Dado un árbol N-ario con un valor asociado con cada Node, la tarea es elegir un subconjunto de estos Nodes de tal manera que la suma de los Nodes elegidos sea máxima bajo la restricción de que no se deben conectar directamente dos Nodes elegidos en el subconjunto, es decir, si hemos tomado un Node en nuestra suma, entonces no podemos tomar en consideración a sus hijos y viceversa.
Ejemplos:
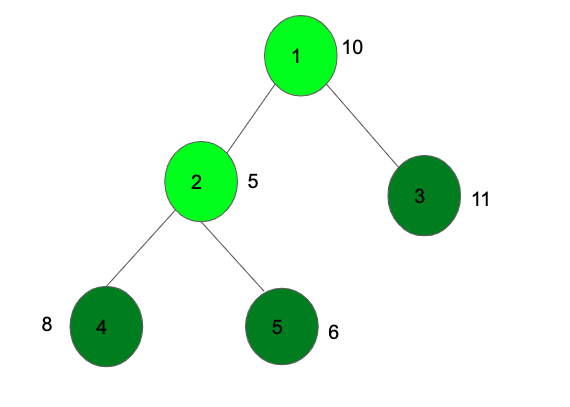
El diagrama anterior selecciona los Nodes con un color verde intenso para obtener el valor máximo 25.
En la publicación anterior se ha discutido un enfoque para este problema usando recursividad .
En esta publicación, discutiremos un enfoque que utiliza la programación dinámica en árboles .
Mientras se resuelve el problema, se presentan dos casos:
- Para un Node en particular, la suma máxima se puede calcular incluyendo el propio Node junto con los Nodes de su subárbol.
- O bien, la suma máxima se calcula excluyendo el Node actual e incluyendo solo los Nodes de su subárbol.
Supongamos :
- dp1[Node] para que sea la suma máxima posible eligiendo Nodes del subárbol de este Node y también incluyendo el Node.
- Y, dp2[Node] para ser la suma máxima posible eligiendo Nodes del subárbol del Node y sin incluir el Node en sí.
En el primer caso, si incluimos el Node actual, entonces se agrega su valor y luego no podemos incluir ninguno de sus hijos inmediatos, por lo tanto, la suma de dp2[] de todos los hijos se tomará en cuenta para calcular dp1[ Node]. Eso es,
dp1[Node] = árbol[Node] + sum(dp2[hijos1], dp2[hijos2], …)
En el segundo caso, si no incluimos el Node actual, entonces no se suma su valor, pero se puede tomar el Node hijo o no tomarlo, por lo que se tendrá en cuenta la suma del máximo de ambos para todos los hijos. contar para calcular dp2[Node]. Eso es,
dp2[Node] = árbol[Node] + sum(max(dp1[hijos1], dp2[hijos1]), max(dp1[hijos2], dp2[hijos2])…)
Al final, la respuesta final será el máximo de dp1[raíz] y dp2[raíz].
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to find maximum sum
// of a subset of nodes that are not adjacent
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find the diameter of the tree
// using Dynamic Programming
void dfs(int node, int parent, int dp1[], int dp2[],
list<int>* adj, int tree[])
{
int sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;
// Traverse for all children of node
for (auto i = adj[node].begin(); i != adj[node].end(); ++i) {
if (*i == parent)
continue;
// Call DFS function again
dfs(*i, node, dp1, dp2, adj, tree);
// Include the current node
// then donot include the children
sum1 += dp2[*i];
// Donot include current node,
// then include children or not include them
sum2 += max(dp1[*i], dp2[*i]);
}
// Recurrence value
dp1[node] = tree[node] + sum1;
dp2[node] = sum2;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
int n = 5;
/* Constructed tree is
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5 */
list<int>* adj = new list<int>[n + 1];
/* create undirected edges */
adj[1].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(1);
adj[1].push_back(3);
adj[3].push_back(1);
adj[2].push_back(4);
adj[4].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(5);
adj[5].push_back(2);
// Numbers to node
int tree[n + 1];
tree[1] = 10;
tree[2] = 5;
tree[3] = 11;
tree[4] = 6;
tree[5] = 8;
int dp1[n + 1], dp2[n + 1];
memset(dp1, 0, sizeof dp1);
memset(dp2, 0, sizeof dp2);
dfs(1, 1, dp1, dp2, adj, tree);
// Find maximum sum by calling function
cout << "Maximum sum: "
<< max(dp1[1], dp2[1]) << endl;
return 0;
}
Python3
# Python3 program to find
# maximum sum of a subset
# of nodes that are not
# adjacent
# Function to find the diameter
# of the tree using Dynamic
# Programming
def dfs(node, parent, dp1,
dp2, adj, tree):
sum1 = 0
sum2 = 0
# Traverse for all
# children of node
for i in adj[node]:
if (i == parent):
continue;
# Call DFS function
# again
dfs(i, node, dp1,
dp2, adj, tree);
# Include the current
# node then donot include
# the children
sum1 += dp2[i];
# Donot include current node,
# then include children or not
# include them
sum2 += max(dp1[i],
dp2[i]);
# Recurrence value
dp1[node] = tree[node] + sum1;
dp2[node] = sum2;
# Driver code
if __name__=="__main__":
n = 5;
''' Constructed tree is
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5 '''
adj = [[] for i in range(n + 1)]
# create undirected edges
adj[1].append(2);
adj[2].append(1);
adj[1].append(3);
adj[3].append(1);
adj[2].append(4);
adj[4].append(2);
adj[2].append(5);
adj[5].append(2);
# Numbers to node
tree = [0 for i in range(n + 1)];
tree[1] = 10;
tree[2] = 5;
tree[3] = 11;
tree[4] = 6;
tree[5] = 8;
dp1 = [0 for i in range(n + 1)];
dp2 = [0 for i in range(n + 1)];
dfs(1, 1, dp1, dp2, adj, tree);
# Find maximum sum by calling
# function
print("Maximum sum:",
max(dp1[1], dp2[1]))
# This code is contributed by Rutvik_56
C#
// C# program to find maximum sum
// of a subset of nodes that are not adjacent
using System;
using System.Collections;
class GFG
{
// Function to find the diameter of the tree
// using Dynamic Programming
public static void dfs(int node, int parent, int []dp1, int []dp2,
ArrayList []adj, int []tree)
{
int sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;
// Traverse for all children of node
foreach(int i in adj[node])
{
if (i == parent)
continue;
// Call DFS function again
dfs(i, node, dp1, dp2, adj, tree);
// Include the current node
// then donot include the children
sum1 += dp2[i];
// Donot include current node,
// then include children or not include them
sum2 += Math.Max(dp1[i], dp2[i]);
}
// Recurrence value
dp1[node] = tree[node] + sum1;
dp2[node] = sum2;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void Main(string []arg)
{
int n = 5;
/* Constructed tree is
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5 */
ArrayList []adj = new ArrayList[n + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
{
adj[i] = new ArrayList();
}
/* create undirected edges */
adj[1].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(1);
adj[1].Add(3);
adj[3].Add(1);
adj[2].Add(4);
adj[4].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(5);
adj[5].Add(2);
// Numbers to node
int []tree = new int[n + 1];
tree[1] = 10;
tree[2] = 5;
tree[3] = 11;
tree[4] = 6;
tree[5] = 8;
int []dp1 = new int[n + 1];
int []dp2 = new int[n + 1];
Array.Fill(dp1, 0);
Array.Fill(dp2, 0);
dfs(1, 1, dp1, dp2, adj, tree);
// Find maximum sum by calling function
Console.Write("Maximum sum: "+ Math.Max(dp1[1], dp2[1]));
}
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76
Javascript
<script>
// Python3 program to find
// maximum sum of a subset
// of nodes that are not
// adjacent
// Function to find the diameter
// of the tree using Dynamic
// Programming
function dfs(node, parent, dp1,dp2, adj, tree){
let sum1 = 0
let sum2 = 0
// Traverse for all
// children of node
for(let i of adj[node]){
if (i == parent)
continue;
// Call DFS function
// again
dfs(i, node, dp1,
dp2, adj, tree);
// Include the current
// node then donot include
// the children
sum1 += dp2[i];
// Donot include current node,
// then include children or not
// include them
sum2 += Math.max(dp1[i],
dp2[i]);
}
// Recurrence value
dp1[node] = tree[node] + sum1;
dp2[node] = sum2;
}
// Driver code
let n = 5;
// Constructed tree is
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \
// 4 5
let adj = new Array(n+1);
for(let i=0;i<n+1;i++){
adj[i] = new Array();
}
// create undirected edges
adj[1].push(2);
adj[2].push(1);
adj[1].push(3);
adj[3].push(1);
adj[2].push(4);
adj[4].push(2);
adj[2].push(5);
adj[5].push(2);
// Numbers to node
let tree = new Array(n+1).fill(0);
tree[1] = 10;
tree[2] = 5;
tree[3] = 11;
tree[4] = 6;
tree[5] = 8;
let dp1 = new Array(n+1).fill(0);
let dp2 = new Array(n+1).fill(0);
dfs(1, 1, dp1, dp2, adj, tree);
// Find maximum sum by calling
// function
document.write("Maximum sum: ", Math.max(dp1[1], dp2[1]),"</br>")
// This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
</script>
Maximum sum: 25
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N), ya que estamos usando la recursividad para recorrer el árbol. Donde N es el número de Nodes en el árbol.
Espacio auxiliar: O(N), ya que estamos usando espacio adicional para el arreglo dp.