Dada una ruta de string que consiste en los caracteres ‘N’, ‘S’, ‘E’ y ‘W’ que denotan 1 unidad de movimiento en las direcciones Norte, Sur, Este y Oeste respectivamente, la tarea es encontrar el tiempo necesario para recorrer la ruta completa. camino que comienza desde el origen, si toma 2 y 1 minutos para viajar en un segmento no visitado y visitado respectivamente.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: ruta = «NNES»
Salida: 8Explicación: Dado que cada segmento se visita solo una vez, costo = 2 * 4 = 8.
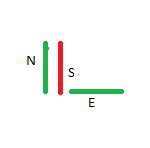
Entrada: ruta = “NSE”
Salida: 5Explicación:
Paso 1: Viaje al norte. Tiempo empleado = 2 minutos.
Paso 2: viaje hacia el sur en ese mismo segmento visitado. Tiempo empleado = 1 minuto.
Paso 3: viaje hacia el este. Tiempo empleado = 2 minutos. Por lo tanto, el tiempo total empleado = 2 + 1 + 2 = 5.
Planteamiento: La idea es usar un Set para almacenar todos los segmentos visitados y antes de visitar cada segmento, verificar si está presente en el Set o no. Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema.
- Inicialice un conjunto s para almacenar un par de enteros. El conjunto almacenará todos los segmentos visitados.
- Inicialice dos enteros x = 0 e y = 0 que denotan la posición actual. Además, inicialice una variable time = 0 para almacenar el tiempo total necesario para recorrer la ruta completa.
- Atraviesa la cuerda y sigue los pasos a continuación.
- Inicialice dos enteros p y q en x e y respectivamente.
- Si path[i] es igual a ‘N’ incrementa y , de lo contrario si path[i] es igual a ‘S’ decrementa y, de lo contrario si path[i] es igual a ‘E’ incrementa x , de lo contrario decrementa x .
- Compruebe si el segmento { p + x , q + y } existe en el conjunto o no . si suma 1 al valor del tiempo , de lo contrario, suma 2 al valor del tiempo.
- Inserta el segmento { p + x , q + y } en el conjunto.
- Después de completar los pasos anteriores, imprima el valor del tiempo.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior.
C++
// C++ code for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to calculate time
// taken to travel the path
void calcTotalTime(string path)
{
// Stores total time
int time = 0;
// Initial position
int x = 0, y = 0;
// Stores visited segments
set<pair<int, int> > s;
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); i++) {
int p = x;
int q = y;
if (path[i] == 'N')
y++;
else if (path[i] == 'S')
y--;
else if (path[i] == 'E')
x++;
else if (path[i] == 'W')
x--;
// Check whether segment
// is present in the set
if (s.find({ p + x, q + y })
== s.end()) {
// Increment the value
// of time by 2
time += 2;
// Insert segment into the set
s.insert({ p + x, q + y });
}
else
time += 1;
}
// Print the value
// of time
cout << time << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
string path = "NSE";
calcTotalTime(path);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to calculate time
// taken to travel the path
static void calcTotalTime(String path)
{
// Stores total time
int time = 0;
// Initial position
int x = 0, y = 0;
// Stores visited segments
Set<String> s = new HashSet<>();
for(int i = 0; i < path.length(); i++)
{
int p = x;
int q = y;
if (path.charAt(i) == 'N')
y++;
else if (path.charAt(i) == 'S')
y--;
else if (path.charAt(i) == 'E')
x++;
else if (path.charAt(i) == 'W')
x--;
// Check whether segment
// is present in the set
String o = (p + x) + " " + (q + y);
if (!s.contains(o))
{
// Increment the value
// of time by 2
time += 2;
// Insert segment into the set
s.add(o);
}
else
time += 1;
}
// Print the value
// of time
System.out.println(time);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String path = "NSE";
calcTotalTime(path);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Hritik
Python3
# Python 3 code for the above approach # Function to calculate time # taken to travel the path def calcTotalTime(path): # Stores total time time = 0 # Initial position x = 0 y = 0 # Stores visited segments s = set([]) for i in range(len(path)): p = x q = y if (path[i] == 'N'): y += 1 elif (path[i] == 'S'): y -= 1 elif (path[i] == 'E'): x += 1 elif (path[i] == 'W'): x -= 1 # Check whether segment # is present in the set if (p + x, q + y) not in s: # Increment the value # of time by 2 time += 2 # Insert segment into the set s.add((p + x, q + y)) else: time += 1 # Print the value # of time print(time) # Driver Code if __name__ == "__main__": path = "NSE" calcTotalTime(path) # This code is contributed by ukasp.
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Function to calculate time
// taken to travel the path
static void calcTotalTime(string path)
{
// Stores total time
int time = 0;
// Initial position
int x = 0, y = 0;
// Stores visited segments
HashSet<string> s = new HashSet<string>();
for(int i = 0; i < path.Length; i++)
{
int p = x;
int q = y;
if (path[i] == 'N')
y++;
else if (path[i] == 'S')
y--;
else if (path[i] == 'E')
x++;
else if (path[i] == 'W')
x--;
// Check whether segment
// is present in the set
string o = (p + x) + " " + (q + y);
if (s.Contains(o) == false)
{
// Increment the value
// of time by 2
time += 2;
// Insert segment into the set
s.Add(o);
}
else
time += 1;
}
// Print the value
// of time
Console.Write(time);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
string path = "NSE";
calcTotalTime(path);
}
}
// This code is contributed by bgangwar59
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript code for the above approach
// Function to calculate time
// taken to travel the path
function calcTotalTime(path)
{
// Stores total time
var time = 0;
// Initial position
var x = 0, y = 0;
// Stores visited segments
var s = new Set();
for(var i = 0; i < path.length; i++)
{
var p = x;
var q = y;
if (path[i] == 'N')
y++;
else if (path[i] == 'S')
y--;
else if (path[i] == 'E')
x++;
else if (path[i] == 'W')
x--;
// Check whether segment
// is present in the set
if (!s.has([p + x, q + y].toString()))
{
// Increment the value
// of time by 2
time += 2;
// Insert segment into the set
s.add([p + x, q + y].toString());
}
else
time += 1;
}
// Print the value
// of time
document.write(time)
}
// Driver Code
var path = "NSE";
calcTotalTime(path);
</script>
5
Complejidad temporal: O(NlogN)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por pawanharwani11 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA