Hashing es una mejora sobre Direct Access Table . La idea es usar una función hash que convierte un número de teléfono dado o cualquier otra clave en un número más pequeño y usa el número pequeño como índice en una tabla llamada tabla hash .
Función hash : una función que convierte un número grande dado en un pequeño valor entero práctico. El valor entero asignado se utiliza como índice en la tabla hash. En términos simples, una función hash asigna un número grande o una string a un entero pequeño que se puede usar como índice en la tabla hash.
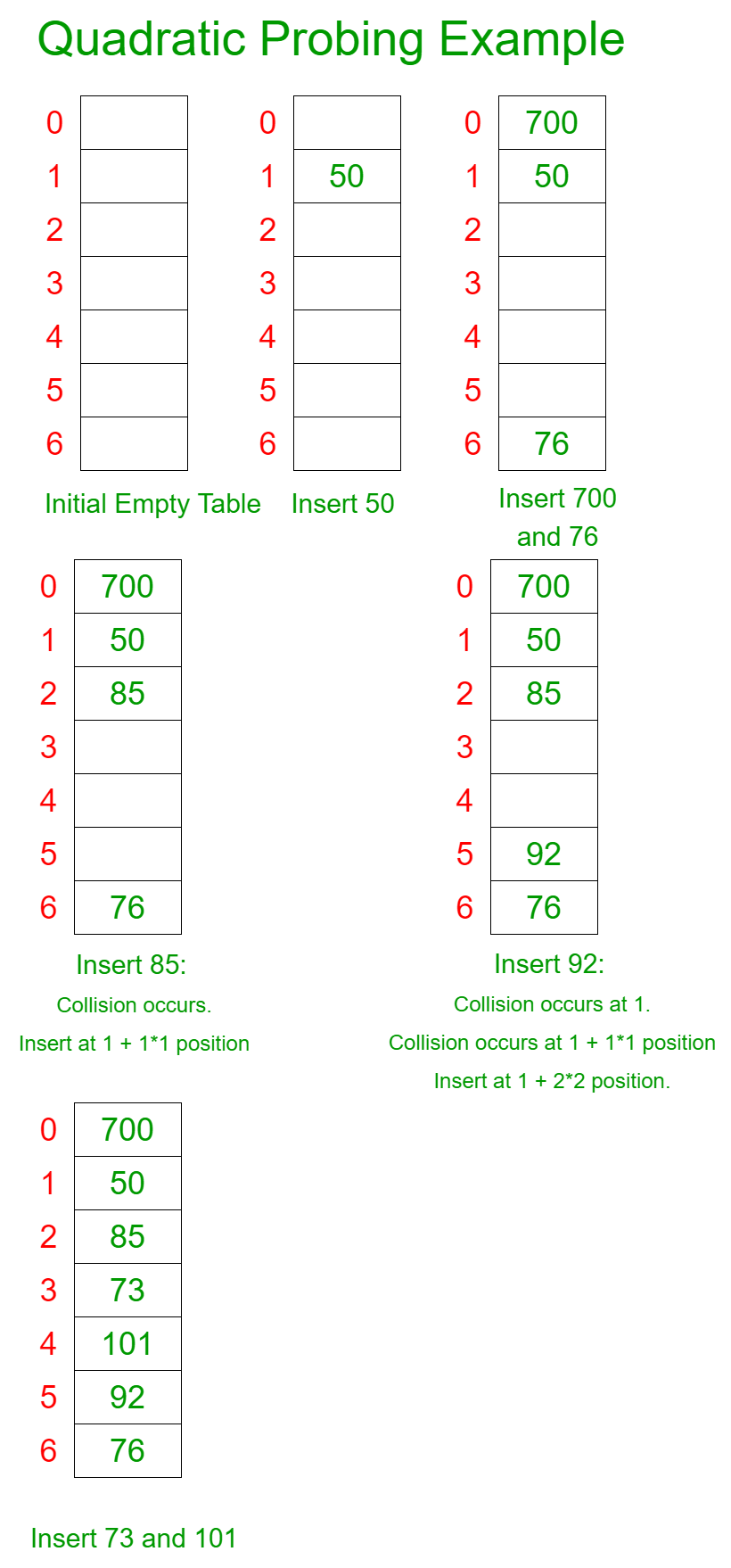
En este artículo, se discute la técnica de colisión , el sondeo cuadrático .
Sondeo cuadrático:El sondeo cuadrático es un esquema de direccionamiento abierto en el que buscamos i 2 ‘th slot en i’th iteración si el valor hash dado x choca en la tabla hash.
¿Cómo se realiza el sondeo cuadrático?
Sea hash(x) el índice de ranura calculado usando la función hash.
- Si la ranura hash(x) % S está llena, entonces intentamos (hash(x) + 1*1) % S.
- Si (hash(x) + 1*1) % S también está lleno, entonces probamos (hash(x) + 2*2) % S.
- Si (hash(x) + 2*2) % S también está lleno, entonces probamos (hash(x) + 3*3) % S.
- Este proceso se repite para todos los valores de i hasta que se encuentra una ranura vacía.
Por ejemplo: Consideremos una función hash simple como » key mod 7 » y una secuencia de teclas como 50, 700, 76, 85, 92, 73, 101 .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of
// the Quadratic Probing
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
// Iterating and printing the array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
}
// Function to implement the
// quadratic probing
void hashing(int table[], int tsize,
int arr[], int N)
{
// Iterating through the array
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// Computing the hash value
int hv = arr[i] % tsize;
// Insert in the table if there
// is no collision
if (table[hv] == -1)
table[hv] = arr[i];
else
{
// If there is a collision
// iterating through all
// possible quadratic values
for (int j = 0; j < tsize; j++)
{
// Computing the new hash value
int t = (hv + j * j) % tsize;
if (table[t] == -1)
{
// Break the loop after
// inserting the value
// in the table
table[t] = arr[i];
break;
}
}
}
}
printArray(table, N);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = {50, 700, 76,
85, 92, 73, 101};
int N = 7;
// Size of the hash table
int L = 7;
int hash_table[7];
// Initializing the hash table
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++)
{
hash_table[i] = -1;
}
// Quadratic probing
hashing(hash_table, L, arr, N);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Java
// Java implementation of the Quadratic Probing
class GFG {
// Function to print an array
static void printArray(int arr[])
{
// Iterating and printing the array
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
// Function to implement the
// quadratic probing
static void hashing(int table[], int tsize,
int arr[], int N)
{
// Iterating through the array
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// Computing the hash value
int hv = arr[i] % tsize;
// Insert in the table if there
// is no collision
if (table[hv] == -1)
table[hv] = arr[i];
else {
// If there is a collision
// iterating through all
// possible quadratic values
for (int j = 0; j < tsize; j++) {
// Computing the new hash value
int t = (hv + j * j) % tsize;
if (table[t] == -1) {
// Break the loop after
// inserting the value
// in the table
table[t] = arr[i];
break;
}
}
}
}
printArray(table);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 50, 700, 76, 85,
92, 73, 101 };
int N = 7;
// Size of the hash table
int L = 7;
int hash_table[] = new int[L];
// Initializing the hash table
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
hash_table[i] = -1;
}
// Quadratic probing
hashing(hash_table, L, arr, N);
}
}
Python3
# Python3 implementation of # the Quadratic Probing # Function to print an array def printArray(arr, n): # Iterating and printing the array for i in range(n): print(arr[i], end = " ") # Function to implement the # quadratic probing def hashing(table, tsize, arr, N): # Iterating through the array for i in range(N): # Computing the hash value hv = arr[i] % tsize # Insert in the table if there # is no collision if (table[hv] == -1): table[hv] = arr[i] else: # If there is a collision # iterating through all # possible quadratic values for j in range(tsize): # Computing the new hash value t = (hv + j * j) % tsize if (table[t] == -1): # Break the loop after # inserting the value # in the table table[t] = arr[i] break printArray(table, N) # Driver code arr = [ 50, 700, 76, 85, 92, 73, 101 ] N = 7 # Size of the hash table L = 7 hash_table = [0] * 7 # Initializing the hash table for i in range(L): hash_table[i] = -1 # Quadratic probing hashing(hash_table, L, arr, N) # This code is contributed by code_hunt
C#
// C# implementation of the Quadratic Probing
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to print an array
static void printArray(int []arr)
{
// Iterating and printing the array
for(int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
// Function to implement the
// quadratic probing
static void hashing(int []table, int tsize,
int []arr, int N)
{
// Iterating through the array
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// Computing the hash value
int hv = arr[i] % tsize;
// Insert in the table if there
// is no collision
if (table[hv] == -1)
table[hv] = arr[i];
else
{
// If there is a collision
// iterating through all
// possible quadratic values
for(int j = 0; j < tsize; j++)
{
// Computing the new hash value
int t = (hv + j * j) % tsize;
if (table[t] == -1)
{
// Break the loop after
// inserting the value
// in the table
table[t] = arr[i];
break;
}
}
}
}
printArray(table);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
int []arr = { 50, 700, 76, 85,
92, 73, 101 };
int N = 7;
// Size of the hash table
int L = 7;
int []hash_table = new int[L];
// Initializing the hash table
for(int i = 0; i < L; i++)
{
hash_table[i] = -1;
}
// Quadratic probing
hashing(hash_table, L, arr, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation of the Quadratic Probing
// Function to print an array
function printArray(arr)
{
// Iterating and printing the array
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
document.write(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
// Function to implement the
// quadratic probing
function hashing(table, tsize,
arr, N)
{
// Iterating through the array
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// Computing the hash value
let hv = arr[i] % tsize;
// Insert in the table if there
// is no collision
if (table[hv] == -1)
table[hv] = arr[i];
else {
// If there is a collision
// iterating through all
// possible quadratic values
for (let j = 0; j < tsize; j++) {
// Computing the new hash value
let t = (hv + j * j) % tsize;
if (table[t] == -1) {
// Break the loop after
// inserting the value
// in the table
table[t] = arr[i];
break;
}
}
}
}
printArray(table);
}
// Driver Code
let arr = [ 50, 700, 76, 85,
92, 73, 101 ];
let N = 7;
// Size of the hash table
let L = 7;
let hash_table = [];
// Initializing the hash table
for (let i = 0; i < L; i++) {
hash_table[i] = -1;
}
// Quadratic probing
hashing(hash_table, L, arr, N);
// This code is contributed by splevel62.
</script>
700 50 85 73 101 92 76
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N * L), donde N es la longitud de la array y L es el tamaño de la tabla hash.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1).
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por shristiuniyal1999 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA