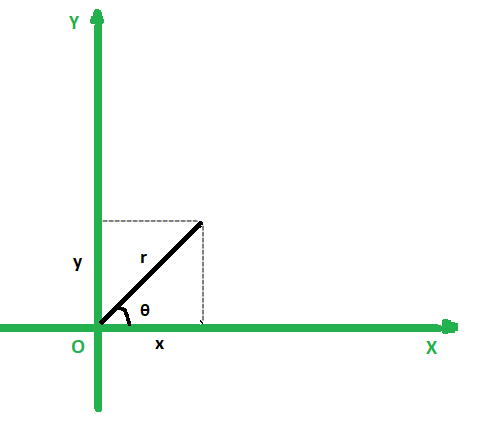
Dados dos números enteros r y θ (en grados) que representan las coordenadas polares de un punto (r, θ) , la tarea es encontrar las coordenadas cartesianas del punto dado.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: r = 1,4142, θ = 45
Salida: 1,000, 1,000Entrada: r = 3, θ = 30
Salida: 2.598, 1.500
Aproximación: Sean las coordenadas cartesianas del punto (x, y). Las coordenadas polares y las coordenadas cartesianas se pueden relacionar mediante las siguientes ecuaciones:
x = r*cosθ y y = r*sinθ
Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Convierta θ de grados a radianes como θ(en radianes) = θ (en grados) * (3.14159 / 180) .
- Almacene las coordenadas x e y en una variable X e Y respectivamente.
- Aplique la fórmula de transformación y actualice el valor de X = r * cosθ e Y = r * sinθ .
- Imprime el valor de X e Y como resultado.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++14
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to convert degree to radian
double ConvertDegToRad(double degree)
{
double pi = 3.14159;
return (degree * (pi / 180.0));
}
// Function to convert the polar
// coordinate to cartesian
void ConvertToCartesian(
pair<double, double> polar)
{
// Convert degrees to radian
polar.second = ConvertDegToRad(
polar.second);
// Applying the formula:
// x = rcos(theta), y = rsin(theta)
pair<double, double> cartesian
= { polar.first * cos(polar.second),
polar.first * sin(polar.second) };
// Print cartesian coordinates
printf("%0.3f, %0.3f",
cartesian.first,
cartesian.second);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given polar coordinates
pair<double,
double>
polar = { 1.4142, 45 };
// Function to convert polar
// coordinates to equivalent
// cartesian coordinates
ConvertToCartesian(polar);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java code of above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to convert degree to radian
static double ConvertDegToRad(double degree)
{
double pi = 3.14159;
return (degree * (pi / 180.0));
}
// Function to convert the polar
// coordinate to cartesian
static void ConvertToCartesian(
double[] polar)
{
// Convert degrees to radian
polar[1] = ConvertDegToRad(
polar[1]);
// Applying the formula:
// x = rcos(theta), y = rsin(theta)
double[] cartesian
= { polar[0] * Math.cos(polar[1]),
polar[0] * Math.sin(polar[1]) };
// Print cartesian coordinates
System.out.print(String.format("%.3f", cartesian[0])+" "+String.format("%.3f", cartesian[1]));
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given polar coordinates
double[] polar = { 1.4142, 45 };
// Function to convert polar
// coordinates to equivalent
// cartesian coordinates
ConvertToCartesian(polar);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat
Python3
# Python 3 program for the above approach
import math
# Function to convert degree to radian
def ConvertDegToRad(degree):
pi = 3.14159
return (degree * (pi / 180.0))
# Function to convert the polar
# coordinate to cartesian
def ConvertToCartesian(polar):
# Convert degrees to radian
polar[1] = ConvertDegToRad(polar[1])
# Applying the formula:
# x = rcos(theta), y = rsin(theta)
cartesian = [polar[0] * math.cos(polar[1]),
polar[0] * math.sin(polar[1])]
# Print cartesian coordinates
print('%.3f' % cartesian[0],
'%.3f' % cartesian[1])
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Given polar coordinates
polar = [1.4142, 45]
# Function to convert polar
# coordinates to equivalent
# cartesian coordinates
ConvertToCartesian(polar)
# This code is contributed by chitranayal.
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to convert degree to radian
static Double ConvertDegToRad(Double degree)
{
Double pi = 3.14159;
return (degree * (pi / 180.0));
}
// Function to convert the polar
// coordinate to cartesian
static void ConvertToCartesian(
Double[] polar)
{
// Convert degrees to radian
polar[1] = ConvertDegToRad(
polar[1]);
// Applying the formula:
// x = rCos(theta), y = rSin(theta)
Double[] cartesian
= { polar[0] * Math.Cos(polar[1]),
polar[0] * Math.Sin(polar[1]) };
// Print cartesian coordinates
Console.Write(String.Format("{0:0.000}", cartesian[0])+
", "+String.Format("{0:0.000}", cartesian[1]));
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
// Given polar coordinates
Double[] polar = { 1.4142, 45 };
// Function to convert polar
// coordinates to equivalent
// cartesian coordinates
ConvertToCartesian(polar);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shubham Singh
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript code of above approach
// Function to convert degree to radian
function ConvertDegToRad(degree)
{
let pi = 3.14159;
return (degree * (pi / 180.0));
}
// Function to convert the polar
// coordinate to cartesian
function ConvertToCartesian(polar)
{
// Convert degrees to radian
polar[1] = ConvertDegToRad(
polar[1]);
// Applying the formula:
// x = rcos(theta), y = rsin(theta)
let cartesian
= [ polar[0] * Math.cos(polar[1]),
polar[0] * Math.sin(polar[1]) ];
// Print cartesian coordinates
document.write((cartesian[0]).toFixed(3)+", "
+(cartesian[1]).toFixed(3));
}
// Driver code
let polar=[1.4142, 45 ];
// Function to convert polar
// coordinates to equivalent
// cartesian coordinates
ConvertToCartesian(polar);
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
Producción:
1.000, 1.000
Tiempo Complejidad: O(1)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)