Una array contiene números positivos y negativos en orden aleatorio. Reorganice los elementos de la array para que los números positivos y negativos se coloquen alternativamente. Un número de números positivos y negativos no tiene por qué ser igual. Si hay más números positivos, aparecen al final de la array. Si hay más números negativos, también aparecen al final de la array.
Por ejemplo, si la array de entrada es [-1, 2, -3, 4, 5, 6, -7, 8, 9], la salida debería ser [9, -7, 8, -3, 5, – 1, 2, 4, 6]
Nota: El proceso de partición cambia el orden relativo de los elementos. Es decir, con este enfoque no se mantiene el orden de aparición de los elementos. Vea esto para mantener el orden de aparición de los elementos en este problema.
La solución es separar primero los números positivos y negativos usando el proceso de partición de QuickSort. En el proceso de partición, considere 0 como el valor del elemento pivote para que todos los números negativos se coloquen antes de los números positivos. Una vez que se separan los números negativos y positivos, comenzamos con el primer número negativo y el primer número positivo e intercambiamos cada número negativo alternativo con el siguiente número positivo.
diagrama de flujo
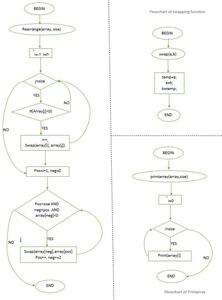
Diagrama de flujo del siguiente código
C++
// A C++ program to put positive
// numbers at even indexes (0, 2, 4,..)
// and negative numbers at odd
// indexes (1, 3, 5, ..)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class GFG
{
public:
void rearrange(int [],int);
void swap(int *,int *);
void printArray(int [],int);
};
// The main function that rearranges
// elements of given array. It puts
// positive elements at even indexes
// (0, 2, ..) and negative numbers
// at odd indexes (1, 3, ..).
void GFG :: rearrange(int arr[], int n)
{
// The following few lines are
// similar to partition process
// of QuickSort. The idea is to
// consider 0 as pivot and
// divide the array around it.
int i = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[j] < 0)
{
i++;
swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);
}
}
// Now all positive numbers are at
// end and negative numbers at the
// beginning of array. Initialize
// indexes for starting point of
// positive and negative numbers
// to be swapped
int pos = i + 1, neg = 0;
// Increment the negative index by
// 2 and positive index by 1,
// i.e., swap every alternate negative
// number with next positive number
while (pos < n && neg < pos &&
arr[neg] < 0)
{
swap(&arr[neg], &arr[pos]);
pos++;
neg += 2;
}
}
// A utility function
// to swap two elements
void GFG :: swap(int *a, int *b)
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
// A utility function to print an array
void GFG :: printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = {-1, 2, -3, 4,
5, 6, -7, 8, 9};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
GFG test;
test.rearrange(arr, n);
test.printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed
// by vt_Yogesh Shukla 1
C
// A C++ program to put positive numbers at even indexes (0,
// 2, 4,..) and negative numbers at odd indexes (1, 3, 5, ..)
#include <stdio.h>
// prototype for swap
void swap(int *a, int *b);
// The main function that rearranges elements of given array.
// It puts positive elements at even indexes (0, 2, ..) and
// negative numbers at odd indexes (1, 3, ..).
void rearrange(int arr[], int n)
{
// The following few lines are similar to partition process
// of QuickSort. The idea is to consider 0 as pivot and
// divide the array around it.
int i = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[j] < 0)
{
i++;
swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);
}
}
// Now all positive numbers are at end and negative numbers
// at the beginning of array. Initialize indexes for starting
// point of positive and negative numbers to be swapped
int pos = i+1, neg = 0;
// Increment the negative index by 2 and positive index by 1,
// i.e., swap every alternate negative number with next
// positive number
while (pos < n && neg < pos && arr[neg] < 0)
{
swap(&arr[neg], &arr[pos]);
pos++;
neg += 2;
}
}
// A utility function to swap two elements
void swap(int *a, int *b)
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
// A utility function to print an array
void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%4d ", arr[i]);
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
int arr[] = {-1, 2, -3, 4, 5, 6, -7, 8, 9};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
rearrange(arr, n);
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Java
// A JAVA program to put positive numbers at even indexes
// (0, 2, 4,..) and negative numbers at odd indexes (1, 3,
// 5, ..)
import java.io.*;
class Alternate {
// The main function that rearranges elements of given
// array. It puts positive elements at even indexes (0,
// 2, ..) and negative numbers at odd indexes (1, 3, ..).
static void rearrange(int arr[], int n)
{
// The following few lines are similar to partition
// process of QuickSort. The idea is to consider 0
// as pivot and divide the array around it.
int i = -1, temp = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[j] < 0)
{
i++;
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
// Now all positive numbers are at end and negative numbers at
// the beginning of array. Initialize indexes for starting point
// of positive and negative numbers to be swapped
int pos = i+1, neg = 0;
// Increment the negative index by 2 and positive index by 1, i.e.,
// swap every alternate negative number with next positive number
while (pos < n && neg < pos && arr[neg] < 0)
{
temp = arr[neg];
arr[neg] = arr[pos];
arr[pos] = temp;
pos++;
neg += 2;
}
}
// A utility function to print an array
static void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
/*Driver function to check for above functions*/
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int arr[] = {-1, 2, -3, 4, 5, 6, -7, 8, 9};
int n = arr.length;
rearrange(arr,n);
System.out.println("Array after rearranging: ");
printArray(arr,n);
}
}
/*This code is contributed by Devesh Agrawal*/
Python3
# Python program to put positive numbers at even indexes (0, // 2, 4,..) and # negative numbers at odd indexes (1, 3, 5, ..) # The main function that rearranges elements of given array. # It puts positive elements at even indexes (0, 2, ..) and # negative numbers at odd indexes (1, 3, ..). def rearrange(arr, n): # The following few lines are similar to partition process # of QuickSort. The idea is to consider 0 as pivot and # divide the array around it. i = -1 for j in range(n): if (arr[j] < 0): i += 1 # swapping of arr arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i] # Now all positive numbers are at end and negative numbers # at the beginning of array. Initialize indexes for starting # point of positive and negative numbers to be swapped pos, neg = i+1, 0 # Increment the negative index by 2 and positive index by 1, # i.e., swap every alternate negative number with next # positive number while (pos < n and neg < pos and arr[neg] < 0): # swapping of arr arr[neg], arr[pos] = arr[pos], arr[neg] pos += 1 neg += 2 # A utility function to print an array def printArray(arr, n): for i in range(n): print (arr[i],end=" ") # Driver program to test above functions arr = [-1, 2, -3, 4, 5, 6, -7, 8, 9] n = len(arr) rearrange(arr, n) printArray(arr, n) # Contributed by Afzal
C#
// A C# program to put positive numbers
// at even indexes (0, 2, 4, ..) and
// negative numbers at odd indexes (1, 3, 5, ..)
using System;
class Alternate {
// The main function that rearranges elements
// of given array. It puts positive elements
// at even indexes (0, 2, ..) and negative
// numbers at odd indexes (1, 3, ..).
static void rearrange(int[] arr, int n)
{
// The following few lines are similar to partition
// process of QuickSort. The idea is to consider 0
// as pivot and divide the array around it.
int i = -1, temp = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[j] < 0) {
i++;
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
// Now all positive numbers are at end
// and negative numbers at the beginning of
// array. Initialize indexes for starting point
// of positive and negative numbers to be swapped
int pos = i + 1, neg = 0;
// Increment the negative index by 2 and
// positive index by 1, i.e., swap every
// alternate negative number with next positive number
while (pos < n && neg < pos && arr[neg] < 0) {
temp = arr[neg];
arr[neg] = arr[pos];
arr[pos] = temp;
pos++;
neg += 2;
}
}
// A utility function to print an array
static void printArray(int[] arr, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
/*Driver function to check for above functions*/
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { -1, 2, -3, 4, 5, 6, -7, 8, 9 };
int n = arr.Length;
rearrange(arr, n);
printArray(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.
PHP
<?php
// A PHP program to put positive numbers
// at even indexes (0, 2, 4,..) and negative
// numbers at odd indexes (1, 3, 5, ..)
// The main function that rearranges elements
// of given array. It puts positive elements
// at even indexes (0, 2, ..) and negative
// numbers at odd indexes (1, 3, ..).
function rearrange(&$arr, $n)
{
// The following few lines are similar
// to partition process of QuickSort.
// The idea is to consider 0 as pivot
// and divide the array around it.
$i = -1;
for ($j = 0; $j < $n; $j++)
{
if ($arr[$j] < 0)
{
$i++;
swap($arr[$i], $arr[$j]);
}
}
// Now all positive numbers are at end and
// negative numbers at the beginning of array.
// Initialize indexes for starting point of
// positive and negative numbers to be swapped
$pos = $i + 1;
$neg = 0;
// Increment the negative index by 2 and
// positive index by 1, i.e., swap every
// alternate negative number with next
// positive number
while ($pos < $n && $neg < $pos &&
$arr[$neg] < 0)
{
swap($arr[$neg], $arr[$pos]);
$pos++;
$neg += 2;
}
}
// A utility function to swap two elements
function swap(&$a, &$b)
{
$temp = $a;
$a = $b;
$b = $temp;
}
// A utility function to print an array
function printArray(&$arr, $n)
{
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
echo " " . $arr[$i] . " ";
}
// Driver Code
$arr = array(-1, 2, -3, 4, 5, 6, -7, 8, 9);
$n = count($arr);
rearrange($arr, $n);
printArray($arr, $n);
// This code is contributed
// by rathbhupendra
?>
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to put positive
// numbers at even indexes
// (0, 2, 4,..) and negative
// numbers at odd indexes (1, 3,
// 5, ..)
// The main function that
// rearranges elements of given
// array. It puts positive elements
// at even indexes (0,
// 2, ..) and negative numbers
// at odd indexes (1, 3, ..).
function rearrange(arr,n)
{
// The following few lines are similar to partition
// process of QuickSort. The idea is to consider 0
// as pivot and divide the array around it.
let i = -1, temp = 0;
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[j] < 0)
{
i++;
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
// Now all positive numbers are
// at end and negative numbers at
// the beginning of array.
// Initialize indexes for starting point
// of positive and negative numbers
// to be swapped
let pos = i+1, neg = 0;
// Increment the negative index
// by 2 and positive index by 1, i.e.,
// swap every alternate negative number
// with next positive number
while (pos < n && neg < pos && arr[neg] < 0)
{
temp = arr[neg];
arr[neg] = arr[pos];
arr[pos] = temp;
pos++;
neg += 2;
}
}
// A utility function to print an array
function printArray(arr,n)
{
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
document.write(arr[i] + " ");
}
/*Driver function to check for above functions*/
let arr = [-1, 2, -3, 4, 5, 6, -7, 8, 9];
let n = arr.length;
rearrange(arr,n);
printArray(arr,n);
// This code is contributed by sravan kumar
</script>
Producción:
4 -3 5 -1 6 -7 2 8 9
Complejidad de tiempo: O (n) donde n es el número de elementos en una array dada. Como estamos usando un bucle para atravesar N veces, nos costará O (N) tiempo
Espacio auxiliar: O (1), ya que no estamos usando ningún espacio adicional.
Artículos relacionados:
Reorganiza números positivos y negativos con espacio adicional constante
Mueve todos los elementos negativos al final en orden con espacio adicional permitido
Este artículo fue compilado por Abhay Rathi . Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Si le gusta GeeksforGeeks y le gustaría contribuir, también puede escribir un artículo y enviarlo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA