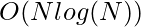Dada una array de 0 y 1 , si algún índice en particular i tiene el valor 1 , entonces es un índice seguro y si el valor es 0 , entonces es un índice inseguro . Un hombre que está parado en el índice -1 (fuente) solo puede aterrizar en un índice seguro y tiene que alcanzar el índice N (última posición). En cada salto, el hombre solo puede recorrer una distancia igual a cualquier número de Fibonacci . Debe minimizar el número de pasos, siempre que el hombre solo pueda saltar en dirección hacia adelante.
Nota: Los primeros números de Fibonacci son: 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21….
Ejemplos:
Entrada: arr[]= {0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}
Salida: 3
La persona saltará de:
1) índice -1 a índice 4 (una distancia de salto = 5)
2) índice 4 al índice 6 (una distancia de salto = 2)
3) índice 6 al destino (una distancia de salto = 5)
Entrada: arr[]= {0, 0}
Salida: 1
La persona saltará desde:
1) índice -1 al destino (una distancia de salto = 3)
Acercarse:
- Primero, crearemos una array fib[] para almacenar números de Fibonacci.
- Luego, crearemos una array DP y la inicializaremos con INT_MAX y el índice 0 DP[0] = 0 y nos moveremos de la misma manera que el problema de cambio de moneda con un número mínimo de monedas .
- La definición y recurrencia de DP es la siguiente:
DP[i] = min( DP[i], 1 + DP[i-fib[j]] ) where i is the current index and j denotes the jth fibonacci number of which the jump is possible
- Aquí DP[i] denota los pasos mínimos requeridos para alcanzar el índice i considerando todos los números de Fibonacci.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque:
C++
// A Dynamic Programming based// C++ program to find minimum// number of jumps to reach// Destination#include <bits/stdc++.h>usingnamespacestd;#define MAX 1e9// Function that returns the min// number of jump to reach the// destinationintminJumps(intarr[],intN){// We consider only those Fibonacci// numbers which are less than n,// where we can consider fib[30]// to be the upper bound as this// will cross 10^5intfib[30];fib[0] = 0;fib[1] = 1;for(inti = 2; i < 30; i++)fib[i] = fib[i - 1] + fib[i - 2];// DP[i] will be storing the minimum// number of jumps required for// the position i. So DP[N+1] will// have the result we consider 0// as source and N+1 as the destinationintDP[N + 2];// Base case (Steps to reach source is)DP[0] = 0;// Initialize all table values as Infinitefor(inti = 1; i <= N + 1; i++)DP[i] = MAX;// Compute minimum jumps required// considering each Fibonacci// numbers one by one.// Go through each positions// till destination.for(inti = 1; i <= N + 1; i++) {// Calculate the minimum of that// position if all the Fibonacci// numbers are consideredfor(intj = 1; j < 30; j++) {// If the position is safe// or the position is the// destination then only we// calculate the minimum// otherwise the cost is// MAX as defaultif((arr[i - 1] == 1|| i == N + 1)&& i - fib[j] >= 0)DP[i] = min(DP[i],1 + DP[i - fib[j]]);}}// -1 denotes if there is// no path possibleif(DP[N + 1] != MAX)returnDP[N + 1];elsereturn-1;}// Driver program to test above functionintmain(){intarr[] = { 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 };intn =sizeof(arr) /sizeof(arr[0]);cout << minJumps(arr, n);return0;}Java
// A Dynamic Programming based// Java program to find minimum// number of jumps to reach// Destinationimportjava.util.*;importjava.lang.*;classGFG{// Function that returns the min// number of jump to reach the// destinationpublicstaticintminJumps(intarr[],intN){intMAX =1000000;// We consider only those Fibonacci// numbers which are less than n,// where we can consider fib[30]// to be the upper bound as this// will cross 10^5int[] fib =newint[30];fib[0] =0;fib[1] =1;for(inti =2; i <30; i++)fib[i] = fib[i -1] + fib[i -2];// DP[i] will be storing the minimum// number of jumps required for// the position i. So DP[N+1] will// have the result we consider 0// as source and N+1 as the destinationint[] DP =newint[N +2];// Base case (Steps to reach source is)DP[0] =0;// Initialize all table values as Infinitefor(inti =1; i <= N +1; i++)DP[i] = MAX;// Compute minimum jumps required// considering each Fibonacci// numbers one by one.// Go through each positions// till destination.for(inti =1; i <= N +1; i++){// Calculate the minimum of that// position if all the Fibonacci// numbers are consideredfor(intj =1; j <30; j++){// If the position is safe// or the position is the// destination then only we// calculate the minimum// otherwise the cost is// MAX as defaultif((i == N +1||arr[i -1] ==1) &&i - fib[j] >=0)DP[i] = Math.min(DP[i],1+DP[i - fib[j]]);}}// -1 denotes if there is// no path possibleif(DP[N +1] != MAX)returnDP[N +1];elsereturn-1;}// Driver Codepublicstaticvoidmain (String[] args){int[] arr =newint[]{0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0};intn =11;intans = minJumps(arr, n);System.out.println(ans);}}// This code is contributed by MehulPython3
# A Dynamic Programming based Python3 program# to find minimum number of jumps to reach# DestinationMAX=1e9# Function that returns the min number# of jump to reach the destinationdefminJumps(arr, N):# We consider only those Fibonacci# numbers which are less than n,# where we can consider fib[30]# to be the upper bound as this# will cross 10^5fib=[0foriinrange(30)]fib[0]=0fib[1]=1foriinrange(2,30):fib[i]=fib[i-1]+fib[i-2]# DP[i] will be storing the minimum# number of jumps required for# the position i. So DP[N+1] will# have the result we consider 0# as source and N+1 as the destinationDP=[0foriinrange(N+2)]# Base case (Steps to reach source is)DP[0]=0# Initialize all table values as Infiniteforiinrange(1, N+2):DP[i]=MAX# Compute minimum jumps required# considering each Fibonacci# numbers one by one.# Go through each positions# till destination.foriinrange(1, N+2):# Calculate the minimum of that# position if all the Fibonacci# numbers are consideredforjinrange(1,30):# If the position is safe or the# position is the destination then# only we calculate the minimum# otherwise the cost is MAX as defaultif((arr[i-1]==1ori==N+1)andi-fib[j] >=0):DP[i]=min(DP[i],1+DP[i-fib[j]])# -1 denotes if there is# no path possibleif(DP[N+1] !=MAX):returnDP[N+1]else:return-1# Driver Codearr=[0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0]n=len(arr)print(minJumps(arr, n-1))# This code is contributed by Mohit KumarC#
// A Dynamic Programming based// C# program to find minimum// number of jumps to reach// DestinationusingSystem;usingSystem.Collections.Generic;classGFG{// Function that returns the min// number of jump to reach the// destinationpublicstaticintminJumps(int[]arr,intN){intMAX = 1000000;// We consider only those Fibonacci// numbers which are less than n,// where we can consider fib[30]// to be the upper bound as this// will cross 10^5int[] fib =newint[30];fib[0] = 0;fib[1] = 1;for(inti = 2; i < 30; i++)fib[i] = fib[i - 1] + fib[i - 2];// DP[i] will be storing the minimum// number of jumps required for// the position i. So DP[N+1] will// have the result we consider 0// as source and N+1 as the destinationint[] DP =newint[N + 2];// Base case (Steps to reach source is)DP[0] = 0;// Initialize all table values as Infinitefor(inti = 1; i <= N + 1; i++)DP[i] = MAX;// Compute minimum jumps required// considering each Fibonacci// numbers one by one.// Go through each positions// till destination.for(inti = 1; i <= N + 1; i++){// Calculate the minimum of that// position if all the Fibonacci// numbers are consideredfor(intj = 1; j < 30; j++){// If the position is safe// or the position is the// destination then only we// calculate the minimum// otherwise the cost is// MAX as defaultif((i == N + 1 ||arr[i - 1] == 1) &&i - fib[j] >= 0)DP[i] = Math.Min(DP[i], 1 +DP[i - fib[j]]);}}// -1 denotes if there is// no path possibleif(DP[N + 1] != MAX)returnDP[N + 1];elsereturn-1;}// Driver CodepublicstaticvoidMain (String[] args){int[] arr =newint[]{ 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0,1, 0, 0, 0, 0 };intn = 11;intans = minJumps(arr, n);Console.WriteLine(ans);}}// This code is contributed by Princi SinghJavaScript
<script>// A Dynamic Programming based// Javascript program to find minimum// number of jumps to reach// Destinationconst MAX = 1000000000;// Function that returns the min// number of jump to reach the// destinationfunctionminJumps(arr, N){// We consider only those Fibonacci// numbers which are less than n,// where we can consider fib[30]// to be the upper bound as this// will cross 10^5let fib =newArray(30);fib[0] = 0;fib[1] = 1;for(let i = 2; i < 30; i++)fib[i] = fib[i - 1] + fib[i - 2];// DP[i] will be storing the minimum// number of jumps required for// the position i. So DP[N+1] will// have the result we consider 0// as source and N+1 as the destinationlet DP =newArray(N + 2);// Base case (Steps to reach source is)DP[0] = 0;// Initialize all table values as Infinitefor(let i = 1; i <= N + 1; i++)DP[i] = MAX;// Compute minimum jumps required// considering each Fibonacci// numbers one by one.// Go through each positions// till destination.for(let i = 1; i <= N + 1; i++) {// Calculate the minimum of that// position if all the Fibonacci// numbers are consideredfor(let j = 1; j < 30; j++) {// If the position is safe// or the position is the// destination then only we// calculate the minimum// otherwise the cost is// MAX as defaultif((arr[i - 1] == 1|| i == N + 1)&& i - fib[j] >= 0)DP[i] = Math.min(DP[i],1 + DP[i - fib[j]]);}}// -1 denotes if there is// no path possibleif(DP[N + 1] != MAX)returnDP[N + 1];elsereturn-1;}// Driver program to test above functionlet arr = [ 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 ];let n = arr.length;document.write(minJumps(arr, n));</script>Producción:3
Complejidad del tiempo: