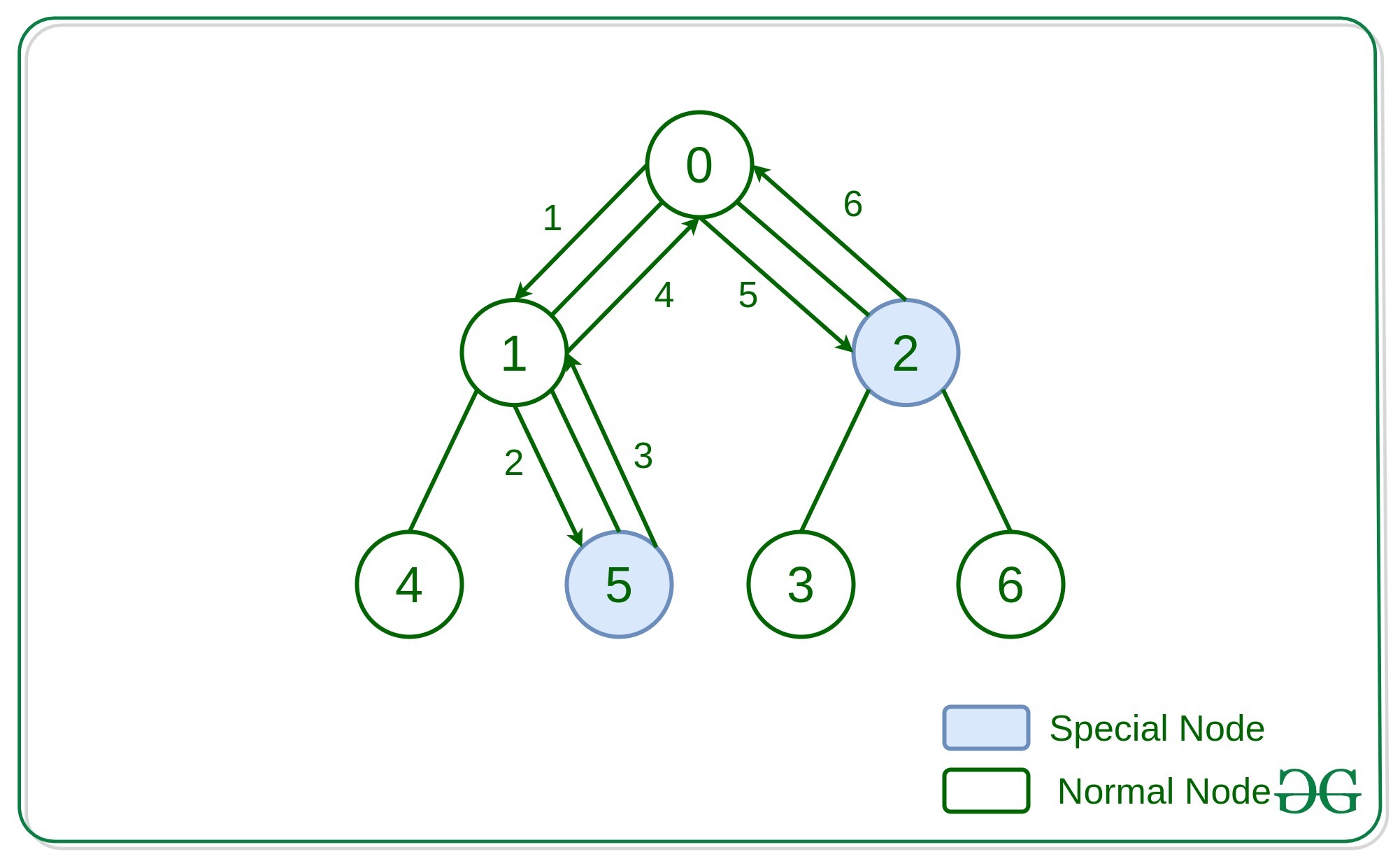
Dado un árbol no dirigido que consta de N vértices donde algunos de los Nodes son Nodes especiales, la tarea es visitar todos los Nodes especiales desde el Node raíz en un tiempo mínimo. El tiempo para viajar de un Node a otro se puede asumir como unidad de tiempo.
Un Node es especial si la ruta desde la raíz hasta el Node consta de Nodes de valores distintos.
Ejemplo:
Entrada: N = 7, bordes[] = {(0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 3), (2, 6)}
esEspecial[] = {falso, falso, verdadero, falso, verdadero, verdadero, falso}
Salida: 8
Explicación:
Entrada: N = 7, bordes[] = {(0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 3), (2, 6)}
esEspecial[] = {falso, falso, verdadero, falso, falso, verdadero, falso}
Salida: 6
Explicación:
Enfoque: la idea es utilizar el recorrido de búsqueda en profundidad primero y recorrer los Nodes. Si algún Node tiene un hijo que es un Node especial, agregue dos a los pasos requeridos para ese Node. También marque ese Node como un Node especial de modo que al subir los pasos se tengan en cuenta.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation to find
// the minimum time required to
// visit special nodes of a tree
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100005;
// Time required to collect
vector<int> ans(N, 0);
vector<int> flag(N, 0);
// Minimum time required to reach
// all the special nodes of tree
void minimumTime(int u, int par,
vector<bool>& hasApple,
vector<int> adj[])
{
// Condition to check if
// the vertex has apple
if (hasApple[u] == true)
flag[u] = 1;
// Iterate all the
// adjacent of vertex u.
for (auto it : adj[u]) {
// if adjacent vertex
// is it's parent
if (it != par) {
minimumTime(it, u, hasApple, adj);
// if any vertex of subtree
// it contain apple
if (flag[it] > 0)
ans[u] += (ans[it] + 2);
// flagbit for node u
// would be on if any vertex
// in it's subtree contain apple
flag[u] |= flag[it];
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Number of the vertex.
int n = 7;
vector<bool> hasApple{ false, false,
true, false,
true, true,
false };
// Store all the edges,
// any edge represented
// by pair of vertex
vector<pair<int, int> > edges;
// Added all the
// edge in edges vector.
edges.push_back(make_pair(0, 1));
edges.push_back(make_pair(0, 2));
edges.push_back(make_pair(1, 4));
edges.push_back(make_pair(1, 5));
edges.push_back(make_pair(2, 3));
edges.push_back(make_pair(2, 6));
// Adjacent list
vector<int> adj[n];
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++) {
int source_node = edges[i].first;
int destination_node
= edges[i].second;
adj[source_node]
.push_back(destination_node);
adj[destination_node]
.push_back(source_node);
}
// Function Call
minimumTime(0, -1, hasApple, adj);
cout << ans[0];
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation to find
// the minimum time required to
// visit special nodes of a tree
import java.util.*;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
class GFG{
static class pair
{
int first, second;
pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
static final int N = 100005;
// Time required to collect
static ArrayList ans;
static ArrayList flag;
// Minimum time required to reach
// all the special nodes of tree
static void minimumTime(int u, int par,
ArrayList hasApple,
ArrayList adj[])
{
// Condition to check if
// the vertex has apple
if ((boolean)hasApple.get(u) == true)
flag.set(u, 1);
// Iterate all the
// adjacent of vertex u.
for(int it : (ArrayList<Integer>)adj[u])
{
// If adjacent vertex
// is it's parent
if (it != par)
{
minimumTime(it, u, hasApple, adj);
// If any vertex of subtree
// it contain apple
if ((int)flag.get(it) > 0)
ans.set(u, (int)ans.get(u) +
(int)ans.get(it) + 2 );
// flagbit for node u
// would be on if any vertex
// in it's subtree contain apple
flag.set(u, (int)flag.get(u) |
(int)flag.get(it));
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String []args)
{
// Number of the vertex.
int n = 7;
ans = new ArrayList();
flag = new ArrayList();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
ans.add(0);
flag.add(0);
}
ArrayList hasApple = new ArrayList();
hasApple.add(false);
hasApple.add(false);
hasApple.add(true);
hasApple.add(false);
hasApple.add(true);
hasApple.add(true);
hasApple.add(false);
// Store all the edges,
// any edge represented
// by pair of vertex
ArrayList edges = new ArrayList();
// Added all the edge in
// edges vector.
edges.add(new pair(0, 1));
edges.add(new pair(0, 2));
edges.add(new pair(1, 4));
edges.add(new pair(1, 5));
edges.add(new pair(2, 3));
edges.add(new pair(2, 6));
// Adjacent list
ArrayList []adj = new ArrayList[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
adj[i] = new ArrayList();
}
for(int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++)
{
int source_node = ((pair)edges.get(i)).first;
int destination_node = ((pair)edges.get(i)).second;
adj[source_node].add(destination_node);
adj[destination_node].add(source_node);
}
// Function Call
minimumTime(0, -1, hasApple, adj);
System.out.print(ans.get(0));
}
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76
Python3
# Python3 implementation to find # the minimum time required to # visit special nodes of a tree N = 100005 # Time required to collect ans = [0 for i in range(N)] flag = [0 for i in range(N)] # Minimum time required to reach # all the special nodes of tree def minimumTime(u, par, hasApple, adj): # Condition to check if # the vertex has apple if (hasApple[u] == True): flag[u] = 1 # Iterate all the # adjacent of vertex u. for it in adj[u]: # if adjacent vertex # is it's parent if (it != par): minimumTime(it, u, hasApple, adj) # if any vertex of subtree # it contain apple if (flag[it] > 0): ans[u] += (ans[it] + 2) # flagbit for node u # would be on if any vertex # in it's subtree contain apple flag[u] |= flag[it] # Driver Code if __name__=='__main__': # Number of the vertex. n = 7 hasApple = [ False, False, True, False, True, True, False ] # Store all the edges, # any edge represented # by pair of vertex edges = [] # Added all the # edge in edges vector. edges.append([0, 1]) edges.append([0, 2]) edges.append([1, 4]) edges.append([1, 5]) edges.append([2, 3]) edges.append([2, 6]) # Adjacent list adj = [[] for i in range(n)] for i in range(len(edges)): source_node = edges[i][0] destination_node = edges[i][1] adj[source_node].append(destination_node) adj[destination_node].append(source_node) # Function Call minimumTime(0, -1, hasApple, adj); print(ans[0]) # This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C#
// C# implementation to find
// the minimum time required to
// visit special nodes of a tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
static int N = 100005;
// Time required to collect
static int[] ans = new int[N];
static int[] flag = new int[N];
// Minimum time required to reach
// all the special nodes of tree
static void minimumTime(int u, int par,
List<bool> hasApple,
List<List<int>> adj)
{
// Condition to check if
// the vertex has apple
if (hasApple[u])
flag[u] = 1;
// Iterate all the
// adjacent of vertex u.
for(int it = 0; it < adj[u].Count; it++)
{
// If adjacent vertex
// is it's parent
if (adj[u][it] != par)
{
minimumTime(adj[u][it], u, hasApple, adj);
// If any vertex of subtree
// it contain apple
if (flag[adj[u][it]] > 0)
ans[u] = ans[u] + ans[adj[u][it]] + 2 ;
// flagbit for node u
// would be on if any vertex
// in it's subtree contain apple
flag[u] = flag[u] | flag[adj[u][it]];
}
}
}
static void Main() {
// Number of the vertex.
int n = 7;
List<bool> hasApple = new List<bool>();
hasApple.Add(false);
hasApple.Add(false);
hasApple.Add(true);
hasApple.Add(false);
hasApple.Add(true);
hasApple.Add(true);
hasApple.Add(false);
// Store all the edges,
// any edge represented
// by pair of vertex
List<Tuple<int,int>> edges = new List<Tuple<int,int>>();
// Added all the edge in
// edges vector.
edges.Add(new Tuple<int,int>(0, 1));
edges.Add(new Tuple<int,int>(0, 2));
edges.Add(new Tuple<int,int>(1, 4));
edges.Add(new Tuple<int,int>(1, 5));
edges.Add(new Tuple<int,int>(2, 3));
edges.Add(new Tuple<int,int>(2, 6));
// Adjacent list
List<List<int>> adj = new List<List<int>>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
adj.Add(new List<int>());
}
for(int i = 0; i < edges.Count; i++)
{
int source_node = edges[i].Item1;
int destination_node = edges[i].Item2;
adj[source_node].Add(destination_node);
adj[destination_node].Add(source_node);
}
// Function Call
minimumTime(0, -1, hasApple, adj);
Console.Write(ans[0]);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript implementation to find
// the minimum time required to
// visit special nodes of a tree
let N = 100005;
// Time required to collect
let ans = [];
let flag = [];
// Minimum time required to reach
// all the special nodes of tree
function minimumTime(u, par, hasApple, adj)
{
// Condition to check if
// the vertex has apple
if (hasApple[u] == true)
flag[u] = 1;
// Iterate all the
// adjacent of vertex u.
for(let it = 0; it < adj[u].length; it++)
{
// If adjacent vertex
// is it's parent
if (adj[u][it] != par)
{
minimumTime(adj[u][it], u, hasApple, adj);
// If any vertex of subtree
// it contain apple
if (flag[adj[u][it]] > 0)
ans[u] = ans[u] + ans[adj[u][it]] + 2 ;
// flagbit for node u
// would be on if any vertex
// in it's subtree contain apple
flag[u] = flag[u] | flag[adj[u][it]];
}
}
}
// Number of the vertex.
let n = 7;
ans = [];
flag = [];
for(let i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
ans.push(0);
flag.push(0);
}
let hasApple = [];
hasApple.push(false);
hasApple.push(false);
hasApple.push(true);
hasApple.push(false);
hasApple.push(true);
hasApple.push(true);
hasApple.push(false);
// Store all the edges,
// any edge represented
// by pair of vertex
let edges = [];
// Added all the edge in
// edges vector.
edges.push([0, 1]);
edges.push([0, 2]);
edges.push([1, 4]);
edges.push([1, 5]);
edges.push([2, 3]);
edges.push([2, 6]);
// Adjacent list
let adj = new Array(n);
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
adj[i] = [];
}
for(let i = 0; i < edges.length; i++)
{
let source_node = edges[i][0];
let destination_node = edges[i][1];
adj[source_node].push(destination_node);
adj[destination_node].push(source_node);
}
// Function Call
minimumTime(0, -1, hasApple, adj);
document.write(ans[0]);
</script>
8
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por ghoshashis545 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA