Dado un tablero de ajedrez de tamaño 8 x 8 y la posición actual de Mirandote. Todas las reglas de este juego de ajedrez son las mismas pero se modifica el caballo. Llamamos al nuevo caballero “Mirandote”. El movimiento de Mirandote está dado por un color azul donde su posición actual se denota por el color rojo en la siguiente imagen:

La tarea es encontrar cuántas posiciones posibles existen en Chessboard que Mirandote puede alcanzar exactamente en S pasos.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: fila = 4, columna = 4, pasos = 1
Salida: 12
Todos los 12 movimientos indicados por la siguiente imagen en color azul:
Entrada: fila = 4, columna = 4, pasos = 2
Salida: 55
Solución:
Podemos observar que todas las posiciones posibles con respecto a la posición actual se pueden escribir en forma de filas y columnas. Esto se ilustra con la siguiente imagen:
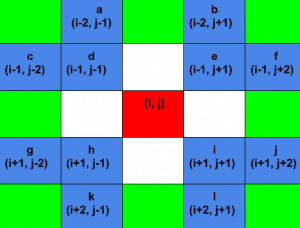
Podemos llamar a una función recursivamente para cada posición posible y contar todas las posiciones posibles.
A continuación se muestra la implementación requerida para encontrar las posiciones:
C++
// C++ implementation to find the
// possible positions
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find the positions
void findSteps(int current_row, int current_column,
int curr, int board_size, int steps,
int* visited)
{
// Bound checking
if (current_row >= board_size || current_row < 0
|| current_column >= board_size || current_column < 0
|| curr > steps) {
return;
}
// If steps is equal to current steps,
// that means current position is reached by Mirandote
if (curr == steps) {
*((visited + (current_row)*board_size) + current_column) = 1;
return;
}
// Recursive calls for each possible position.
// Position of a, b, c, ..., l given in above image.
/* a = */ findSteps(current_row - 2, current_column - 1,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* b = */ findSteps(current_row - 2, current_column + 1,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* c = */ findSteps(current_row - 1, current_column - 2,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* d = */ findSteps(current_row - 1, current_column - 1,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* e = */ findSteps(current_row - 1, current_column + 1,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* f = */ findSteps(current_row - 1, current_column + 2,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* g = */ findSteps(current_row + 1, current_column - 2,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* h = */ findSteps(current_row + 1, current_column - 1,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* i = */ findSteps(current_row + 1, current_column + 1,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* j = */ findSteps(current_row + 1, current_column + 2,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* k = */ findSteps(current_row + 2, current_column - 1,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* l = */ findSteps(current_row + 2, current_column + 1,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
return;
}
int countSteps(int current_row, int current_column,
int board_size, int steps)
{
// Visited array
int visited[board_size][board_size];
// Initialize visited array to zero
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board_size; j++) {
visited[i][j] = 0;
}
}
int answer = 0;
// Function call where initial step count is 0
findSteps(current_row, current_column, 0,
board_size, steps, (int*)visited);
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board_size; j++) {
// If value of element is 1, that implies,
// the position can be reached by Mirandote.
if (visited[i][j] == 1) {
answer++;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int board_size = 8, steps = 1;
int current_row = 4, current_column = 4;
cout << countSteps(current_row, current_column,
board_size, steps);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation to find the
// possible positions
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int [][] visited = new int [500][500];
// Function to find the positions
static void findSteps(int current_row,
int current_column,
int curr, int board_size,
int steps)
{
// Bound checking
if (current_row >= board_size ||
current_row < 0 ||
current_column >= board_size ||
current_column < 0 || curr > steps)
{
return;
}
// If steps is equal to current steps,
// that means current position is
// reached by Mirandote
if (curr == steps)
{
visited[current_row][current_column] = 1;
return;
}
// Recursive calls for each possible position.
// Position of a, b, c, ..., l given in
// above image.
/* a = */ findSteps(current_row - 2,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* b = */ findSteps(current_row - 2,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* c = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column - 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* d = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* e = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* f = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column + 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* g = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column - 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* h = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* i = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* j = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column + 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* k = */ findSteps(current_row + 2,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* l = */ findSteps(current_row + 2,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
}
static int countSteps(int current_row,
int current_column,
int board_size, int steps)
{
// Initialize visited array to zero
for(int i = 0; i < board_size; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < board_size; j++)
{
visited[i][j] = 0;
}
}
int answer = 0;
// Function call where initial step count is 0
findSteps(current_row, current_column, 0,
board_size,steps);
for(int i = 0; i < board_size; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < board_size; j++)
{
// If value of element is 1, that implies,
// the position can be reached by Mirandote.
if (visited[i][j] == 1)
{
answer++;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int board_size = 8, steps = 1;
int current_row = 4, current_column = 4;
System.out.print(countSteps(current_row,
current_column,
board_size, steps));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_Cipher
Python3
# Python3 implementation to find the possible positions visited = [[0 for i in range(500)] for j in range(500)] # Function to find the positions def findSteps(current_row, current_column, curr, board_size, steps): global visited # Bound checking if current_row >= board_size or current_row < 0 or current_column >= board_size or current_column < 0 or curr > steps: return # If steps is equal to current steps, # that means current position is # reached by Mirandote if curr == steps: visited[current_row][current_column] = 1 return # Recursive calls for each possible position. # Position of a, b, c, ..., l given in # above image. """ a = """ findSteps(current_row - 2, current_column - 1, curr + 1, board_size, steps) """ b = """ findSteps(current_row - 2, current_column + 1, curr + 1, board_size, steps) """ c = """ findSteps(current_row - 1, current_column - 2, curr + 1, board_size, steps) """ d = """ findSteps(current_row - 1, current_column - 1, curr + 1, board_size, steps) """ e = """ findSteps(current_row - 1, current_column + 1, curr + 1, board_size, steps) """ f = """ findSteps(current_row - 1, current_column + 2, curr + 1, board_size, steps) """ g = """ findSteps(current_row + 1, current_column - 2, curr + 1, board_size, steps) """ h = """ findSteps(current_row + 1, current_column - 1, curr + 1, board_size, steps) """ i = """ findSteps(current_row + 1, current_column + 1, curr + 1, board_size, steps) """ j = """ findSteps(current_row + 1, current_column + 2, curr + 1, board_size, steps) """ k = """ findSteps(current_row + 2, current_column - 1, curr + 1, board_size, steps) """ l = """ findSteps(current_row + 2, current_column + 1, curr + 1, board_size, steps) def countSteps(current_row, current_column, board_size, steps): # Initialize visited array to zero for i in range(board_size): for j in range(board_size): visited[i][j] = 0 answer = 0 # Function call where initial step count is 0 findSteps(current_row, current_column, 0, board_size,steps) for i in range(board_size): for j in range(board_size): # If value of element is 1, that implies, # the position can be reached by Mirandote. if visited[i][j] == 1: answer+=1 return answer board_size, steps = 8, 1 current_row, current_column = 4, 4 print(countSteps(current_row, current_column, board_size, steps)) # This code is contributed by rameshtravel07.
C#
// C# implementation to find the
// possible positions
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System;
class GFG{
static int [,] visited = new int[500, 500];
// Function to find the positions
static void findSteps(int current_row,
int current_column,
int curr, int board_size,
int steps)
{
// Bound checking
if (current_row >= board_size ||
current_row < 0 ||
current_column >= board_size ||
current_column < 0 || curr > steps)
{
return;
}
// If steps is equal to current steps,
// that means current position is
// reached by Mirandote
if (curr == steps)
{
visited[current_row, current_column] = 1;
return;
}
// Recursive calls for each possible position.
// Position of a, b, c, ..., l given in above image.
/* a = */ findSteps(current_row - 2,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* b = */ findSteps(current_row - 2,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* c = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column - 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* d = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* e = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* f = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column + 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* g = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column - 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* h = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* i = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* j = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column + 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* k = */ findSteps(current_row + 2,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* l = */ findSteps(current_row + 2,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
}
static int countSteps(int current_row,
int current_column,
int board_size, int steps)
{
// Initialize visited array to zero
for(int i = 0; i < board_size; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < board_size; j++)
{
visited[i, j] = 0;
}
}
int answer = 0;
// Function call where initial step count is 0
findSteps(current_row, current_column, 0,
board_size,steps);
for(int i = 0; i < board_size; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < board_size; j++)
{
// If value of element is 1,
// that implies, the position
// can be reached by Mirandote.
if (visited[i, j] == 1)
{
answer++;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int board_size = 8, steps = 1;
int current_row = 4, current_column = 4;
Console.WriteLine(countSteps(current_row,
current_column,
board_size, steps));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_Cipher
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation to find the
// possible positions
let visited = new Array(500);
// Function to find the positions
function findSteps(current_row, current_column, curr, board_size, steps)
{
// Bound checking
if (current_row >= board_size ||
current_row < 0 ||
current_column >= board_size ||
current_column < 0 || curr > steps)
{
return;
}
// If steps is equal to current steps,
// that means current position is
// reached by Mirandote
if (curr == steps)
{
visited[current_row][current_column] = 1;
return;
}
// Recursive calls for each possible position.
// Position of a, b, c, ..., l given in
// above image.
/* a = */ findSteps(current_row - 2,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* b = */ findSteps(current_row - 2,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* c = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column - 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* d = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* e = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* f = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column + 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* g = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column - 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* h = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* i = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* j = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column + 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* k = */ findSteps(current_row + 2,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* l = */ findSteps(current_row + 2,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
}
function countSteps(current_row, current_column, board_size, steps)
{
// Initialize visited array to zero
for(let i = 0; i < board_size; i++)
{
visited[i] = new Array(board_size);
for(let j = 0; j < board_size; j++)
{
visited[i][j] = 0;
}
}
let answer = 0;
// Function call where initial step count is 0
findSteps(current_row, current_column, 0,
board_size,steps);
for(let i = 0; i < board_size; i++)
{
for(let j = 0; j < board_size; j++)
{
// If value of element is 1, that implies,
// the position can be reached by Mirandote.
if (visited[i][j] == 1)
{
answer++;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
let board_size = 8, steps = 1;
let current_row = 4, current_column = 4;
document.write(countSteps(current_row,
current_column,
board_size, steps));
</script>
12
La complejidad temporal del algoritmo anterior es O(12 S ), donde S es el número de pasos.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por sauravchandra1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA
