Eulerian Path es un camino en el gráfico que visita cada borde exactamente una vez. El Circuito Euleriano es un Camino Euleriano que comienza y termina en el mismo vértice.
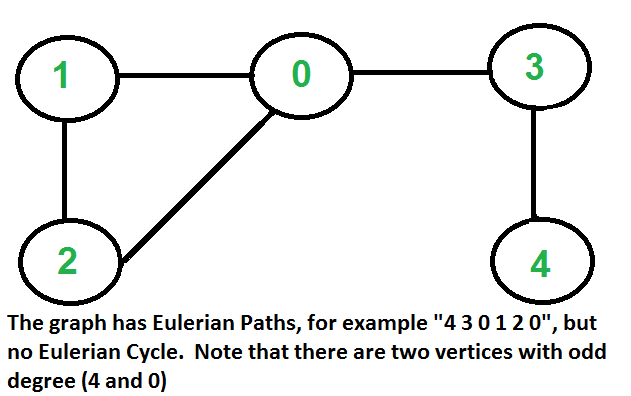
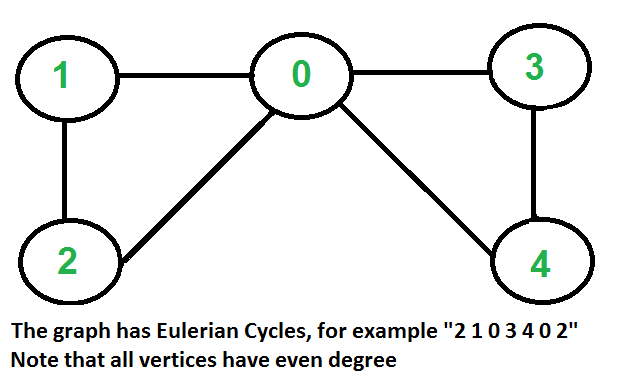
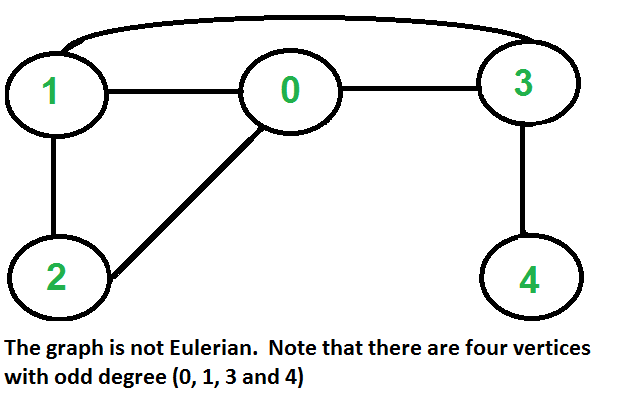
¿Cómo encontrar si un gráfico dado es Euleriano o no?
El problema es el mismo que la siguiente pregunta. “¿Es posible dibujar un gráfico dado sin levantar el lápiz del papel y sin trazar ninguno de los bordes más de una vez?”.
Un grafo se llama euleriano si tiene un ciclo euleriano y se llama semieuleriano si tiene un camino euleriano. El problema parece similar al camino hamiltoniano, que es un problema completo NP para un gráfico general. Afortunadamente, podemos encontrar si un gráfico dado tiene un Camino Euleriano o no en tiempo polinomial. De hecho, podemos encontrarlo en tiempo O(V+E).
A continuación se presentan algunas propiedades interesantes de los grafos no dirigidos con un camino y un ciclo eulerianos. Podemos usar estas propiedades para saber si un grafo es euleriano o no.
Ciclo euleriano: un gráfico no dirigido tiene un ciclo euleriano si las siguientes dos condiciones son verdaderas.
- Todos los vértices con grado distinto de cero están conectados. No nos importan los vértices con grado cero porque no pertenecen al ciclo o camino euleriano (solo consideramos todas las aristas).
- Todos los vértices tienen grado par.
Eulerian Path: un gráfico no dirigido tiene Eulerian Path si las dos condiciones siguientes son verdaderas.
- Igual que la condición (a) para el Ciclo Euleriano.
- Si cero o dos vértices tienen grado impar y todos los demás vértices tienen grado par. Tenga en cuenta que solo un vértice con grado impar no es posible en un gráfico no dirigido (la suma de todos los grados siempre es par en un gráfico no dirigido)
Tenga en cuenta que un gráfico sin bordes se considera euleriano porque no hay bordes para atravesar.
¿Como funciona esto?
En el camino euleriano, cada vez que visitamos un vértice v, caminamos a través de dos aristas no visitadas con un punto final como v. Por lo tanto, todos los vértices medios en el camino euleriano deben tener un grado par. Para el Ciclo Euleriano, cualquier vértice puede ser un vértice medio, por lo tanto, todos los vértices deben tener un grado par.
Implementación:
C++
// A C++ program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not
#include<iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
// A class that represents an undirected graph
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
list<int> *adj; // A dynamic array of adjacency lists
public:
// Constructor and destructor
Graph(int V) {this->V = V; adj = new list<int>[V]; }
~Graph() { delete [] adj; } // To avoid memory leak
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w);
// Method to check if this graph is Eulerian or not
int isEulerian();
// Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
bool isConnected();
// Function to do DFS starting from v. Used in isConnected();
void DFSUtil(int v, bool visited[]);
};
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w);
adj[w].push_back(v); // Note: the graph is undirected
}
void Graph::DFSUtil(int v, bool visited[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
list<int>::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
DFSUtil(*i, visited);
}
// Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected.
// It mainly does DFS traversal starting from
bool Graph::isConnected()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
bool visited[V];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Find a vertex with non-zero degree
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() != 0)
break;
// If there are no edges in the graph, return true
if (i == V)
return true;
// Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree
DFSUtil(i, visited);
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false && adj[i].size() > 0)
return false;
return true;
}
/* The function returns one of the following values
0 --> If graph is not Eulerian
1 --> If graph has an Euler path (Semi-Eulerian)
2 --> If graph has an Euler Circuit (Eulerian) */
int Graph::isEulerian()
{
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
if (isConnected() == false)
return 0;
// Count vertices with odd degree
int odd = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() & 1)
odd++;
// If count is more than 2, then graph is not Eulerian
if (odd > 2)
return 0;
// If odd count is 2, then semi-eulerian.
// If odd count is 0, then eulerian
// Note that odd count can never be 1 for undirected graph
return (odd)? 1 : 2;
}
// Function to run test cases
void test(Graph &g)
{
int res = g.isEulerian();
if (res == 0)
cout << "graph is not Eulerian\n";
else if (res == 1)
cout << "graph has a Euler path\n";
else
cout << "graph has a Euler cycle\n";
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
// Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures
Graph g1(5);
g1.addEdge(1, 0);
g1.addEdge(0, 2);
g1.addEdge(2, 1);
g1.addEdge(0, 3);
g1.addEdge(3, 4);
test(g1);
Graph g2(5);
g2.addEdge(1, 0);
g2.addEdge(0, 2);
g2.addEdge(2, 1);
g2.addEdge(0, 3);
g2.addEdge(3, 4);
g2.addEdge(4, 0);
test(g2);
Graph g3(5);
g3.addEdge(1, 0);
g3.addEdge(0, 2);
g3.addEdge(2, 1);
g3.addEdge(0, 3);
g3.addEdge(3, 4);
g3.addEdge(1, 3);
test(g3);
// Let us create a graph with 3 vertices
// connected in the form of cycle
Graph g4(3);
g4.addEdge(0, 1);
g4.addEdge(1, 2);
g4.addEdge(2, 0);
test(g4);
// Let us create a graph with all vertices
// with zero degree
Graph g5(3);
test(g5);
return 0;
}
Java
// A Java program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
// This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list
// representation
class Graph
{
private int V; // No. of vertices
// Array of lists for Adjacency List Representation
private LinkedList<Integer> adj[];
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
for (int i=0; i<v; ++i)
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
//Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].add(w);// Add w to v's list.
adj[w].add(v); //The graph is undirected
}
// A function used by DFS
void DFSUtil(int v,boolean visited[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
Iterator<Integer> i = adj[v].listIterator();
while (i.hasNext())
{
int n = i.next();
if (!visited[n])
DFSUtil(n, visited);
}
}
// Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are
// connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from
boolean isConnected()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Find a vertex with non-zero degree
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() != 0)
break;
// If there are no edges in the graph, return true
if (i == V)
return true;
// Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree
DFSUtil(i, visited);
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false && adj[i].size() > 0)
return false;
return true;
}
/* The function returns one of the following values
0 --> If graph is not Eulerian
1 --> If graph has an Euler path (Semi-Eulerian)
2 --> If graph has an Euler Circuit (Eulerian) */
int isEulerian()
{
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
if (isConnected() == false)
return 0;
// Count vertices with odd degree
int odd = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size()%2!=0)
odd++;
// If count is more than 2, then graph is not Eulerian
if (odd > 2)
return 0;
// If odd count is 2, then semi-eulerian.
// If odd count is 0, then eulerian
// Note that odd count can never be 1 for undirected graph
return (odd==2)? 1 : 2;
}
// Function to run test cases
void test()
{
int res = isEulerian();
if (res == 0)
System.out.println("graph is not Eulerian");
else if (res == 1)
System.out.println("graph has a Euler path");
else
System.out.println("graph has a Euler cycle");
}
// Driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures
Graph g1 = new Graph(5);
g1.addEdge(1, 0);
g1.addEdge(0, 2);
g1.addEdge(2, 1);
g1.addEdge(0, 3);
g1.addEdge(3, 4);
g1.test();
Graph g2 = new Graph(5);
g2.addEdge(1, 0);
g2.addEdge(0, 2);
g2.addEdge(2, 1);
g2.addEdge(0, 3);
g2.addEdge(3, 4);
g2.addEdge(4, 0);
g2.test();
Graph g3 = new Graph(5);
g3.addEdge(1, 0);
g3.addEdge(0, 2);
g3.addEdge(2, 1);
g3.addEdge(0, 3);
g3.addEdge(3, 4);
g3.addEdge(1, 3);
g3.test();
// Let us create a graph with 3 vertices
// connected in the form of cycle
Graph g4 = new Graph(3);
g4.addEdge(0, 1);
g4.addEdge(1, 2);
g4.addEdge(2, 0);
g4.test();
// Let us create a graph with all vertices
// with zero degree
Graph g5 = new Graph(3);
g5.test();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aakash Hasija
Python3
# Python program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not
#Complexity : O(V+E)
from collections import defaultdict
# This class represents a undirected graph using adjacency list representation
class Graph:
def __init__(self, vertices):
self.V = vertices # No. of vertices
self.graph = defaultdict(list) # default dictionary to store graph
# function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
self.graph[v].append(u)
# A function used by isConnected
def DFSUtil(self, v, visited):
# Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = True
# Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
for i in self.graph[v]:
if visited[i] == False:
self.DFSUtil(i, visited)
'''Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are
connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from
node with non-zero degree'''
def isConnected(self):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
visited = [False]*(self.V)
# Find a vertex with non-zero degree
for i in range(self.V):
if len(self.graph[i]) > 1:
break
# If there are no edges in the graph, return true
if i == self.V-1:
return True
# Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree
self.DFSUtil(i, visited)
# Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited
for i in range(self.V):
if visited[i] == False and len(self.graph[i]) > 0:
return False
return True
'''The function returns one of the following values
0 --> If graph is not Eulerian
1 --> If graph has an Euler path (Semi-Eulerian)
2 --> If graph has an Euler Circuit (Eulerian) '''
def isEulerian(self):
# Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
if self.isConnected() == False:
return 0
else:
# Count vertices with odd degree
odd = 0
for i in range(self.V):
if len(self.graph[i]) % 2 != 0:
odd += 1
'''If odd count is 2, then semi-eulerian.
If odd count is 0, then eulerian
If count is more than 2, then graph is not Eulerian
Note that odd count can never be 1 for undirected graph'''
if odd == 0:
return 2
elif odd == 2:
return 1
elif odd > 2:
return 0
# Function to run test cases
def test(self):
res = self.isEulerian()
if res == 0:
print("graph is not Eulerian")
elif res == 1:
print("graph has a Euler path")
else:
print("graph has a Euler cycle")
# Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures
g1 = Graph(5)
g1.addEdge(1, 0)
g1.addEdge(0, 2)
g1.addEdge(2, 1)
g1.addEdge(0, 3)
g1.addEdge(3, 4)
g1.test()
g2 = Graph(5)
g2.addEdge(1, 0)
g2.addEdge(0, 2)
g2.addEdge(2, 1)
g2.addEdge(0, 3)
g2.addEdge(3, 4)
g2.addEdge(4, 0)
g2.test()
g3 = Graph(5)
g3.addEdge(1, 0)
g3.addEdge(0, 2)
g3.addEdge(2, 1)
g3.addEdge(0, 3)
g3.addEdge(3, 4)
g3.addEdge(1, 3)
g3.test()
# Let us create a graph with 3 vertices
# connected in the form of cycle
g4 = Graph(3)
g4.addEdge(0, 1)
g4.addEdge(1, 2)
g4.addEdge(2, 0)
g4.test()
# Let us create a graph with all vertices
# with zero degree
g5 = Graph(3)
g5.test()
# This code is contributed by Neelam Yadav
C#
// A C# program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list
// representation
public class Graph
{
private int V; // No. of vertices
// Array of lists for Adjacency List Representation
private List<int> []adj;
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new List<int>[v];
for (int i=0; i<v; ++i)
adj[i] = new List<int>();
}
//Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].Add(w);// Add w to v's list.
adj[w].Add(v); //The graph is undirected
}
// A function used by DFS
void DFSUtil(int v,bool []visited)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
foreach(int i in adj[v]){
int n = i;
if (!visited[n])
DFSUtil(n, visited);
}
}
// Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are
// connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from
bool isConnected()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
bool []visited = new bool[V];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Find a vertex with non-zero degree
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].Count != 0)
break;
// If there are no edges in the graph, return true
if (i == V)
return true;
// Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree
DFSUtil(i, visited);
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false && adj[i].Count > 0)
return false;
return true;
}
/* The function returns one of the following values
0 --> If graph is not Eulerian
1 --> If graph has an Euler path (Semi-Eulerian)
2 --> If graph has an Euler Circuit (Eulerian) */
int isEulerian()
{
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
if (isConnected() == false)
return 0;
// Count vertices with odd degree
int odd = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].Count%2!=0)
odd++;
// If count is more than 2, then graph is not Eulerian
if (odd > 2)
return 0;
// If odd count is 2, then semi-eulerian.
// If odd count is 0, then eulerian
// Note that odd count can never be 1 for undirected graph
return (odd==2)? 1 : 2;
}
// Function to run test cases
void test()
{
int res = isEulerian();
if (res == 0)
Console.WriteLine("graph is not Eulerian");
else if (res == 1)
Console.WriteLine("graph has a Euler path");
else
Console.WriteLine("graph has a Euler cycle");
}
// Driver method
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures
Graph g1 = new Graph(5);
g1.addEdge(1, 0);
g1.addEdge(0, 2);
g1.addEdge(2, 1);
g1.addEdge(0, 3);
g1.addEdge(3, 4);
g1.test();
Graph g2 = new Graph(5);
g2.addEdge(1, 0);
g2.addEdge(0, 2);
g2.addEdge(2, 1);
g2.addEdge(0, 3);
g2.addEdge(3, 4);
g2.addEdge(4, 0);
g2.test();
Graph g3 = new Graph(5);
g3.addEdge(1, 0);
g3.addEdge(0, 2);
g3.addEdge(2, 1);
g3.addEdge(0, 3);
g3.addEdge(3, 4);
g3.addEdge(1, 3);
g3.test();
// Let us create a graph with 3 vertices
// connected in the form of cycle
Graph g4 = new Graph(3);
g4.addEdge(0, 1);
g4.addEdge(1, 2);
g4.addEdge(2, 0);
g4.test();
// Let us create a graph with all vertices
// with zero degree
Graph g5 = new Graph(3);
g5.test();
}
}
// This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Javascript
<script>
// A Javascript program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not
// This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list
// representation
class Graph
{
// Constructor
constructor(v)
{
this.V = v;
this.adj = new Array(v);
for (let i = 0; i < v; ++i)
this.adj[i] = [];
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
addEdge(v,w)
{
this.adj[v].push(w);// Add w to v's list.
this.adj[w].push(v); //The graph is undirected
}
// A function used by DFS
DFSUtil(v,visited)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
for(let i of this.adj[v])
{
let n = i;
if (!visited[n])
this.DFSUtil(n, visited);
}
}
// Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are
// connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from
isConnected()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
let visited = new Array(this.V);
let i;
for (i = 0; i < this.V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Find a vertex with non-zero degree
for (i = 0; i < this.V; i++)
if (this.adj[i].length != 0)
break;
// If there are no edges in the graph, return true
if (i == this.V)
return true;
// Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree
this.DFSUtil(i, visited);
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited
for (i = 0; i < this.V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false && this.adj[i].length > 0)
return false;
return true;
}
/* The function returns one of the following values
0 --> If graph is not Eulerian
1 --> If graph has an Euler path (Semi-Eulerian)
2 --> If graph has an Euler Circuit (Eulerian) */
isEulerian()
{
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
if (this.isConnected() == false)
return 0;
// Count vertices with odd degree
let odd = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < this.V; i++)
if (this.adj[i].length%2!=0)
odd++;
// If count is more than 2, then graph is not Eulerian
if (odd > 2)
return 0;
// If odd count is 2, then semi-eulerian.
// If odd count is 0, then eulerian
// Note that odd count can never be 1 for undirected graph
return (odd==2)? 1 : 2;
}
// Function to run test cases
test()
{
let res = this.isEulerian();
if (res == 0)
document.write("graph is not Eulerian<br>");
else if (res == 1)
document.write("graph has a Euler path<br>");
else
document.write("graph has a Euler cycle<br>");
}
}
// Driver method
// Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures
let g1 = new Graph(5);
g1.addEdge(1, 0);
g1.addEdge(0, 2);
g1.addEdge(2, 1);
g1.addEdge(0, 3);
g1.addEdge(3, 4);
g1.test();
let g2 = new Graph(5);
g2.addEdge(1, 0);
g2.addEdge(0, 2);
g2.addEdge(2, 1);
g2.addEdge(0, 3);
g2.addEdge(3, 4);
g2.addEdge(4, 0);
g2.test();
let g3 = new Graph(5);
g3.addEdge(1, 0);
g3.addEdge(0, 2);
g3.addEdge(2, 1);
g3.addEdge(0, 3);
g3.addEdge(3, 4);
g3.addEdge(1, 3);
g3.test();
// Let us create a graph with 3 vertices
// connected in the form of cycle
let g4 = new Graph(3);
g4.addEdge(0, 1);
g4.addEdge(1, 2);
g4.addEdge(2, 0);
g4.test();
// Let us create a graph with all vertices
// with zero degree
let g5 = new Graph(3);
g5.test();
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
graph has a Euler path graph has a Euler cycle graph is not Eulerian graph has a Euler cycle graph has a Euler cycle
Complejidad temporal: O(V+E)
Próximos Artículos:
Camino Euleriano y Circuito para Grafos Dirigidos.
¿Algoritmo de Fleury para imprimir un camino o circuito euleriano?
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA