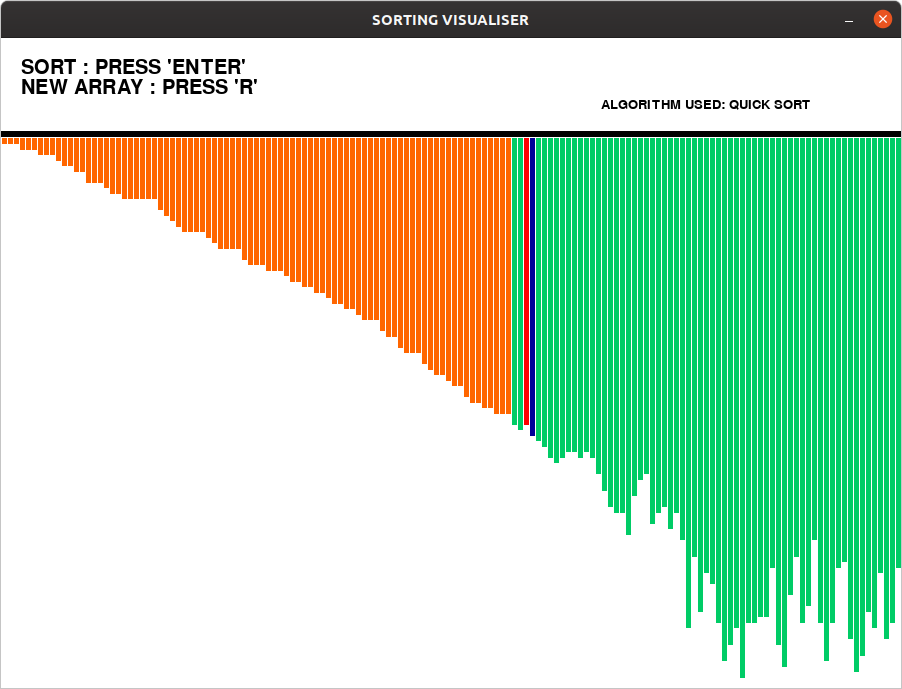
Un algoritmo como el algoritmo Quicksort es difícil de entender teóricamente. Podemos entender fácilmente visualizando este tipo de algoritmos. En este artículo se ha implementado un programa que visualiza el Algoritmo Quicksort .
La interfaz gráfica de usuario (GUI) se implementa en python utilizando la biblioteca pygame .
Acercarse:
- Se genera una array de valores aleatorios y se dibujan como líneas (barras) en la ventana.
- Dado que el algoritmo realiza la operación muy rápido, se ha utilizado pygame.time.delay() para ralentizar el proceso.
- Asigne teclas específicas para cada operación (comenzar a clasificar, restablecer barras).
- Las acciones se realizan utilizando
‘pygame.event.get()’el método, que almacena todos los eventos que realiza el usuario. - Se utilizan diferentes colores para indicar los tipos de barra.
- Verde: barra sin clasificar
- Azul – Barra de pivote
- Naranja – Barra ordenada
Ejemplos:
Entrada:
presione la tecla «Enter» para realizar la visualización.
Presione la tecla «r» para generar una nueva array.
Salida:
Inicial: Clasificación: Final:
Asegúrese de instalar la biblioteca pygame en su sistema.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del visualizador anterior:
Python
# Python implementation of the
# Sorting visualiser: Quick Sort
# Imports
import pygame
import random
pygame.font.init()
# Total window
screen = pygame.display.set_mode(
(900, 650)
)
# Title and Icon
pygame.display.set_caption("SORTING VISUALISER")
# Uncomment below lines for setting
# up the icon for the visuliser
# img = pygame.image.load('sort_icon.png')
# pygame.display.set_icon(img)
# Boolean variable to run
# the program in while loop
run = True
# Window size and some initials
width = 900
length = 600
array =[0]*151
arr_clr =[(0, 204, 102)]*151
clr_ind = 0
clr =[(0, 204, 102), (255, 0, 0),\
(0, 0, 153), (255, 102, 0)]
fnt = pygame.font.SysFont("comicsans", 30)
fnt1 = pygame.font.SysFont("comicsans", 20)
# Function to generate new Array
def generate_arr():
for i in range(1, 151):
arr_clr[i]= clr[0]
array[i]= random.randrange(1, 100)
# Initially generate a array
generate_arr()
# Function to refill the
# updates on the window
def refill():
screen.fill((255, 255, 255))
draw()
pygame.display.update()
pygame.time.delay(30)
# Sorting Algo:Quick sort
def quicksort(array, l, r):
if l<r:
pi = partition(array, l, r)
quicksort(array, l, pi-1)
refill()
for i in range(0, pi + 1):
arr_clr[i]= clr[3]
quicksort(array, pi + 1, r)
# Function to partition the array
def partition(array, low, high):
pygame.event.pump()
pivot = array[high]
arr_clr[high]= clr[2]
i = low-1
for j in range(low, high):
arr_clr[j]= clr[1]
refill()
arr_clr[high]= clr[2]
arr_clr[j]= clr[0]
arr_clr[i]= clr[0]
if array[j]<pivot:
i = i + 1
arr_clr[i]= clr[1]
array[i], array[j]= array[j], array[i]
refill()
arr_clr[i]= clr[0]
arr_clr[high]= clr[0]
array[i + 1], array[high] = array[high], array[i + 1]
return ( i + 1 )
# Function to Draw the
# array values
def draw():
# Text should be rendered
txt = fnt.render("SORT : PRESS 'ENTER'",\
1, (0, 0, 0))
# Position where text is placed
screen.blit(txt, (20, 20))
txt1 = fnt.render("NEW ARRAY : PRESS 'R'",\
1, (0, 0, 0))
screen.blit(txt1, (20, 40))
txt2 = fnt1.render("ALGORITHM USED: QUICK SORT",\
1, (0, 0, 0))
screen.blit(txt2, (600, 60))
element_width =(width-150)//150
boundry_arr = 900 / 150
boundry_grp = 550 / 100
pygame.draw.line(screen, (0, 0, 0),\
(0, 95), (900, 95), 6)
# Drawing the array values as lines
for i in range(1, 151):
pygame.draw.line(screen,\
arr_clr[i], (boundry_arr * i-3, 100),\
(boundry_arr * i-3,\
array[i]*boundry_grp + 100),\
element_width)
# Program should be run
# continuously to keep the window open
while run:
# background
screen.fill((255, 255, 255))
# Event handler stores all event
for event in pygame.event.get():
# If we click Close button in window
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
run = False
if event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:
if event.key == pygame.K_r:
generate_arr()
if event.key == pygame.K_RETURN:
quicksort(array, 1, len(array)-1)
draw()
pygame.display.update()
pygame.quit()
Producción: