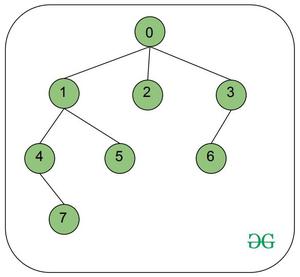
Dado un árbol enraizado que tiene N vértices, una array de valores[ ] , que representa el valor asignado a cada Node y un vértice V , la tarea es calcular la suma de los valores de los Nodes y los vecinos inmediatos que se encuentran en el camino desde la raíz ( siempre 0 ) a V .
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 8, valores = {1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 4, 3, 6}, V = 7
Salida: 16
Explicación:
Ruta desde la raíz (0) a V (7) = 0 -> 1 -> 4 -> 7
Vecinos de 0 = (2, 3), Suma = 1 (Node 0) + 3 (Node 2) + 0 (Node 3) = 4
Vecinos de 1 = (5), Suma = 2 (Node 1) + 4 (Node 5) = 6
Sin vecino de 4, Suma = 0 (Node 4) = 0
Sin vecino de 7, Suma = 6 (Node 7) = 6
Suma total = 4 + 6 + 0 + 6 = 16Entrada: N = 5, valores = {5, 6, 2, 9, 0}, V = 2
Salida: 13
Acercarse:
La idea es almacenar el padre de cada Node en una array y agregar el valor de cada padre con su hijo y almacenarlo en el Node padre . Ahora, cada Node tendrá la suma de su valor y el valor de los vecinos correspondientes. Use esta array para encontrar la suma requerida de la ruta desde la raíz hasta el vértice V.
Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Inicialice una array para almacenar los valores de cada Node y sus vecinos correspondientes utilizando DFS Traversal .
- Itere desde el vértice V hasta la raíz usando la array y siga agregando el valor de todos los Nodes encontrados en la ruta.
- Finalmente, imprima la suma obtenida .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ Program to implement
// the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Creating Adjacency list
vector<vector<int>> constructTree(int n,
vector<vector<int>> edges)
{
vector<vector<int>> adjl(n);
for (auto e : edges)
{
int u = e[0];
int v = e[1];
adjl[u].push_back(v);
adjl[v].push_back(u);
}
return adjl;
}
// Function to perform DFS traversal
void DFS(vector<vector<int>> adjl,
vector<int> &parent, int u, int p)
{
// Initializing parent of each node to p
parent[u] = p;
// Iterate over the children
for (int v : adjl[u])
{
if (v != p)
{
DFS(adjl, parent, v, u);
}
}
}
// Function to add values of children to
// respective parent nodes
vector<int> valuesFromChildren(vector<int> parent,
vector<int> values)
{
vector<int> valuesChildren(parent.size());
for (int i = 0; i < parent.size(); i++)
{
// Root node
if (parent[i] == -1)
continue;
else
{
int p = parent[i];
valuesChildren[p] += values[i];
}
}
return valuesChildren;
}
// Function to return sum of values of
// each node in path from V to the root
int findSumOfValues(int v, vector<int> parent,
vector<int> valuesChildren)
{
int cur_node = v;
int sum = 0;
// Path from node V to root node
while (cur_node != -1)
{
sum += valuesChildren[cur_node];
cur_node = parent[cur_node];
}
return sum;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 8;
// Insert edges into the graph
vector<vector<int>> edges = {{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {0, 3}, {1, 4},
{1, 5}, {4, 7}, {3, 6}};
int v = 7;
// Values assigned to each vertex
vector<int> values = {1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 4, 3, 6};
// Constructing the tree
// using adjacency list
vector<vector<int>> adjl = constructTree(n, edges);
// Parent array
vector<int> parent(n);
// store values in the parent array
DFS(adjl, parent, 0, -1);
// Add values of children to the parent
vector<int> valuesChildren = valuesFromChildren(parent, values);
// Find sum of nodes lying in the path
int sum = findSumOfValues(v, parent, valuesChildren);
// Add root node since
// its value is not included yet
sum += values[0];
cout << sum << endl;
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552
Java
// Java Program to implement
// the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Creating Adjacency list
private static List<List<Integer> >
constructTree(int n, int[][] edges)
{
List<List<Integer> > adjl
= new ArrayList<List<Integer> >();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
adjl.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
for (int[] e : edges) {
int u = e[0];
int v = e[1];
adjl.get(u).add(v);
adjl.get(v).add(u);
}
return adjl;
}
// Function to perform DFS traversal
private static void DFS(
List<List<Integer> > adjl,
int[] parent, int u, int p)
{
// Initializing parent of each node to p
parent[u] = p;
// Iterate over the children
for (int v : adjl.get(u)) {
if (v != p) {
DFS(adjl, parent, v, u);
}
}
}
// Function to add values of children to
// respective parent nodes
private static int[] valuesFromChildren(
int[] parent, int[] values)
{
int[] valuesChildren
= new int[parent.length];
for (int i = 0; i < parent.length; i++) {
// Root node
if (parent[i] == -1)
continue;
else {
int p = parent[i];
valuesChildren[p] += values[i];
}
}
return valuesChildren;
}
// Function to return sum of values of
// each node in path from V to the root
private static int findSumOfValues(
int v, int[] parent,
int[] valuesChildren)
{
int cur_node = v;
int sum = 0;
// Path from node V to root node
while (cur_node != -1) {
sum += valuesChildren[cur_node];
cur_node = parent[cur_node];
}
return sum;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 8;
// Insert edges into the graph
int[][] edges = { { 0, 1 },
{ 0, 2 },
{ 0, 3 },
{ 1, 4 },
{ 1, 5 },
{ 4, 7 },
{ 3, 6 } };
int v = 7;
// Values assigned to each vertex
int[] values = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 0,
0, 4, 3, 6 };
// Constructing the tree
// using adjacency list
List<List<Integer> > adjl
= constructTree(n, edges);
// Parent array
int[] parent = new int[n];
// store values in the parent array
DFS(adjl, parent, 0, -1);
// Add values of children to the parent
int[] valuesChildren
= valuesFromChildren(parent, values);
// Find sum of nodes lying in the path
int sum = findSumOfValues(
v, parent,
valuesChildren);
// Add root node since
// its value is not included yet
sum += values[0];
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
Python3
# Python3 program to implement the above approach # Creating Adjacency list def constructTree(n, edges): adjl = [] for i in range(n): adjl.append([]) for i in range(len(edges)): u = edges[i][0] v = edges[i][1] adjl[u].append(v) adjl[v].append(u) return adjl # Function to perform DFS traversal def DFS(adjl, parent, u, p): # Initializing parent of each node to p parent[u] = p # Iterate over the children for v in adjl[u]: if (v != p): DFS(adjl, parent, v, u) # Function to add values of children to # respective parent nodes def valuesFromChildren(parent, values): valuesChildren = [0]*(len(parent)) for i in range(len(parent)): # Root node if (parent[i] == -1): continue else: p = parent[i] valuesChildren[p] += values[i] return valuesChildren # Function to return sum of values of # each node in path from V to the root def findSumOfValues(v, parent, valuesChildren): cur_node = v Sum = 0 # Path from node V to root node while (cur_node != -1): Sum += valuesChildren[cur_node] cur_node = parent[cur_node] return Sum n = 8 # Insert edges into the graph edges = [ [ 0, 1 ], [ 0, 2 ], [ 0, 3 ], [ 1, 4 ], [ 1, 5 ], [ 4, 7 ], [ 3, 6 ] ] v = 7 # Values assigned to each vertex values = [ 1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 4, 3, 6 ] # Constructing the tree # using adjacency list adjl = constructTree(n, edges) # Parent array parent = [0]*(n) # store values in the parent array DFS(adjl, parent, 0, -1) # Add values of children to the parent valuesChildren = valuesFromChildren(parent, values) # Find sum of nodes lying in the path Sum = findSumOfValues(v, parent, valuesChildren) # Add root node since # its value is not included yet Sum += values[0] print(Sum) # This code is contributed by suresh07.
C#
// C# program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Creating Adjacency list
private static List<List<int>> constructTree(int n, int[,] edges)
{
List<List<int> > adjl = new List<List<int> >();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
adjl.Add(new List<int>());
}
for(int i = 0; i < edges.GetLength(0); i++)
{
int u = edges[i, 0];
int v = edges[i, 1];
adjl[u].Add(v);
adjl[v].Add(u);
}
return adjl;
}
// Function to perform DFS traversal
private static void DFS(List<List<int> > adjl,
int[] parent, int u, int p)
{
// Initializing parent of each node to p
parent[u] = p;
// Iterate over the children
foreach(int v in adjl[u])
{
if (v != p)
{
DFS(adjl, parent, v, u);
}
}
}
// Function to add values of children to
// respective parent nodes
private static int[] valuesFromChildren(int[] parent,
int[] values)
{
int[] valuesChildren = new int[parent.Length];
for(int i = 0; i < parent.Length; i++)
{
// Root node
if (parent[i] == -1)
continue;
else
{
int p = parent[i];
valuesChildren[p] += values[i];
}
}
return valuesChildren;
}
// Function to return sum of values of
// each node in path from V to the root
private static int findSumOfValues(int v, int[] parent,
int[] valuesChildren)
{
int cur_node = v;
int sum = 0;
// Path from node V to root node
while (cur_node != -1)
{
sum += valuesChildren[cur_node];
cur_node = parent[cur_node];
}
return sum;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 8;
// Insert edges into the graph
int[, ] edges = { { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 }, { 0, 3 },
{ 1, 4 }, { 1, 5 }, { 4, 7 },
{ 3, 6 } };
int v = 7;
// Values assigned to each vertex
int[] values = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 0,
0, 4, 3, 6 };
// Constructing the tree
// using adjacency list
List<List<int>> adjl = constructTree(n, edges);
// Parent array
int[] parent = new int[n];
// store values in the parent array
DFS(adjl, parent, 0, -1);
// Add values of children to the parent
int[] valuesChildren = valuesFromChildren(parent,
values);
// Find sum of nodes lying in the path
int sum = findSumOfValues(v, parent,
valuesChildren);
// Add root node since
// its value is not included yet
sum += values[0];
Console.WriteLine(sum);
}
}
// This code is contributed by ukasp
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to implement
// the above approach
// Creating Adjacency list
function constructTree(n, edges)
{
let adjl = [];
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
adjl.push([]);
}
for(let e = 0; e < edges.length; e++)
{
let u = edges[e][0];
let v = edges[e][1];
adjl[u].push(v);
adjl[v].push(u);
}
return adjl;
}
// Function to perform DFS traversal
function DFS(adjl, parent, u, p)
{
// Initializing parent of each node to p
parent[u] = p;
// Iterate over the children
for(let v = 0; v < adjl[u].length; v++)
{
if (adjl[u][v] != p)
{
DFS(adjl, parent, adjl[u][v], u);
}
}
}
// Function to add values of children to
// respective parent nodes
function valuesFromChildren(parent, values)
{
let valuesChildren = new Array(parent.length);
for(let i = 0; i < parent.length; i++)
{
valuesChildren[i] = 0;
}
for(let i = 0; i < parent.length; i++)
{
// Root node
if (parent[i] == -1)
continue;
else
{
let p = parent[i];
valuesChildren[p] += values[i];
}
}
return valuesChildren;
}
// Function to return sum of values of
// each node in path from V to the root
function findSumOfValues(v, parent, valuesChildren)
{
let cur_node = v;
let sum = 0;
// Path from node V to root node
while (cur_node != -1)
{
sum += valuesChildren[cur_node];
cur_node = parent[cur_node];
}
return sum;
}
// Driver Code
let n = 8;
// Insert edges into the graph
let edges = [ [ 0, 1 ], [ 0, 2 ],
[ 0, 3 ], [ 1, 4 ],
[ 1, 5 ], [ 4, 7 ],
[ 3, 6 ] ];
let v = 7;
// Values assigned to each vertex
let values = [ 1, 2, 3, 0,
0, 4, 3, 6 ];
// Constructing the tree
// using adjacency list
let adjl = constructTree(n, edges);
// Parent array
let parent = new Array(n);
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
parent[i] = 0;
}
// Store values in the parent array
DFS(adjl, parent, 0, -1);
// Add values of children to the parent
let valuesChildren = valuesFromChildren(
parent, values);
// Find sum of nodes lying in the path
let sum = findSumOfValues(
v, parent, valuesChildren);
// Add root node since
// its value is not included yet
sum += values[0];
document.write(sum);
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
16
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)