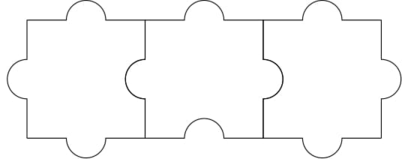
Dado un rompecabezas especial que consta de N filas y M columnas, todas las piezas son idénticas. Cada pieza tiene tres pestañas y una en blanco. La tarea es verificar si el rompecabezas se puede resolver colocando las piezas de tal manera que la pestaña de una pieza encaje perfectamente en un espacio en blanco de otra pieza.
Nota : gira y traslada las piezas para resolver el rompecabezas.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 2, M = 2
Salida: SíEntrada: N = 1, M = 3
Salida: Sí
Enfoque: La observación clave en el problema es que:
- Si el Rompecabezas tiene solo una fila o solo una columna. Entonces es posible resolver el rompecabezas colocando una pestaña en blanco en ese lado compartido.
- Si el Rompecabezas tiene dos filas y dos columnas. Luego, el rompecabezas se puede resolver colocando las pestañas en blanco en una string circular.
- De lo contrario, no es posible resolver el rompecabezas.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to check if the jigsaw
// Puzzle is solveable or not
void checkSolveable(int n, int m)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 1 or m == 1)
cout << "YES";
// By placing the blank tabs
// as a chain
else if (m == 2 and n == 2)
cout << "YES";
else
cout << "NO";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 1, m = 3;
checkSolveable(n, m);
}
// This code is contributed by jana_sayantan
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to check if the jigsaw
// Puzzle is solveable or not
static void checkSolveable(int n, int m)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 1 || m == 1)
System.out.print("YES");
// By placing the blank tabs
// as a chain
else if (m == 2 && n == 2)
System.out.print("YES");
else
System.out.print("NO");
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 1, m = 3;
checkSolveable(n, m);
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjoy_62
Python
# Python program for the above approach
# Function to check if the jigsaw
# Puzzle is solveable or not
def checkSolveable(n, m):
# Base Case
if n == 1 or m == 1:
print("YES")
# By placing the blank tabs
# as a chain
elif m == 2 and n == 2:
print("YES")
else:
print("NO")
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
n = 1
m = 3
checkSolveable(n, m)
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to check if the jigsaw
// Puzzle is solveable or not
static void checkSolveable(int n, int m)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 1 || m == 1)
Console.WriteLine("YES");
// By placing the blank tabs
// as a chain
else if (m == 2 && n == 2)
Console.WriteLine("YES");
else
Console.WriteLine("NO");
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int n = 1, m = 3;
checkSolveable(n, m);
}
}
// This code is contributed by susmitakundugoaldanga
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript implementation of the above approach
// Function to check if the jigsaw
// Puzzle is solveable or not
function checkSolveable(n, m)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 1 || m == 1)
document.write("YES");
// By placing the blank tabs
// as a chain
else if (m == 2 && n == 2)
document.write("YES");
else
document.write("NO");
}
// Driver code
let n = 1, m = 3;
checkSolveable(n, m);
// This code is contributed by code_hunt.
</script>
YES
Tiempo Complejidad: O(1)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por harshdhiman725 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA