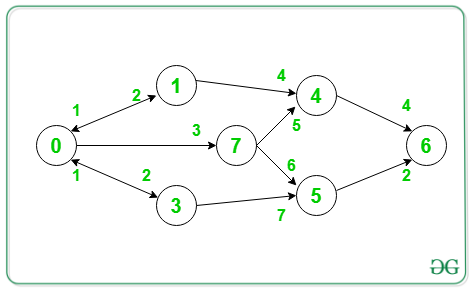
Dado un gráfico dirigido y ponderado G , una array V[] que consta de vértices, la tarea es encontrar la ruta de costo mínimo que pasa por todos los vértices del conjunto V , desde una fuente S dada hasta un destino D .
Ejemplos:
Entrada: V = {7}, S = 0, D = 6
Salida: 11
Explicación: Ruta
mínima 0->7->5->6.
Por lo tanto, el costo del camino = 3 + 6 + 2 = 11Entrada: V = {7, 4}, S = 0, D = 6
Salida: 12
Explicación: Ruta
mínima 0->7->4->6.
Por lo tanto el costo del camino = 3 + 5 + 4 = 12
Enfoque:
Para resolver el problema, la idea es utilizar el recorrido Breadth-First-Search . BFS se usa generalmente para encontrar las rutas más cortas en el gráfico y la distancia mínima de todos los Nodes desde el origen, los Nodes intermedios y el destino puede calcularse mediante el BFS a partir de estos Nodes.
Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Inicialice minSum a INT_MAX .
- Atraviese el gráfico desde el Node de origen S utilizando BFS .
- Marque cada Node vecino de la fuente como la nueva fuente y realice BFS desde ese Node.
- Una vez que se encuentra el Node de destino D , verifique si se visitan todos los Nodes intermedios o no.
- Si se visitan todos los Nodes intermedios, actualice minSum y devuelva el valor mínimo.
- Si no se visitan todos los Nodes intermedios, devuelva minSum .
- Marque la fuente como no visitada.
- Imprime el valor final de minSum obtenido.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ Program to implement
// the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Stores minimum-cost of path from source
int minSum = INT_MAX;
// Function to Perform BFS on graph g
// starting from vertex v
void getMinPathSum(unordered_map<int,
vector<pair<int,
int> > >& graph,
vector<bool>& visited,
vector<int> necessary,
int src, int dest, int currSum)
{
// If destination is reached
if (src == dest) {
// Set flag to true
bool flag = true;
// Visit all the intermediate nodes
for (int i : necessary) {
// If any intermediate node
// is not visited
if (!visited[i]) {
flag = false;
break;
}
}
// If all intermediate
// nodes are visited
if (flag)
// Update the minSum
minSum = min(minSum, currSum);
return;
}
else {
// Mark the current node
// visited
visited[src] = true;
// Traverse adjacent nodes
for (auto node : graph[src]) {
if (!visited[node.first]) {
// Mark the neighbour visited
visited[node.first] = true;
// Find minimum cost path
// considering the neighbour
// as the source
getMinPathSum(graph, visited,
necessary, node.first,
dest, currSum + node.second);
// Mark the neighbour unvisited
visited[node.first] = false;
}
}
// Mark the source unvisited
visited[src] = false;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Stores the graph
unordered_map<int, vector<pair<int,
int> > >
graph;
graph[0] = { { 1, 2 }, { 2, 3 }, { 3, 2 } };
graph[1] = { { 4, 4 }, { 0, 1 } };
graph[2] = { { 4, 5 }, { 5, 6 } };
graph[3] = { { 5, 7 }, { 0, 1 } };
graph[4] = { { 6, 4 } };
graph[5] = { { 6, 2 } };
graph[6] = { { 7, 11 } };
// Number of nodes
int n = 7;
// Source
int source = 0;
// Destination
int dest = 6;
// Keeps a check on visited
// and unvisited nodes
vector<bool> visited(n, false);
// Stores intermediate nodes
vector<int> necessary{ 2, 4 };
getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary,
source, dest, 0);
// If no path is found
if (minSum == INT_MAX)
cout << "-1\n";
else
cout << minSum << '\n';
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to implement
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static class pair
{
int first, second;
pair(int f, int s)
{
this.first = f;
this.second = s;
}
}
// Stores minimum-cost of path from source
static int minSum = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// Function to Perform BFS on graph g
// starting from vertex v
static void getMinPathSum(Map<Integer, ArrayList<pair>> graph,
boolean[] visited,
ArrayList<Integer> necessary,
int source, int dest, int currSum)
{
// If destination is reached
if (src == dest)
{
// Set flag to true
boolean flag = true;
// Visit all the intermediate nodes
for(int i : necessary)
{
// If any intermediate node
// is not visited
if (!visited[i])
{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
// If all intermediate
// nodes are visited
if (flag)
// Update the minSum
minSum = Math.min(minSum, currSum);
return;
}
else
{
// Mark the current node
// visited
visited[src] = true;
// Traverse adjacent nodes
for(pair node : graph.get(src))
{
if (!visited[node.first])
{
// Mark the neighbour visited
visited[node.first] = true;
// Find minimum cost path
// considering the neighbour
// as the source
getMinPathSum(graph, visited,
necessary, node.first,
dest, currSum + node.second);
// Mark the neighbour unvisited
visited[node.first] = false;
}
}
// Mark the source unvisited
visited[src] = false;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Stores the graph
Map<Integer, ArrayList<pair>> graph = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i <= 6; i++)
graph.put(i, new ArrayList<pair>());
graph.get(0).add(new pair(1, 2));
graph.get(0).add(new pair(2, 3));
graph.get(0).add(new pair(3, 2));
graph.get(1).add(new pair(4, 4));
graph.get(1).add(new pair(0, 1));
graph.get(2).add(new pair(4, 5));
graph.get(2).add(new pair(5, 6));
graph.get(3).add(new pair(5, 7));
graph.get(3).add(new pair(0, 1));
graph.get(4).add(new pair(6, 4));
graph.get(5).add(new pair(4, 2));
graph.get(6).add(new pair(7, 11));
// Number of nodes
int n = 7;
// Source
int source = 0;
// Destination
int dest = 6;
// Keeps a check on visited
// and unvisited nodes
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
// Stores intermediate nodes
ArrayList<Integer> necessary = new ArrayList<>(
Arrays.asList(2, 4));
getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary,
source, dest, 0);
// If no path is found
if (minSum == Integer.MAX_VALUE)
System.out.println(-1);
else
System.out.println(minSum);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat
Python3
# Python3 Program to implement # the above approach # Stores minimum-cost of path from source minSum = 1000000000 # Function to Perform BFS on graph g # starting from vertex v def getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, source, dest, currSum): global minSum # If destination is reached if (src == dest): # Set flag to true flag = True; # Visit all the intermediate nodes for i in necessary: # If any intermediate node # is not visited if (not visited[i]): flag = False; break; # If all intermediate # nodes are visited if (flag): # Update the minSum minSum = min(minSum, currSum); return; else: # Mark the current node # visited visited[src] = True; # Traverse adjacent nodes for node in graph[src]: if not visited[node[0]]: # Mark the neighbour visited visited[node[0]] = True; # Find minimum cost path # considering the neighbour # as the source getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, node[0], dest, currSum + node[1]); # Mark the neighbour unvisited visited[node[0]] = False; # Mark the source unvisited visited[src] = False; # Driver Code if __name__=='__main__': # Stores the graph graph=dict() graph[0] = [ [ 1, 2 ], [ 2, 3 ], [ 3, 2 ] ]; graph[1] = [ [ 4, 4 ], [ 0, 1 ] ]; graph[2] = [ [ 4, 5 ], [ 5, 6 ] ]; graph[3] = [ [ 5, 7 ], [ 0, 1 ] ]; graph[4] = [ [ 6, 4 ] ]; graph[5] = [ [ 6, 2 ] ]; graph[6] = [ [ 7, 11 ] ]; # Number of nodes n = 7; # Source source = 0; # Destination dest = 6; # Keeps a check on visited # and unvisited nodes visited=[ False for i in range(n + 1)] # Stores intermediate nodes necessary = [ 2, 4 ]; getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, source, dest, 0); # If no path is found if (minSum == 1000000000): print(-1) else: print(minSum) # This code is contributed by pratham76
C#
// C# program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
class pair
{
public int first, second;
public pair(int f, int s)
{
this.first = f;
this.second = s;
}
}
// Stores minimum-cost of path from source
static int minSum = 100000000;
// Function to Perform BFS on graph g
// starting from vertex v
static void getMinPathSum(Dictionary<int, ArrayList> graph,
bool[] visited, ArrayList necessary,
int source, int dest, int currSum)
{
// If destination is reached
if (src == dest)
{
// Set flag to true
bool flag = true;
// Visit all the intermediate nodes
foreach(int i in necessary)
{
// If any intermediate node
// is not visited
if (!visited[i])
{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
// If all intermediate
// nodes are visited
if (flag)
// Update the minSum
minSum = Math.Min(minSum, currSum);
return;
}
else
{
// Mark the current node
// visited
visited[src] = true;
// Traverse adjacent nodes
foreach(pair node in graph)
{
if (!visited[node.first])
{
// Mark the neighbour visited
visited[node.first] = true;
// Find minimum cost path
// considering the neighbour
// as the source
getMinPathSum(graph, visited,
necessary, node.first,
dest, currSum + node.second);
// Mark the neighbour unvisited
visited[node.first] = false;
}
}
// Mark the source unvisited
visited[src] = false;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Stores the graph
Dictionary<int, ArrayList> graph = new Dictionary<int, ArrayList>();
for(int i = 0; i <= 6; i++)
graph[i] = new ArrayList();
graph[0].Add(new pair(1, 2));
graph[0].Add(new pair(2, 3));
graph[0].Add(new pair(3, 2));
graph[1].Add(new pair(4, 4));
graph[1].Add(new pair(0, 1));
graph[2].Add(new pair(4, 5));
graph[2].Add(new pair(5, 6));
graph[3].Add(new pair(5, 7));
graph[3].Add(new pair(0, 1));
graph[4].Add(new pair(6, 4));
graph[5].Add(new pair(4, 2));
graph[6].Add(new pair(7, 11));
// Number of nodes
int n = 7;
// Source
int source = 0;
// Destination
int dest = 6;
// Keeps a check on visited
// and unvisited nodes
bool[] visited = new bool[n];
// Stores intermediate nodes
ArrayList necessary = new ArrayList();
necessary.Add(2);
necessary.Add(4);
getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, source, dest, 0);
// If no path is found
if (minSum == 100000000)
Console.WriteLine(-1);
else
Console.WriteLine(minSum);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to implement
// the above approach
class pair
{
constructor(f, s)
{
this.first = f;
this.second = s;
}
}
// Stores minimum-cost of path from source
var minSum = 100000000;
// Function to Perform BFS on graph g
// starting from vertex v
function getMinPathSum(graph, visited,necessary, src, dest, currSum)
{
// If destination is reached
if (src == dest)
{
// Set flag to true
var flag = true;
// Visit all the intermediate nodes
for(var i of necessary)
{
// If any intermediate node
// is not visited
if (!visited[i])
{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
// If all intermediate
// nodes are visited
if (flag)
// Update the minSum
minSum = Math.min(minSum, currSum);
return;
}
else
{
// Mark the current node
// visited
visited[src] = true;
// Traverse adjacent nodes
for(var node of graph[src])
{
if (!visited[node.first])
{
// Mark the neighbour visited
visited[node.first] = true;
// Find minimum cost path
// considering the neighbour
// as the source
getMinPathSum(graph, visited,
necessary, node.first,
dest, currSum + node.second);
// Mark the neighbour unvisited
visited[node.first] = false;
}
}
// Mark the source unvisited
visited[src] = false;
}
}
// Driver code
// Stores the graph
var graph = Array.from(Array(7), ()=>Array());
graph[0].push(new pair(1, 2));
graph[0].push(new pair(2, 3));
graph[0].push(new pair(3, 2));
graph[1].push(new pair(4, 4));
graph[1].push(new pair(0, 1));
graph[2].push(new pair(4, 5));
graph[2].push(new pair(5, 6));
graph[3].push(new pair(5, 7));
graph[3].push(new pair(0, 1));
graph[4].push(new pair(6, 4));
graph[5].push(new pair(4, 2));
graph[6].push(new pair(7, 11));
// Number of nodes
var n = 7;
// Source
var source = 0;
// Destination
var dest = 6;
// Keeps a check on visited
// and unvisited nodes
var visited = Array(n).fill(false);
// Stores intermediate nodes
var necessary = [];
necessary.push(2);
necessary.push(4);
getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, source, dest, 0);
// If no path is found
if (minSum == 100000000)
document.write(-1);
else
document.write(minSum);
</script>
12
Complejidad temporal: O(N+M)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N+M)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por AnshulVerma1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA