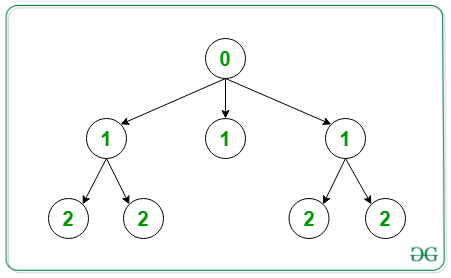
Salida:
A continuación se muestra la representación de la salida anterior:
Entrada: arr[] = {1, 3, 2, 3, 4, 2, 5, 6, 0, 0, 2, 8, 9}
A continuación se muestra el árbol N-ario del recorrido de orden de nivel de array anterior:
Salida:
A continuación se muestra la representación de la salida anterior:
Acercarse:
- Atraviesa el árbol comenzando desde la raíz.
- Mientras atraviesa, pase la profundidad del Node como parámetro.
- Realice un seguimiento de la profundidad pasándola como 0 para raíz y (1 + nivel actual) para niños.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
CPP
// C++ program to implement node with
// it's depth value
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Treenode class using template
template <typename T>
class TreeNode {
public:
// To store node value
T data;
// Pointer to TreeNode to store
// the child node
vector<TreeNode<T>*> children;
// Constructor to assign data
// to node
TreeNode(T data)
{
this->data = data;
}
// Destructors to delete a node
~TreeNode()
{
for (int i = 0;
i < children.size(); i++) {
delete children[i];
}
}
};
// Function to take input level wise
// i.e., in level order traversal
TreeNode<int>* takeInputLevelWise(int arr[])
{
int idx = 1;
// Input root
int rootData = arr[0];
// Initialize tree with a root node
TreeNode<int>* root
= new TreeNode<int>(rootData);
// Initialise queue for appending
// node as a child of parent in
// N-ary tree
queue<TreeNode<int>*> pendingNodes;
// Push the root node in queue
pendingNodes.push(root);
// While queue is not empty append
// child to the root
while (pendingNodes.size() != 0) {
// Take the first node
TreeNode<int>* front
= pendingNodes.front();
pendingNodes.pop();
// Input number of child
int numChild = arr[idx];
idx++;
for (int i = 0; i < numChild; i++) {
int childData = arr[idx];
idx++;
// Make child Node
TreeNode<int>* child
= new TreeNode<int>(childData);
// Append child node to
// it's parent
front->children.push_back(child);
pendingNodes.push(child);
}
}
return root;
}
// Function to print each node data
// in level order
void printLevelATNewLine(TreeNode<int>* root)
{
queue<TreeNode<int>*> q;
q.push(root);
q.push(NULL);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode<int>* first = q.front();
q.pop();
if (first == NULL) {
if (q.empty()) {
break;
}
cout << endl;
q.push(NULL);
continue;
}
cout << first->data << " ";
for (int i = 0;
i < first->children.size(); i++) {
q.push(first->children[i]);
}
}
}
// Helper function to replace the
// node data with their level value
void helper(TreeNode<int>* root,
int depth)
{
// Replace the node data with
// it's depth
root->data = depth;
for (int i = 0;
i < root->children.size(); i++) {
helper(root->children[i], depth + 1);
}
}
// Function to replace with depth
void replaceWithDepthValue(TreeNode<int>* root)
{
helper(root, 0);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given level order traversal in
// the array arr[]
int arr[] = { 10, 3, 20, 30, 40, 2,
40, 50, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
// Initialise Tree
TreeNode<int>* root;
root = takeInputLevelWise(arr);
// Function call to replace with
// depth value
replaceWithDepthValue(root);
// Function call to print
// in level order
printLevelATNewLine(root);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to replace node with
// it's depth value
// Importing classes and interface
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class GFG {
// TreeNode class
static class TreeNode<T> {
// To store node value
T data;
// List of TreeNode to store
// the child nodes
ArrayList<TreeNode<T> > children;
// Constructor to assign data to node
TreeNode(T data)
{
this.data = data;
children = new ArrayList<TreeNode<T> >();
}
}
// Function to take input level wise
// i.e., in level order traversal
static TreeNode<Integer> takeInputLevelWise(int arr[])
{
int idx = 1;
// Input root
int rootData = arr[0];
// Initialize tree with a root node
TreeNode<Integer> root
= new TreeNode<Integer>(rootData);
// Initialize queue for appending
// node as a child of parent in
// N-ary tree
Queue<TreeNode<Integer> > pendingNodes
= new LinkedList<TreeNode<Integer> >();
// Push the root node in queue
pendingNodes.add(root);
// While queue is not empty append
// child to the node
while (pendingNodes.size() != 0) {
// Take the first node
TreeNode<Integer> front = pendingNodes.peek();
pendingNodes.poll();
// Input number of its child
int numChild = arr[idx];
idx++;
for (int i = 0; i < numChild; i++) {
int childData = arr[idx];
idx++;
// Make child Node
TreeNode<Integer> child
= new TreeNode<Integer>(childData);
// Append child node to
// it's parent
front.children.add(child);
pendingNodes.add(child);
}
}
return root;
}
// Function to print each node data
// in level order
static void printLevelATNewLine(TreeNode<Integer> root)
{
Queue<TreeNode<Integer> > q
= new LinkedList<TreeNode<Integer> >();
q.add(root);
q.add(null);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode<Integer> first = q.peek();
q.poll();
if (first == null) {
// If there is no more nodes
if (q.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
// All the nodes of current level are
// visited
System.out.println();
q.add(null);
continue;
}
System.out.print(first.data + " ");
// Append current node's child to queue
for (int i = 0; i < first.children.size();
i++) {
q.add(first.children.get(i));
}
}
}
// Helper function to replace the
// node data with their level value
static void helper(TreeNode<Integer> root, int depth)
{
// Replace the node data with
// it's depth
root.data = depth;
for (int i = 0; i < root.children.size(); i++) {
helper(root.children.get(i), depth + 1);
}
}
// Function to replace with depth
static void
replaceWithDepthValue(TreeNode<Integer> root)
{
helper(root, 0);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given level order traversal in
// the array arr[]
int arr[]
= { 10, 3, 20, 30, 40, 2, 40, 50, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
// Initialise Tree
TreeNode<Integer> root;
root = takeInputLevelWise(arr);
// Function call to replace with
// depth value
replaceWithDepthValue(root);
// Function call to print
// in level order
printLevelATNewLine(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by jainlovely450
0 1 1 1 2 2
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N), donde N es el número de Nodes en el árbol.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(N), donde N es el número de Nodes en el Árbol.
Otro enfoque: también podemos reemplazar el valor del Node con su profundidad al crear el árbol. Estamos atravesando el nivel de array, lo que significa que los Nodes actualmente presentes en la cola tienen la misma profundidad. A medida que agreguemos sus Nodes secundarios a la cola, estarán presentes en el siguiente nivel. Podemos inicializar una variable como profundidad actual igual a 1 y cuando creamos un Node secundario podemos asignar su valor al nivel de profundidad actual. Después de atravesar todos los Nodes presentes en el nivel actual, incrementaremos el nivel de profundidad actual en 1.
C++
// C++ program to implement node with
// it's depth value
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Treenode class using template
template <typename T> class TreeNode {
public:
// To store node value
T data;
// Pointer to TreeNode to store
// the child node
vector<TreeNode<T>*> children;
// Constructor to assign data
// to node
TreeNode(T data) { this->data = data; }
// Destructors to delete a node
~TreeNode()
{
for (int i = 0; i < children.size(); i++) {
delete children[i];
}
}
};
// Function to take input level wise
// i.e., in level order traversal
TreeNode<int>* takeInputLevelWise(int arr[])
{
int idx = 1;
int depthLevel = 1;
// Initialize tree with a root node
// with depth 0
TreeNode<int>* root = new TreeNode<int>(0);
// Initialise queue for appending
// node as a child of parent in
// N-ary tree
queue<TreeNode<int>*> pendingNodes;
// Push the root node in queue
pendingNodes.push(root);
// While queue is not empty append
// child to the node
while (pendingNodes.size() != 0) {
// Number of nodes present in the current level
int size = pendingNodes.size();
while (size > 0) {
// Take the first node
TreeNode<int>* front = pendingNodes.front();
pendingNodes.pop();
// Input number of its child
int numChild = arr[idx];
idx++;
for (int i = 0; i < numChild; i++) {
idx++;
// Make child Node and assign its data
// value equal to depthLevel
TreeNode<int>* child
= new TreeNode<int>(depthLevel);
// Append child node to
// it's parent
front->children.push_back(child);
pendingNodes.push(child);
}
size--;
}
// Increment depth level
depthLevel++;
}
return root;
}
// Function to print each node data
// in level order
void printLevelATNewLine(TreeNode<int>* root)
{
queue<TreeNode<int>*> q;
q.push(root);
q.push(NULL);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode<int>* first = q.front();
q.pop();
if (first == NULL) {
// If there is no more nodes to visit
if (q.empty()) {
break;
}
// All the nodes of current level are visited
cout << endl;
q.push(NULL);
continue;
}
cout << first->data << " ";
// Append current node's child to queue
for (int i = 0; i < first->children.size(); i++) {
q.push(first->children[i]);
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given level order traversal in
// the array arr[]
int arr[]
= { 10, 3, 20, 30, 40, 2, 40, 50, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
// Initialise Tree
TreeNode<int>* root;
root = takeInputLevelWise(arr);
// Function call to print
// in level order
printLevelATNewLine(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by jainlovely450
Java
// Java program to implement node with
// it's depth value
// Importing classes and interface
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class GFG {
// TreeNode class
static class TreeNode<T> {
// To store node value
T data;
// List of TreeNode to store
// the child nodes
ArrayList<TreeNode<T> > children;
// Constructor to assign data to node
TreeNode(T data)
{
this.data = data;
children = new ArrayList<TreeNode<T> >();
}
}
// Function to take input level wise
// i.e., in level order traversal and
// assign value of node equal to its depth
static TreeNode<Integer> takeInputLevelWise(int arr[])
{
int idx = 1;
int depthLevel = 1;
// Initialize tree with a root node
// with depth 0
TreeNode<Integer> root = new TreeNode<Integer>(0);
// Initialize queue for appending
// node as a child of parent in
// N-ary tree
Queue<TreeNode<Integer> > pendingNodes
= new LinkedList<TreeNode<Integer> >();
// Push the root node in queue
pendingNodes.add(root);
// While queue is not empty append
// child to the node
while (!pendingNodes.isEmpty()) {
// Number of nodes present in the current level
int size = pendingNodes.size();
while (size > 0) {
TreeNode<Integer> front
= pendingNodes.peek();
pendingNodes.poll();
// Input number of child
int numChild = arr[idx];
idx++;
for (int i = 0; i < numChild; i++) {
idx++;
// Make child Node and assign its data
// value equal to depthLevel
TreeNode<Integer> child
= new TreeNode<Integer>(depthLevel);
// Append child node to
// it's parent
front.children.add(child);
pendingNodes.add(child);
}
size--;
}
// Increment depth level
depthLevel++;
}
return root;
}
// Function to print each node data
// in level order
static void printLevelATNewLine(TreeNode<Integer> root)
{
Queue<TreeNode<Integer> > q
= new LinkedList<TreeNode<Integer> >();
q.add(root);
q.add(null);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode<Integer> first = q.peek();
q.poll();
if (first == null) {
// If there is no more nodes to visit
if (q.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
// All the nodes of current level are
// visited
System.out.println();
q.add(null);
continue;
}
System.out.print(first.data + " ");
// Append current node's child to queue
for (int i = 0; i < first.children.size();
i++) {
q.add(first.children.get(i));
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given level order traversal in
// the array arr[]
int arr[]
= { 10, 3, 20, 30, 40, 2, 40, 50, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
// Initialize Tree
TreeNode<Integer> root;
root = takeInputLevelWise(arr);
// Function call to print
// in level order
printLevelATNewLine(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by jainlovely450
0 1 1 1 2 2
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por priyanshu21101997 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA