Para una ecuación diferencial dada ![]() con condición inicial,
con condición inicial, ![]()
encuentre la solución aproximada utilizando el método Predictor-Corrector.
Método predictor-corrector:
El método predictor-corrector también se conoce como método de Euler modificado .
En el método de Euler , la tangente se dibuja en un punto y la pendiente se calcula para un tamaño de paso determinado. Por lo tanto, este método funciona mejor con funciones lineales, pero para otros casos, sigue existiendo un error de truncamiento. Para resolver este problema se introduce el método de Euler Modificado. En este método, en lugar de un punto, se usa el promedio aritmético de la pendiente en un intervalo ![]() .
.
Así, en el método Predictor-Corrector para cada paso, el valor predicho de ![]() se calcula primero utilizando el método de Euler y luego se calculan las pendientes en los puntos
se calcula primero utilizando el método de Euler y luego se calculan las pendientes en los puntos ![]() y
y ![]() se suma la media aritmética de estas pendientes
se suma la media aritmética de estas pendientes ![]() para calcular el valor corregido de
para calcular el valor corregido de ![]() .
.
Asi que,
- Paso – 1: Primero se predice el valor para un paso (aquí t+1):
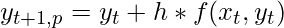 aquí
aquí
h es el tamaño del paso para cada incremento
- Paso – 2: Luego se corrige el valor predicho :
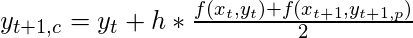
- Paso – 3: El incremento está hecho:
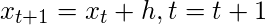
- Paso – 4: Verifique la continuación, si
 luego vaya al paso – 1.
luego vaya al paso – 1.
- Paso – 5: Terminar el proceso.
Como en este método se utiliza la pendiente media, el error se reduce significativamente. Además, podemos repetir el proceso de corrección por convergencia. Por lo tanto, en cada paso, estamos reduciendo el error al mejorar el valor de y.
Ejemplos:
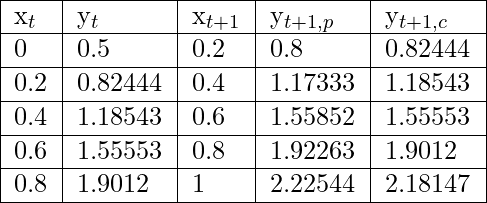
Entrada: eq =
, y(0) = 0,5, tamaño de paso (h) = 0,2
Para encontrar: y(1)
Salida: y(1) = 2,18147
Explicación:
El valor final de y en x = 1 es y=2,18147
Implementación: Aquí estamos considerando la ecuación diferencial: ![]()
C++
// C++ code for solving the differential equation
// using Predictor-Corrector or Modified-Euler method
// with the given conditions, y(0) = 0.5, step size(h) = 0.2
// to find y(1)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// consider the differential equation
// for a given x and y, return v
double f(double x, double y)
{
double v = y - 2 * x * x + 1;
return v;
}
// predicts the next value for a given (x, y)
// and step size h using Euler method
double predict(double x, double y, double h)
{
// value of next y(predicted) is returned
double y1p = y + h * f(x, y);
return y1p;
}
// corrects the predicted value
// using Modified Euler method
double correct(double x, double y,
double x1, double y1,
double h)
{
// (x, y) are of previous step
// and x1 is the increased x for next step
// and y1 is predicted y for next step
double e = 0.00001;
double y1c = y1;
do {
y1 = y1c;
y1c = y + 0.5 * h * (f(x, y) + f(x1, y1));
} while (fabs(y1c - y1) > e);
// every iteration is correcting the value
// of y using average slope
return y1c;
}
void printFinalValues(double x, double xn,
double y, double h)
{
while (x < xn) {
double x1 = x + h;
double y1p = predict(x, y, h);
double y1c = correct(x, y, x1, y1p, h);
x = x1;
y = y1c;
}
// at every iteration first the value
// of for next step is first predicted
// and then corrected.
cout << "The final value of y at x = "
<< x << " is : " << y << endl;
}
int main()
{
// here x and y are the initial
// given condition, so x=0 and y=0.5
double x = 0, y = 0.5;
// final value of x for which y is needed
double xn = 1;
// step size
double h = 0.2;
printFinalValues(x, xn, y, h);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java code for solving the differential
// equation using Predictor-Corrector
// or Modified-Euler method with the
// given conditions, y(0) = 0.5, step
// size(h) = 0.2 to find y(1)
import java.text.*;
class GFG
{
// consider the differential equation
// for a given x and y, return v
static double f(double x, double y)
{
double v = y - 2 * x * x + 1;
return v;
}
// predicts the next value for a given (x, y)
// and step size h using Euler method
static double predict(double x, double y, double h)
{
// value of next y(predicted) is returned
double y1p = y + h * f(x, y);
return y1p;
}
// corrects the predicted value
// using Modified Euler method
static double correct(double x, double y,
double x1, double y1,
double h)
{
// (x, y) are of previous step
// and x1 is the increased x for next step
// and y1 is predicted y for next step
double e = 0.00001;
double y1c = y1;
do
{
y1 = y1c;
y1c = y + 0.5 * h * (f(x, y) + f(x1, y1));
}
while (Math.abs(y1c - y1) > e);
// every iteration is correcting the value
// of y using average slope
return y1c;
}
static void printFinalValues(double x, double xn,
double y, double h)
{
while (x < xn)
{
double x1 = x + h;
double y1p = predict(x, y, h);
double y1c = correct(x, y, x1, y1p, h);
x = x1;
y = y1c;
}
// at every iteration first the value
// of for next step is first predicted
// and then corrected.
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.#####");
System.out.println("The final value of y at x = "+
x + " is : "+df.format(y));
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// here x and y are the initial
// given condition, so x=0 and y=0.5
double x = 0, y = 0.5;
// final value of x for which y is needed
double xn = 1;
// step size
double h = 0.2;
printFinalValues(x, xn, y, h);
}
}
// This code is contributed by mits
Python3
# Python3 code for solving the differential equation
# using Predictor-Corrector or Modified-Euler method
# with the given conditions, y(0) = 0.5, step size(h) = 0.2
# to find y(1)
# consider the differential equation
# for a given x and y, return v
def f(x, y):
v = y - 2 * x * x + 1;
return v;
# predicts the next value for a given (x, y)
# and step size h using Euler method
def predict(x, y, h):
# value of next y(predicted) is returned
y1p = y + h * f(x, y);
return y1p;
# corrects the predicted value
# using Modified Euler method
def correct(x, y, x1, y1, h):
# (x, y) are of previous step
# and x1 is the increased x for next step
# and y1 is predicted y for next step
e = 0.00001;
y1c = y1;
while (abs(y1c - y1) > e + 1):
y1 = y1c;
y1c = y + 0.5 * h * (f(x, y) + f(x1, y1));
# every iteration is correcting the value
# of y using average slope
return y1c;
def printFinalValues(x, xn, y, h):
while (x < xn):
x1 = x + h;
y1p = predict(x, y, h);
y1c = correct(x, y, x1, y1p, h);
x = x1;
y = y1c;
# at every iteration first the value
# of for next step is first predicted
# and then corrected.
print("The final value of y at x =",
int(x), "is :", y);
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# here x and y are the initial
# given condition, so x=0 and y=0.5
x = 0; y = 0.5;
# final value of x for which y is needed
xn = 1;
# step size
h = 0.2;
printFinalValues(x, xn, y, h);
# This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
C#
// C# code for solving the differential
// equation using Predictor-Corrector
// or Modified-Euler method with the
// given conditions, y(0) = 0.5, step
// size(h) = 0.2 to find y(1)
using System;
class GFG
{
// consider the differential equation
// for a given x and y, return v
static double f(double x, double y)
{
double v = y - 2 * x * x + 1;
return v;
}
// predicts the next value for a given (x, y)
// and step size h using Euler method
static double predict(double x, double y, double h)
{
// value of next y(predicted) is returned
double y1p = y + h * f(x, y);
return y1p;
}
// corrects the predicted value
// using Modified Euler method
static double correct(double x, double y,
double x1, double y1,
double h)
{
// (x, y) are of previous step
// and x1 is the increased x for next step
// and y1 is predicted y for next step
double e = 0.00001;
double y1c = y1;
do
{
y1 = y1c;
y1c = y + 0.5 * h * (f(x, y) + f(x1, y1));
}
while (Math.Abs(y1c - y1) > e);
// every iteration is correcting the value
// of y using average slope
return y1c;
}
static void printFinalValues(double x, double xn,
double y, double h)
{
while (x < xn)
{
double x1 = x + h;
double y1p = predict(x, y, h);
double y1c = correct(x, y, x1, y1p, h);
x = x1;
y = y1c;
}
// at every iteration first the value
// of for next step is first predicted
// and then corrected.
Console.WriteLine("The final value of y at x = "+
x + " is : " + Math.Round(y, 5));
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
// here x and y are the initial
// given condition, so x=0 and y=0.5
double x = 0, y = 0.5;
// final value of x for which y is needed
double xn = 1;
// step size
double h = 0.2;
printFinalValues(x, xn, y, h);
}
}
// This code is contributed by mits
PHP
<?php
// PHP code for solving the differential equation
// using Predictor-Corrector or Modified-Euler
// method with the given conditions, y(0) = 0.5,
// step size(h) = 0.2 to find y(1)
// consider the differential equation
// for a given x and y, return v
function f($x, $y)
{
$v = $y - 2 * $x * $x + 1;
return $v;
}
// predicts the next value for a given (x, y)
// and step size h using Euler method
function predict($x, $y, $h)
{
// value of next y(predicted) is returned
$y1p = $y + $h * f($x, $y);
return $y1p;
}
// corrects the predicted value
// using Modified Euler method
function correct($x, $y, $x1, $y1, $h)
{
// (x, y) are of previous step and
// x1 is the increased x for next step
// and y1 is predicted y for next step
$e = 0.00001;
$y1c = $y1;
do
{
$y1 = $y1c;
$y1c = $y + 0.5 * $h * (f($x, $y) +
f($x1, $y1));
} while (abs($y1c - $y1) > $e);
// every iteration is correcting the
// value of y using average slope
return $y1c;
}
function printFinalValues($x, $xn, $y, $h)
{
while ($x < $xn)
{
$x1 = $x + $h;
$y1p = predict($x, $y, $h);
$y1c = correct($x, $y, $x1, $y1p, $h);
$x = $x1;
$y = $y1c;
}
// at every iteration first the value
// of for next step is first predicted
// and then corrected.
echo "The final value of y at x = " . $x .
" is : " . round($y, 5) . "\n";
}
// here x and y are the initial
// given condition, so x=0 and y=0.5
$x = 0;
$y = 0.5;
// final value of x for which y is needed
$xn = 1;
// step size
$h = 0.2;
printFinalValues($x, $xn, $y, $h);
// This code is contributed by mits
?>
Javascript
<script>
// javascript code for solving the differential
// equation using Predictor-Corrector
// or Modified-Euler method with the
// given conditions, y(0) = 0.5, step
// size(h) = 0.2 to find y(1)
// consider the differential equation
// for a given x and y, return v
function f(x , y) {
var v = y - 2 * x * x + 1;
return v;
}
// predicts the next value for a given (x, y)
// and step size h using Euler method
function predict(x , y , h) {
// value of next y(predicted) is returned
var y1p = y + h * f(x, y);
return y1p;
}
// corrects the predicted value
// using Modified Euler method
function correct(x , y , x1 , y1 , h) {
// (x, y) are of previous step
// and x1 is the increased x for next step
// and y1 is predicted y for next step
var e = 0.00001;
var y1c = y1;
do {
y1 = y1c;
y1c = y + 0.5 * h * (f(x, y) + f(x1, y1));
} while (Math.abs(y1c - y1) > e);
// every iteration is correcting the value
// of y using average slope
return y1c;
}
function printFinalValues(x , xn , y , h) {
while (x < xn) {
var x1 = x + h;
var y1p = predict(x, y, h);
var y1c = correct(x, y, x1, y1p, h);
x = x1;
y = y1c;
}
// at every iteration first the value
// of for next step is first predicted
// and then corrected.
document.write("The final value of y at x = " + x + " is : " + y.toFixed(5));
}
// Driver code
// here x and y are the initial
// given condition, so x=0 and y=0.5
var x = 0, y = 0.5;
// final value of x for which y is needed
var xn = 1;
// step size
var h = 0.2;
printFinalValues(x, xn, y, h);
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
The final value of y at x = 1 is : 2.18147
Complejidad de tiempo: O(1)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por Arghyadip_Manna y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA