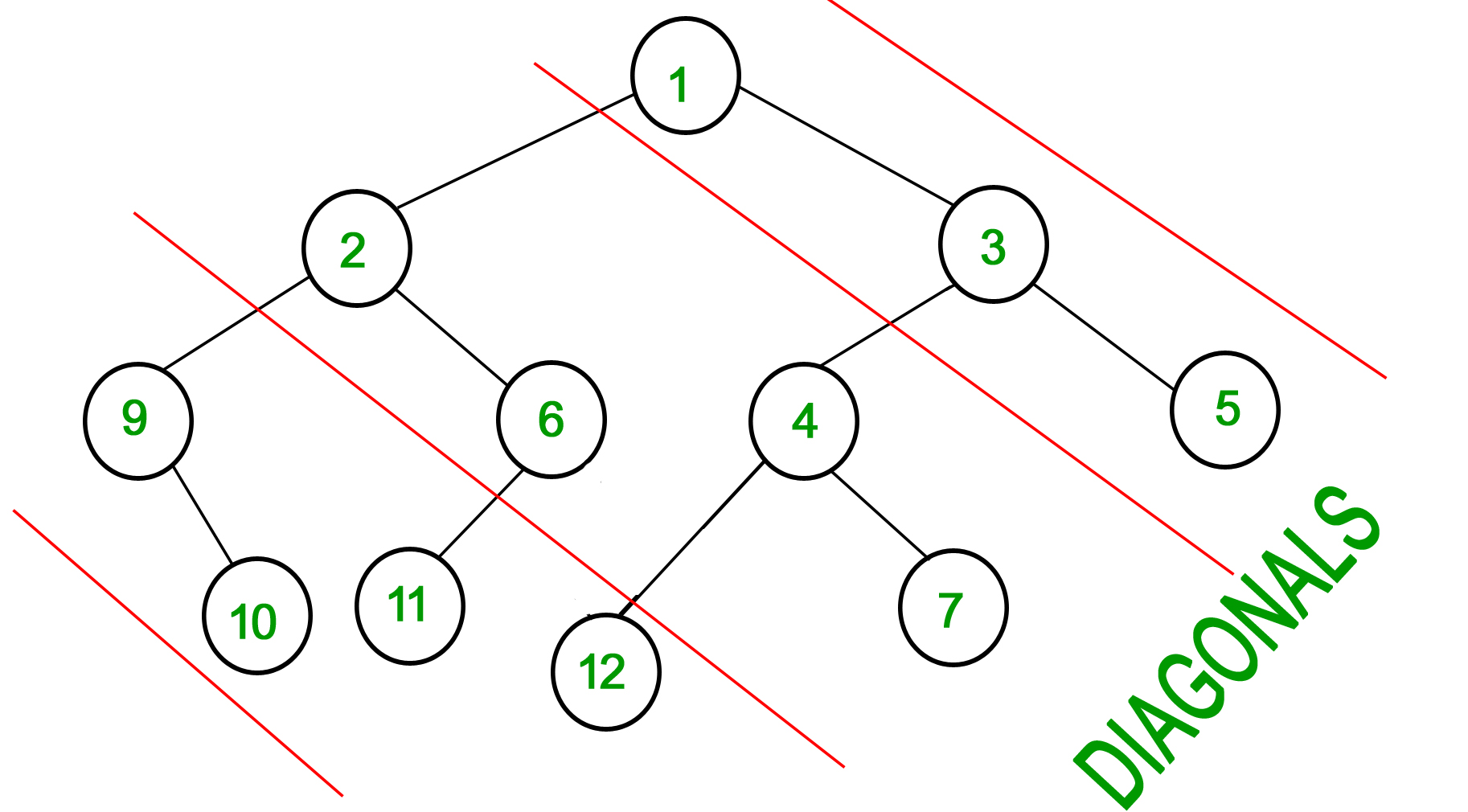
Considere las líneas de pendiente -1 que pasan entre los Nodes (líneas punteadas en el diagrama a continuación). La suma diagonal en un árbol binario es la suma de todos los datos de los Nodes que se encuentran entre estas líneas. Dado un árbol binario, imprima todas las sumas diagonales.
For the following input tree, the output should be 9, 19, 42. 9 is sum of 1, 3 and 5. 19 is sum of 2, 6, 4 and 7. 42 is sum of 9, 10, 11 and 12.
Algoritmo:
La idea es realizar un seguimiento de la distancia vertical desde la diagonal superior que pasa por la raíz. Incrementamos la distancia vertical que bajamos a la siguiente diagonal.
- Agregue raíz con distancia vertical como 0 a la cola.
- Procese la suma de todos los hijos derechos y los derechos del hijo derecho y así sucesivamente.
- Agregue el Node actual secundario izquierdo a la cola para su posterior procesamiento. La distancia vertical del hijo izquierdo es la distancia vertical del Node actual más 1.
- Siga haciendo el segundo, tercer y cuarto paso hasta que la cola esté vacía.
A continuación se muestra la implementación de la idea anterior.
C++
// C++ Program to find diagonal
// sum in a Binary Tree
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
};
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node* Node =
(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
Node->data = data;
Node->left = Node->right = NULL;
return Node;
}
// root - root of the binary tree
// vd - vertical distance diagonally
// diagonalSum - map to store Diagonal
// Sum(Passed by Reference)
void diagonalSumUtil(struct Node* root,
int vd, map<int, int> &diagonalSum)
{
if(!root)
return;
diagonalSum[vd] += root->data;
// increase the vertical distance if left child
diagonalSumUtil(root->left, vd + 1, diagonalSum);
// vertical distance remains same for right child
diagonalSumUtil(root->right, vd, diagonalSum);
}
// Function to calculate diagonal
// sum of given binary tree
void diagonalSum(struct Node* root)
{
// create a map to store Diagonal Sum
map<int, int> diagonalSum;
diagonalSumUtil(root, 0, diagonalSum);
map<int, int>::iterator it;
cout << "Diagonal sum in a binary tree is - ";
for(it = diagonalSum.begin();
it != diagonalSum.end(); ++it)
{
cout << it->second << " ";
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(9);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->left = newNode(4);
root->right->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left->right = newNode(7);
root->right->left->left = newNode(12);
root->left->right->left = newNode(11);
root->left->left->right = newNode(10);
diagonalSum(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Goel
Java
// Java Program to find diagonal sum in a Binary Tree
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
//Tree node
class TreeNode
{
int data; //node data
int vd; //vertical distance diagonally
TreeNode left, right; //left and right child's reference
// Tree node constructor
public TreeNode(int data)
{
this.data = data;
vd = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
left = right = null;
}
}
// Tree class
class Tree
{
TreeNode root;//Tree root
// Tree constructor
public Tree(TreeNode root) { this.root = root; }
// Diagonal sum method
public void diagonalSum()
{
// Queue which stores tree nodes
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
// Map to store sum of node's data lying diagonally
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
// Assign the root's vertical distance as 0.
root.vd = 0;
// Add root node to the queue
queue.add(root);
// Loop while the queue is not empty
while (!queue.isEmpty())
{
// Remove the front tree node from queue.
TreeNode curr = queue.remove();
// Get the vertical distance of the dequeued node.
int vd = curr.vd;
// Sum over this node's right-child, right-of-right-child
// and so on
while (curr != null)
{
int prevSum = (map.get(vd) == null)? 0: map.get(vd);
map.put(vd, prevSum + curr.data);
// If for any node the left child is not null add
// it to the queue for future processing.
if (curr.left != null)
{
curr.left.vd = vd+1;
queue.add(curr.left);
}
// Move to the current node's right child.
curr = curr.right;
}
}
// Make an entry set from map.
Set<Entry<Integer, Integer>> set = map.entrySet();
// Make an iterator
Iterator<Entry<Integer, Integer>> iterator = set.iterator();
// Traverse the map elements using the iterator.
System.out.print("Diagonal sum in a binary tree is - ");
while (iterator.hasNext())
{
Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> me = iterator.next();
System.out.print(me.getValue()+" ");
}
}
}
//Driver class
public class DiagonalSum
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(1);
root.left = new TreeNode(2);
root.right = new TreeNode(3);
root.left.left = new TreeNode(9);
root.left.right = new TreeNode(6);
root.right.left = new TreeNode(4);
root.right.right = new TreeNode(5);
root.right.left.left = new TreeNode(12);
root.right.left.right = new TreeNode(7);
root.left.right.left = new TreeNode(11);
root.left.left.right = new TreeNode(10);
Tree tree = new Tree(root);
tree.diagonalSum();
}
}
Python3
# Program to find diagonal sum in a Binary Tree
class newNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = self.right = None
# Function to compute height and
# root - root of the binary tree
# vd - vertical distance diagonally
# diagonalSum - map to store Diagonal
# Sum(Passed by Reference)
def diagonalSumUtil(root, vd, diagonalSum) :
if(not root):
return
if vd not in diagonalSum:
diagonalSum[vd] = 0
diagonalSum[vd] += root.data
# increase the vertical distance
# if left child
diagonalSumUtil(root.left, vd + 1,
diagonalSum)
# vertical distance remains same
# for right child
diagonalSumUtil(root.right, vd,
diagonalSum)
# Function to calculate diagonal
# sum of given binary tree
def diagonalSum(root) :
# create a map to store Diagonal Sum
diagonalSum = dict()
diagonalSumUtil(root, 0, diagonalSum)
print("Diagonal sum in a binary tree is - ",
end = "")
for it in diagonalSum:
print(diagonalSum[it], end = " ")
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(9)
root.left.right = newNode(6)
root.right.left = newNode(4)
root.right.right = newNode(5)
root.right.left.right = newNode(7)
root.right.left.left = newNode(12)
root.left.right.left = newNode(11)
root.left.left.right = newNode(10)
diagonalSum(root)
# This code is contributed
# by SHUBHAMSINGH10
C#
// C# Program to find diagonal sum in a Binary Tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// Tree node
public
class TreeNode
{
public
int data; // node data
public
int vd; // vertical distance diagonally
public
TreeNode left, right; // left and right child's reference
// Tree node constructor
public TreeNode(int data)
{
this.data = data;
vd = int.MaxValue;
left = right = null;
}
}
// Tree class
public class Tree
{
TreeNode root;//T ree root
// Tree constructor
public Tree(TreeNode root)
{
this.root = root;
}
// Diagonal sum method
public void diagonalSum()
{
// Queue which stores tree nodes
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new Queue<TreeNode>();
// Map to store sum of node's data lying diagonally
Dictionary<int, int> map = new Dictionary<int,int>();
// Assign the root's vertical distance as 0.
root.vd = 0;
// Add root node to the queue
queue.Enqueue(root);
// Loop while the queue is not empty
while (queue.Count != 0)
{
// Remove the front tree node from queue.
TreeNode curr = queue.Dequeue();
// Get the vertical distance of the dequeued node.
int vd = curr.vd;
// Sum over this node's right-child, right-of-right-child
// and so on
while (curr != null)
{
int prevSum;
if(!map.ContainsKey(vd))
prevSum = 0;
else
prevSum = map[vd];
if(map.ContainsKey(vd))
map[vd] = prevSum + curr.data;
else
map.Add(vd, prevSum + curr.data);
// If for any node the left child is not null add
// it to the queue for future processing.
if (curr.left != null)
{
curr.left.vd = vd + 1;
queue.Enqueue(curr.left);
}
// Move to the current node's right child.
curr = curr.right;
}
}
// Traverse the map elements using the iterator.
Console.Write("Diagonal sum in a binary tree is - ");
foreach(KeyValuePair<int, int> iterator in map)
{
// Map.Entry<int, int> me = iterator.next();
Console.Write(iterator.Value + " ");
}
}
}
// Driver class
public class DiagonalSum
{
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(1);
root.left = new TreeNode(2);
root.right = new TreeNode(3);
root.left.left = new TreeNode(9);
root.left.right = new TreeNode(6);
root.right.left = new TreeNode(4);
root.right.right = new TreeNode(5);
root.right.left.left = new TreeNode(12);
root.right.left.right = new TreeNode(7);
root.left.right.left = new TreeNode(11);
root.left.left.right = new TreeNode(10);
Tree tree = new Tree(root);
tree.diagonalSum();
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript Program to find diagonal
// sum in a Binary Tree
// Tree node
class TreeNode {
// Tree node constructor
constructor(data) {
this.data = data; // node data
this.vd = 2147483647; // vertical distance diagonally
this.left = null; // left and right child's reference
this.right = null;
}
}
// Tree class
class Tree {
// Tree constructor
constructor(root) {
this.root = root; //T ree root
}
// Diagonal sum method
diagonalSum() {
// Queue which stores tree nodes
var queue = [];
// Map to store sum of node's data lying diagonally
var map = {};
// Assign the root's vertical distance as 0.
this.root.vd = 0;
// Add root node to the queue
queue.push(this.root);
// Loop while the queue is not empty
while (queue.length != 0) {
// Remove the front tree node from queue.
var curr = queue.shift();
// Get the vertical distance of the dequeued node.
var vd = curr.vd;
// Sum over this node's right-child,
// right-of-right-child
// and so on
while (curr != null) {
var prevSum;
if (!map.hasOwnProperty(vd))
prevSum = 0;
else prevSum = map[vd];
if (map.hasOwnProperty(vd))
map[vd] = prevSum + curr.data;
else
map[vd] = prevSum + curr.data;
// If for any node the left child is not null add
// it to the queue for future processing.
if (curr.left != null) {
curr.left.vd = vd + 1;
queue.push(curr.left);
}
// Move to the current node's right child.
curr = curr.right;
}
}
// Traverse the map elements using the iterator.
document.write("Diagonal sum in a binary tree is - ");
for (const [key, value] of Object.entries(map)) {
// Map.Entry<int, int> me = iterator.next();
document.write(value + " ");
}
}
}
// Driver class
var root = new TreeNode(1);
root.left = new TreeNode(2);
root.right = new TreeNode(3);
root.left.left = new TreeNode(9);
root.left.right = new TreeNode(6);
root.right.left = new TreeNode(4);
root.right.right = new TreeNode(5);
root.right.left.left = new TreeNode(12);
root.right.left.right = new TreeNode(7);
root.left.right.left = new TreeNode(11);
root.left.left.right = new TreeNode(10);
var tree = new Tree(root);
tree.diagonalSum();
</script>
Diagonal sum in a binary tree is - 9 19 42
Complejidad de tiempo: O(n)
Como cada Node se visita una sola vez.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(h+d)
Aquí h es la altura del árbol y d es el número de diagonales. El espacio adicional es necesario para la pila de llamadas recursivas y para almacenar la suma diagonal en el mapa. En el peor de los casos (árbol sesgado a la izquierda), esto puede llegar hasta O(n).
Ejercicio:
Este problema era para diagonales de arriba a abajo y pendiente -1. Pruebe el mismo problema para la pendiente +1.
Método 2:
La idea detrás de este método está inspirada en la relación diagonal en arrays. Podemos observar que todos los elementos que se encuentran en la misma diagonal en una array tienen su diferencia de fila y columna igual. Por ejemplo, considere la diagonal principal en una array cuadrada, podemos observar que la diferencia de los índices de fila y columna respectivos de cada elemento en la diagonal es la misma, es decir, cada elemento en la diagonal principal tiene la diferencia de fila y columna 0, por ejemplo: 0-0, 1-1, 2-2,…nn.
Del mismo modo, cada diagonal tiene su propia diferencia única de filas y columnas, y con la ayuda de esto, podemos identificar cada elemento, a qué diagonal pertenece.
La misma idea se aplica para resolver este problema.
- Trataremos el nivel de los Nodes del árbol como sus índices de fila y el ancho de los Nodes del árbol como sus índices de columna.
- Denotaremos la celda de cada Node como (nivel, ancho)
Ejemplo- ( Tomando el mismo árbol que el anterior )
| Nodes | Índice de nivel | Índice de ancho |
|
1 |
0 | 0 |
|
2 |
1 | -1 |
|
3 |
1 | 1 |
|
4 |
2 | 0 |
|
5 |
2 | 2 |
|
6 |
2 | 0 |
|
7 |
3 | 1 |
|
9 |
2 | -2 |
|
10 |
3 | -1 |
|
11 |
3 | -1 |
|
12 |
3 | -1 |
Para ayudarlo a visualizar, dibujemos una array, la primera fila y la primera columna son índices respectivos de ancho y nivel.
| -2 |
-1 |
0 | 1 | 2 | |
| 0 | 1 | ||||
| 1 |
2 |
3 | |||
| 2 | 9 | 6+4 | 5 | ||
| 3 | 10+11+12 | 7 |
A continuación se muestra la implementación de la idea anterior:
C++
// C++ Program to calculate the
// sum of diagonal nodes.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Node Structure
struct Node {
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
// to map the node with level - index
map<int, int> grid;
// Function to create new node
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node* Node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
Node->data = data;
Node->left = Node->right = NULL;
return Node;
}
// recursvise function to calculate sum of elements
// where level - index is same.
void addConsideringGrid(Node* root, int level, int index)
{
// if there is no child then return
if (root == NULL)
return;
// add the element in the group of node
// whose level - index is equal
grid[level - index] += (root->data);
// left child call
addConsideringGrid(root->left, level + 1, index - 1);
// right child call
addConsideringGrid(root->right, level + 1, index + 1);
}
vector<int> diagonalSum(Node* root)
{
grid.clear();
// Function call
addConsideringGrid(root, 0, 0);
vector<int> ans;
// for different values of level - index
// add te sum of those node to answer
for (auto x : grid) {
ans.push_back(x.second);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// build binary tree
struct Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(9);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->left = newNode(4);
root->right->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left->right = newNode(7);
root->right->left->left = newNode(12);
root->left->right->left = newNode(11);
root->left->left->right = newNode(10);
// Function Call
vector<int> v = diagonalSum(root);
// print the diagonal sums
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
cout << v[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
Java
// Java Program to calculate the
// sum of diagonal nodes.
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Node Structure
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
};
// to map the node with level - index
static HashMap<Integer,Integer> grid = new HashMap<>();
// Function to create new node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node Node = new Node();
Node.data = data;
Node.left = Node.right = null;
return Node;
}
// recursvise function to calculate sum of elements
// where level - index is same.
static void addConsideringGrid(Node root, int level, int index)
{
// if there is no child then return
if (root == null)
return;
// add the element in the group of node
// whose level - index is equal
if(grid.containsKey(level-index))
grid.put(level - index,grid.get(level-index) + (root.data));
else
grid.put(level-index, root.data);
// left child call
addConsideringGrid(root.left, level + 1, index - 1);
// right child call
addConsideringGrid(root.right, level + 1, index + 1);
}
static Vector<Integer> diagonalSum(Node root)
{
grid.clear();
// Function call
addConsideringGrid(root, 0, 0);
Vector<Integer> ans = new Vector<>();
// for different values of level - index
// add te sum of those node to answer
for (Map.Entry<Integer,Integer> x : grid.entrySet())
{
ans.add(x.getValue());
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// build binary tree
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(9);
root.left.right = newNode(6);
root.right.left = newNode(4);
root.right.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left.right = newNode(7);
root.right.left.left = newNode(12);
root.left.right.left = newNode(11);
root.left.left.right = newNode(10);
// Function Call
Vector<Integer> v = diagonalSum(root);
// print the diagonal sums
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
System.out.print(v.get(i) + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji .
Python3
# Python3 program calculate the
# sum of diagonal nodes.
from collections import deque
# A binary tree node structure
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# To map the node with level - index
grid = {}
# Recursvise function to calculate
# sum of elements where level - index
# is same
def addConsideringGrid(root, level, index):
global grid
# If there is no child then return
if (root == None):
return
# Add the element in the group of node
# whose level - index is equal
grid[level - index] = (grid.get(level - index, 0) +
root.data)
# Left child call
addConsideringGrid(root.left, level + 1,
index - 1)
# Right child call
addConsideringGrid(root.right, level + 1,
index + 1)
def diagonalSum(root):
# grid.clear()
# Function call
addConsideringGrid(root, 0, 0)
ans = []
# For different values of level - index
# add te sum of those node to answer
for x in grid:
ans.append(grid[x])
return ans
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Build binary tree
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(9)
root.left.right = Node(6)
root.right.left = Node(4)
root.right.right = Node(5)
root.right.left.right = Node(7)
root.right.left.left = Node(12)
root.left.right.left = Node(11)
root.left.left.right = Node(10)
# Function Call
v = diagonalSum(root)
# Print the diagonal sums
for i in v:
print(i, end = " ")
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
// C# Program to calculate the
// sum of diagonal nodes.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
// Node Structure
public
class Node
{
public
int data;
public
Node left, right;
};
// to map the node with level - index
static Dictionary<int, int> grid = new Dictionary<int, int>();
// Function to create new node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node Node = new Node();
Node.data = data;
Node.left = Node.right = null;
return Node;
}
// recursvise function to calculate sum of elements
// where level - index is same.
static void addConsideringGrid(Node root, int level, int index)
{
// if there is no child then return
if (root == null)
return;
// add the element in the group of node
// whose level - index is equal
if(grid.ContainsKey(level - index))
grid[level - index] = grid[level - index] + (root.data);
else
grid.Add(level-index, root.data);
// left child call
addConsideringGrid(root.left, level + 1, index - 1);
// right child call
addConsideringGrid(root.right, level + 1, index + 1);
}
static List<int> diagonalSum(Node root)
{
grid.Clear();
// Function call
addConsideringGrid(root, 0, 0);
List<int> ans = new List<int>();
// for different values of level - index
// add te sum of those node to answer
foreach (KeyValuePair<int,int> x in grid)
{
ans.Add(x.Value);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// build binary tree
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(9);
root.left.right = newNode(6);
root.right.left = newNode(4);
root.right.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left.right = newNode(7);
root.right.left.left = newNode(12);
root.left.right.left = newNode(11);
root.left.left.right = newNode(10);
// Function Call
List<int> v = diagonalSum(root);
// print the diagonal sums
for (int i = 0; i < v.Count; i++)
Console.Write(v[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript Program to calculate the
// sum of diagonal nodes.
// Node Structure
class Node
{
// Function to create new node
constructor(data)
{
this.data=data;
this.left=null;
this.right=null;
}
}
// to map the node with level - index
let grid = new Map();
// recursvise function to calculate
// sum of elements
// where level - index is same.
function addConsideringGrid(root,level,index)
{
// if there is no child then return
if (root == null)
return;
// add the element in the group of node
// whose level - index is equal
if(grid.has(level-index))
{
grid.set(level - index,grid.get(level-index) +
(root.data));
}
else
{
grid.set(level-index, root.data);
}
// left child call
addConsideringGrid(root.left, level + 1, index - 1);
// right child call
addConsideringGrid(root.right, level + 1, index + 1);
}
function diagonalSum(root)
{
// Function call
addConsideringGrid(root, 0, 0);
let ans = [];
// for different values of level - index
// add te sum of those node to answer
for (let [key, value] of grid)
{
ans.push(value);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
// build binary tree
let root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(9);
root.left.right = new Node(6);
root.right.left = new Node(4);
root.right.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left.left = new Node(12);
root.left.right.left = new Node(11);
root.left.left.right = new Node(10);
// Function Call
let v = diagonalSum(root);
// print the diagonal sums
for (let i = 0; i < v.length; i++)
document.write(v[i] + " ");
// This code is contributed by unknown2108
</script>
9 19 42
Complejidad del tiempo- O(n)
Como cada Node se visita una sola vez.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(h+d)
Aquí h es la altura del árbol y d es el número de diagonales. El espacio adicional es necesario para la pila de llamadas recursivas y para almacenar la suma diagonal en el mapa. En el peor de los casos (árbol sesgado a la izquierda), esto puede llegar hasta O(n).
Método – 3
No es necesario usar el mapa para obtener espacio adicional.
espacio: o (n), cola utilizada para el elemento izquierdo del Node izquierdo para su procesamiento posterior
Complejidad del tiempo – o(n)
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Node Structure
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *left,*right;
};
// to map the node with level - index
// Function to create new node
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* node = new Node();
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
vector<int> diagonalSum(Node* root){
// list for storing diagonal sum
vector<int>list;
// list for processing diagonal left while traversing right
/*
1
2 3
4
1->3 while moving diagonally right
queue 2,4 // for processing later
*/
queue<Node*>Queue;
int sum = 0; // sum of digoanl element
int count = 0; // number of element in next diagonal
int last = 0; // Number of element left to traverse current diagonal
while(root != NULL)
{
if(root->left != NULL)
{ // queue left
Queue.push(root->left);
count++; // count of next diagonal elements
}
sum += root->data;
root = root->right; //move diagonally right
if(root == NULL){ // all element of diagonal is traversed
if(!Queue.empty()){ // check queue for processing any left
root = Queue.front();
Queue.pop();
}
if(last == 0){ // new diagonal sum , traversal of all element in current diagonal done or not
list.push_back(sum);
sum = 0;
last = count; // keep element in one diagonal
count = 0;
}
last--;
}
}
return list;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// build binary tree
Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(9);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->left = newNode(4);
root->right->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left->right = newNode(7);
root->right->left->left = newNode(12);
root->left->right->left = newNode(11);
root->left->left->right = newNode(10);
// Function Call
vector<int>v = diagonalSum(root);
// print the diagonal sums
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
// This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Node Structure
static class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
};
// to map the node with level - index
// Function to create new node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node Node = new Node();
Node.data = data;
Node.left = Node.right = null;
return Node;
}
public static ArrayList<Integer> diagonalSum(Node root)
{
// list for storing diagonal sum
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// list for processing diagonal left while
// traversing right
/*
1
2 3
4
1->3 while moving diagonally right
queue 2,4 // for processing later
*/
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
int sum = 0; // sum of digoanl element
int count = 0; // number of element in next diagonal
int last = 0; // Number of element left to traverse
// current diagonal
while (root != null) {
if (root.left != null) { // queue left
queue.add(root.left);
count++; // count of next diagonal elements
}
sum += root.data;
root = root.right; // move diagonally right
if (root == null) { // all element of diagonal
// is traversed
if (!queue.isEmpty()) { // check queue for
// processing any
// left
root = queue.poll();
}
if (last
== 0) { // new diagonal sum , traversal
// of all element in current
// diagonal done or not
list.add(sum);
sum = 0;
last = count; // keep element in one
// diagonal
count = 0;
}
last--;
}
}
return list;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// build binary tree
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(9);
root.left.right = newNode(6);
root.right.left = newNode(4);
root.right.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left.right = newNode(7);
root.right.left.left = newNode(12);
root.left.right.left = newNode(11);
root.left.left.right = newNode(10);
// Function Call
ArrayList<Integer> v = diagonalSum(root);
// print the diagonal sums
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
System.out.print(v.get(i) + " ");
}
}
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach from collections import deque # A binary tree node structure class Node: def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None def diagonalSum(root): # list for storing diagonal sum list = [] # list for processing diagonal left while # traversing right # # 1 # 2 3 # 4 # 1->3 while moving diagonally right # queue 2,4 // for processing later # queue = [] sum = 0 # sum of digoanl element count = 0 # number of element in next diagonal last = 0 # Number of element left to traverse # current diagonal while (root != None): if (root.left != None): # queue left queue.append(root.left) count += 1 # count of next diagonal elements sum += root.data root = root.right # move diagonally right if (root == None): # all element of diagonal # is traversed if (len(queue) != 0): # check queue for processing # any left root = queue.pop(0) if (last == 0): # new diagonal sum , traversal # of all element in current # diagonal done or not list.append(sum) sum = 0 last = count # keep element in one # diagonal count = 0 last -= 1 return list # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': # Build binary tree root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(9) root.left.right = Node(6) root.right.left = Node(4) root.right.right = Node(5) root.right.left.right = Node(7) root.right.left.left = Node(12) root.left.right.left = Node(11) root.left.left.right = Node(10) # Function Call v = diagonalSum(root) # Print the diagonal sums for i in v: print(i, end=" ") # This code is contributed by Abhijeet Kumar(abhijeet19403)
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG {
// Node Structure
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
};
// Function to create new node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node Node = new Node();
Node.data = data;
Node.left = Node.right = null;
return Node;
}
static List<int> diagonalSum(Node root)
{
// list for storing diagonal sum
List<int> list = new List<int>();
// list for processing diagonal left while
// traversing right
/*
1
2 3
4
1->3 while moving diagonally right
queue 2,4 // for processing later
*/
Queue<Node> queue = new Queue<Node>();
int sum = 0; // sum of digoanl element
int count = 0; // number of element in next diagonal
int last = 0; // Number of element left to traverse
// current diagonal
while (root != null) {
if (root.left != null) { // queue left
queue.Enqueue(root.left);
count++; // count of next diagonal elements
}
sum += root.data;
root = root.right; // move diagonally right
if (root == null) { // all element of diagonal
// is traversed
if (queue.Count
!= 0) { // check queue for processing
// any left
root = queue.Dequeue();
}
if (last
== 0) { // new diagonal sum , traversal
// of all element in current
// diagonal done or not
list.Add(sum);
sum = 0;
last = count; // keep element in one
// diagonal
count = 0;
}
last--;
}
}
return list;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// build binary tree
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(9);
root.left.right = newNode(6);
root.right.left = newNode(4);
root.right.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left.right = newNode(7);
root.right.left.left = newNode(12);
root.left.right.left = newNode(11);
root.left.left.right = newNode(10);
// Function Call
List<int> v = diagonalSum(root);
// print the diagonal sums
for (int i = 0; i < v.Count; i++)
Console.Write(v[i] + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Abhijeet Kumar(abhijeet19403)
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program for the above approach
// Node Structure
class Node
{
constructor(data = 0,left = null,right = null){
this.data = data;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
// to map the node with level - index
// Function to create new node
function newNode(data)
{
let node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = node.right = null;
return node;
}
function diagonalSum(root){
// list for storing diagonal sum
let list = [];
// list for processing diagonal left while traversing right
/*
1
2 3
4
1.3 while moving diagonally right
queue 2,4 // for processing later
*/
let Queue = [];
let sum = 0; // sum of digoanl element
let count = 0; // number of element in next diagonal
let last = 0; // Number of element left to traverse current diagonal
while(root != null)
{
if(root.left != null)
{ // queue left
Queue.push(root.left);
count++; // count of next diagonal elements
}
sum += root.data;
root = root.right; //move diagonally right
if(root == null){ // all element of diagonal is traversed
if(Queue.length > 0){ // check queue for processing any left
root = Queue.shift();
}
if(last == 0){ // new diagonal sum , traversal of all element in current diagonal done or not
list.push(sum);
sum = 0;
last = count; // keep element in one diagonal
count = 0;
}
last--;
}
}
return list;
}
// Driver code
// build binary tree
let root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(9);
root.left.right = newNode(6);
root.right.left = newNode(4);
root.right.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left.right = newNode(7);
root.right.left.left = newNode(12);
root.left.right.left = newNode(11);
root.left.left.right = newNode(10);
// Function Call
let v = diagonalSum(root);
// print the diagonal sums
for (let i = 0; i < v.length; i++)
document.write(v[i] + " ");
// This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
</script>
9 19 42
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA