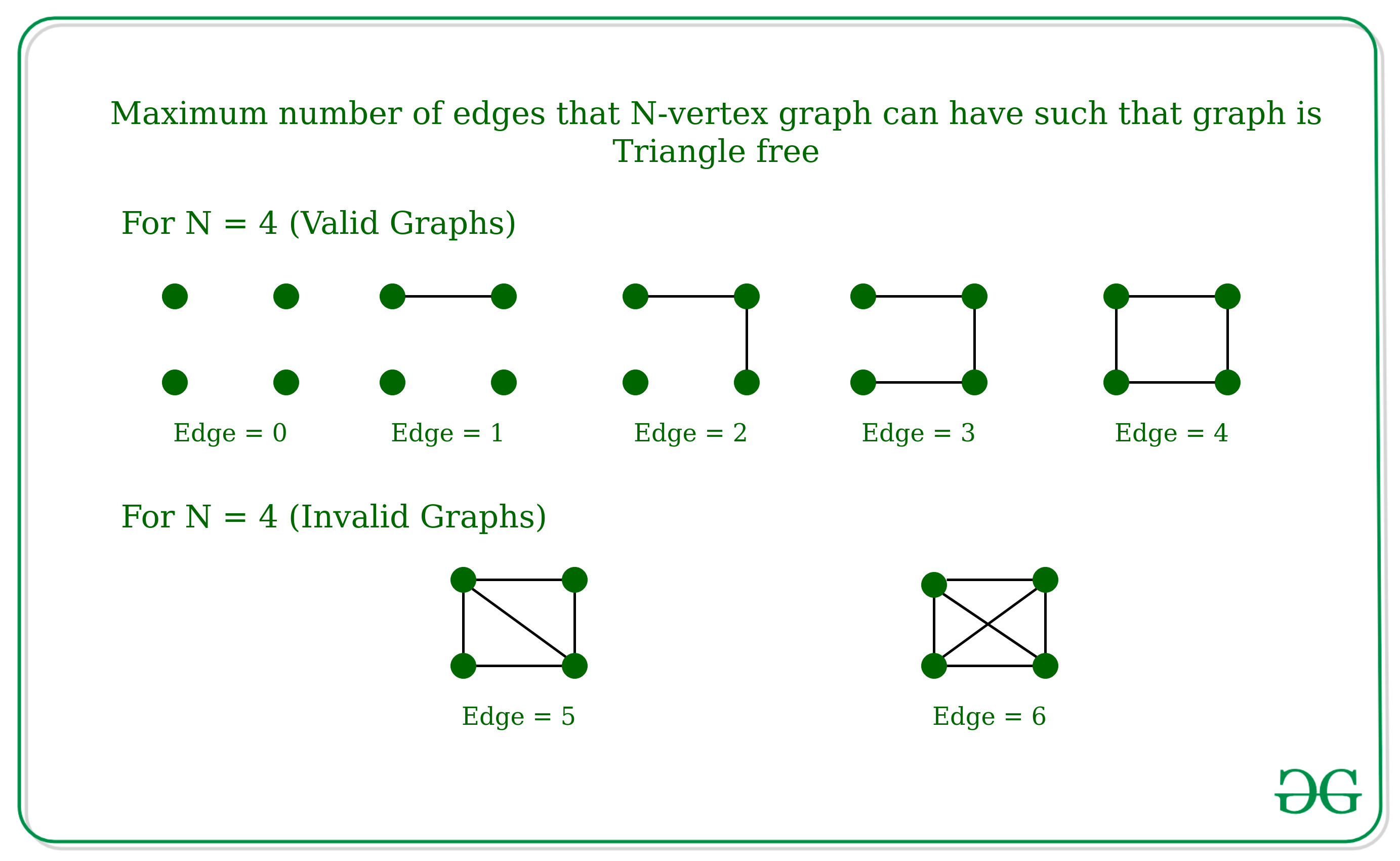
Dado un número N , que es el número de Nodes en un gráfico, la tarea es encontrar el número máximo de aristas que puede tener un gráfico de N vértices de modo que el gráfico no tenga triángulos (lo que significa que no debe haber tres aristas A, B, C en el gráfico tal que A está conectado a B, B está conectado a C y C está conectado a A). El gráfico no puede contener un bucle automático o varios bordes.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 4
Salida: 4
Explicación:
Entrada: N = 3
Salida: 2
Explicación:
Si hay tres aristas en un gráfico de 3 vértices, entonces tendrá un triángulo.
Enfoque: este problema se puede resolver utilizando el teorema de Mantel , que establece que el número máximo de aristas en un gráfico que no contiene ningún triángulo es piso (n 2 /4). En otras palabras, se debe eliminar casi la mitad de los bordes para obtener un gráfico sin triángulos.
¿Cómo funciona el teorema de Mantel?
Para cualquier gráfico , tal que el gráfico no tenga triángulos, entonces para cualquier vértice Z solo se puede conectar a cualquiera de los vértices de x e y, es decir, para cualquier borde conectado entre x e y, d(x) + d(y) ≤ N, donde d(x) y d(y) es el grado del vértice x e y.
- Entonces, el Grado de todos los vértices –
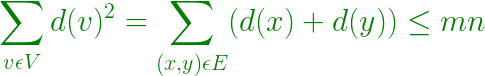
- Por la desigualdad de Cauchy-Schwarz –
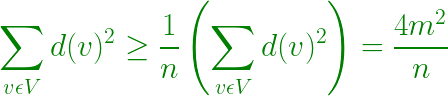
- Por lo tanto, 4m 2 / n ≤ mn, lo que implica m ≤ n 2 / 4
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation to find the maximum
// number of edges for triangle free graph
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find the maximum number of
// edges in a N-vertex graph.
int solve(int n)
{
// According to the Mantel's theorem
// the maximum number of edges will be
// floor of [(n^2)/4]
int ans = (n * n / 4);
return ans;
}
// Driver Function
int main()
{
int n = 10;
cout << solve(n) << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation to find the maximum
// number of edges for triangle free graph
class GFG
{
// Function to find the maximum number of
// edges in a N-vertex graph.
public static int solve(int n)
{
// According to the Mantel's theorem
// the maximum number of edges will be
// floor of [(n^2)/4]
int ans = (n * n / 4);
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n = 10;
System.out.println(solve(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyamohan123
C#
// C# implementation to find the maximum
// number of edges for triangle free graph
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to find the maximum number of
// edges in a N-vertex graph.
public static int solve(int n)
{
// According to the Mantel's theorem
// the maximum number of edges will be
// floor of [(n^2)/4]
int ans = (n * n / 4);
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int n = 10;
Console.WriteLine(solve(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by AnkitRai01
Python3
# Python3 implementation to find the maximum # number of edges for triangle free graph # Function to find the maximum number of # edges in a N-vertex graph. def solve(n): # According to the Mantel's theorem # the maximum number of edges will be # floor of [(n^2)/4] ans = (n * n // 4) return ans # Driver Function if __name__ == '__main__': n = 10 print(solve(n)) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation to find the maximum
// number of edges for triangle free graph
// Function to find the maximum number of
// edges in a N-vertex graph.
function solve(n)
{
// According to the Mantel's theorem
// the maximum number of edges will be
// floor of [(n^2)/4]
var ans = (n * n / 4);
return ans;
}
// Driver code
var n = 10;
document.write(solve(n));
// This code is contributed by aashish1995
</script>
25
Complejidad de tiempo: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por andrew1234 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA