Requisito previo: graphics.h , ¿Cómo incluir graphics.h?
En C/C++ hay un archivo de encabezado graphics.h que se usa para crear el objeto como línea, círculo, etc.
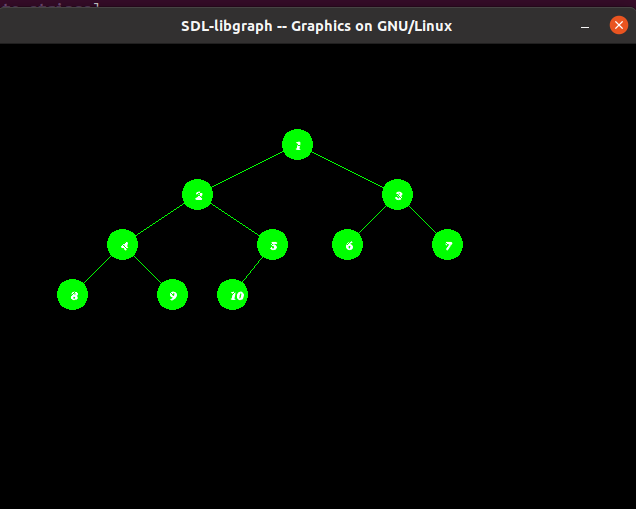
Dada una array arr[] de N enteros, la tarea es escribir el programa C++ para crear el árbol usando graphics.h .
Enfoque: para ejecutar el programa, tenemos que incluir el siguiente archivo de encabezado:
#include
Crearemos un árbol con las siguientes funciones de ayuda:
- setcolor(color) : esta función presente en el archivo de encabezado graphic.h que se utiliza para establecer el color de dibujo actual en el nuevo color.
- floodfill (patrón, color) : la función se usa para llenar un área cerrada. El patrón de relleno actual y el color de relleno se utilizan para rellenar el área.
- circle(x, y, radius) : El archivo de encabezado graphics.h contiene la función circle() que dibuja un círculo con centro en (x, y) y radio dado.
- outtextxy() : El archivo de encabezado graphics.h contiene la función outtextxy() que muestra el texto o la string en un punto específico (x, y) en la pantalla.
A continuación se muestra la implementación de dibujar un árbol usando gráficos en C++:
C++
// C++ program to draw the tree
// in graphics.h
#include <graphics.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
// Function that prints Tree using
// functions graphic.h header file
void printTree(int x, int y, int* array,
int index,
int total_elements)
{
// Base Case
if (index >= total_elements)
return NULL;
// Convert int value into string
ostringstream str1;
str1 << array[index];
string str2 = str1.str();
char* str = &str2[0u];
// Set color of the boundary of
// circle as green
setcolor(GREEN);
// Draw the circle of radius 15
// that represent node of Tree
circle(x, y, 15);
floodfill(x, y, GREEN);
// Print the values of the node
// in the circle
outtextxy(x - 2, y - 3, str);
// Set the color of the line
// from parent to child as green
setcolor(GREEN);
// Evaluating left and right child
int left = 2 * index + 1;
int right = 2 * index + 2;
// Recursively draw the left subtree
// and the right subtree
printTree(x - y / (index + 1), y + 50,
array, left, total_elements);
printTree(x + y / (index + 1), y + 50,
array, right, total_elements);
// Draw the line (or link) when the
// node is not the leaf node
if (left < total_elements) {
line(x, y, x - y / (index + 1), y + 50);
}
if (right < total_elements) {
line(x, y, x + y / (index + 1), y + 50);
}
return NULL;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Initialize graphic driver
int gd = DETECT, gm;
initgraph(&gd, &gm, "None");
// Consider the tree as represented
/*
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
/ \ /
8 9 10
*/
// Given array arr[]
int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
// Function Call
printTree(300, 100, array, 0, 10);
getch();
// closegraph function closes the
// graphics mode and deallocates
// all memory allocated by
// graphics system
closegraph();
}
Producción: