Dada una array Arr de enteros positivos y un valor X . La tarea es encontrar el número de valores que es mayor o igual a X .
Pero el giro es que los valores de la array siguen cambiando después de cada operación. Hay dos posibilidades:
- Si se selecciona el valor actual, todos los valores restantes de la array se reducirán en 1 .
- Si no se selecciona el valor actual, todos los valores restantes de la array se incrementarán en 1 .
Ejemplos:
Entrada: arr[] = {10, 5, 5, 4, 9}, X = 10
Salida: 2
Explicación:
Arr = {10, 5, 5, 4, 9}, pos = 0
Se selecciona 10
Arr = {10 , 4, 4, 3, 8}, pos = 1
4 no se elige
Arr = {10, 4, 5, 4, 9}, pos = 2
5 no se elige
Arr = {10, 4, 5, 5, 10 }, pos = 3
5 no se selecciona
Arr = {10, 4, 5, 5, 11}, pos = 4
11 se selecciona
Por lo tanto, se seleccionan dos elementos.
Entrada: arr[] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1}, X = 4
Salida: 1
Enfoque ingenuo: la idea es iterar a través de cada valor en una array y verificar si el i – ésimo valor es mayor, menor o igual que el valor requerido X. Si el i -ésimo valor es menor que el valor requerido, entonces aumente el valor desde (i+1) hasta el final de la array en 1 ; de lo contrario, si el i -ésimo valor es mayor o igual que el valor requerido, entonces disminuya el valor en 1 desde ( i+1) th al final de la array .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to count number
// of values greater or equal to x
int increaseDecreaseValue(int arr[],
int x, int n)
{
int TotalValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < x)
{
// Current value is less
// than required value
// then we need to increase
// the value from i + 1 to
// len(arr) by 1
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
arr[j] += 1;
}
}
else
{
// Current value is greater
// or equal to required
// value then we need to
// decrease the value from
// (i + 1) to len(arr)-1 by 1
TotalValue += 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[j] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
arr[j] -= 1;
}
}
}
}
return TotalValue;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int x = 4;
int arr[] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x, n);
cout << countValue;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to count number
// of values greater or equal to x
static int increaseDecreaseValue(int []arr, int x)
{
int TotalValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < x)
{
// Current value is less
// than required value
// then we need to increase
// the value from i + 1 to
// len(arr) by 1
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++)
{
arr[j] += 1;
}
}
else
{
// Current value is greater
// or equal to required
// value then we need to
// decrease the value from
// (i + 1) to len(arr)-1 by 1
TotalValue += 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++)
{
if (arr[j] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
arr[j] -= 1;
}
}
}
}
return TotalValue;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 4;
int[] arr = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
System.out.println(countValue);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Python3
# Python3 implementation # of the approach # Function to count number # of values greater or equal to x def increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x): TotalValue = 0 for i in range(len(arr)): if arr[i] < x: # Current value is less # than required value # then we need to increase # the value from i + 1 to # len(arr) by 1 for j in range(i + 1, len(arr)): arr[j] += 1 else: # Current value is greater # or equal to required # value then we need to # decrease the value from # (i + 1) to len(arr)-1 by 1 TotalValue += 1 for j in range(i + 1, len(arr)): if arr[j] == 0: continue arr[j] -= 1 return TotalValue # Driver Code if __name__ == "__main__": x = 4 arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] countValue =\ increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x) print(countValue)
C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to count number
// of values greater or equal to x
static int increaseDecreaseValue(int []arr, int x)
{
int TotalValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < x)
{
// Current value is less
// than required value
// then we need to increase
// the value from i + 1 to
// len(arr) by 1
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.Length; j++)
{
arr[j] += 1;
}
}
else
{
// Current value is greater
// or equal to required
// value then we need to
// decrease the value from
// (i + 1) to len(arr)-1 by 1
TotalValue += 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.Length; j++)
{
if (arr[j] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
arr[j] -= 1;
}
}
}
}
return TotalValue;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int x = 4;
int[] arr = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
Console.WriteLine(countValue);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation of the approach
// Function to count number
// of values greater or equal to x
function increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x)
{
let TotalValue = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < x)
{
// Current value is less
// than required value
// then we need to increase
// the value from i + 1 to
// len(arr) by 1
for (let j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++)
{
arr[j] += 1;
}
}
else
{
// Current value is greater
// or equal to required
// value then we need to
// decrease the value from
// (i + 1) to len(arr)-1 by 1
TotalValue += 1;
for (let j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++)
{
if (arr[j] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
arr[j] -= 1;
}
}
}
}
return TotalValue;
}
let x = 4;
let arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
let countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
document.write(countValue);
</script>
1
ime Complejidad: ![]()
Eficiente Enfoque:
- Este problema se puede optimizar aún más para
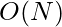 .
. - Aquí la idea principal es verificar cuánto debe cambiar este valor de índice.
- Esto se puede hacer usando una variable temporal, aquí es currentStatus que mantendrá el efecto neto en el índice actual por las decisiones anteriores.
- El efecto se agregará al valor de ese índice y eso nos dirá el valor original actualizado de la array.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Function to count number
// of values greater or equal to x
int increaseDecreaseValue(int arr[],
int x, int n)
{
int TotalValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < x)
{
// Current value is less
// than required value
// then we need to increase
// the value from i + 1 to
// len(arr) by 1
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
arr[j] += 1;
}
}
else
{
// Current value is greater
// or equal to required
// value then we need to
// decrease the value from
// (i + 1) to len(arr)-1 by 1
TotalValue += 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[j] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
arr[j] -= 1;
}
}
}
}
return TotalValue;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int x = 4;
int arr[] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x, n);
cout << countValue;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG
{
// Function to count number
// of students got selected
static int increaseDecreaseValue(int arr[], int x)
{
int currentStatus = 0;
int totalValue = 0;
int i;
int len = arr.length;
for (i = 0; i < len ; i++ )
{
// Adding currentStatus to the
// value of that index to get
// the original value
// if it is less than X
if (arr[i] + currentStatus < x)
currentStatus += 1;
else
{
currentStatus -= 1;
totalValue += 1;
}
}
return totalValue;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int x = 4;
int arr[] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
System.out.println(countValue);
}
}
// This code is contributed by AnkitRai01
Python3
# Python3 implementation # of the approach # Function to count number # of students got selected def increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x): currentStatus = 0 totalValue = 0 for i in arr: # Adding currentStatus to the # value of that index to get # the original value # if it is less than X if i + currentStatus < x: currentStatus += 1 else: currentStatus -= 1 totalValue += 1 return totalValue # Drivers Code if __name__ == "__main__": x = 4 arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x) print(countValue)
C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to count number
// of students got selected
static int increaseDecreaseValue(int []arr,
int x)
{
int currentStatus = 0;
int totalValue = 0;
int i;
int len = arr.Length;
for (i = 0; i < len ; i++ )
{
// Adding currentStatus to the
// value of that index to get
// the original value
// if it is less than X
if (arr[i] + currentStatus < x)
currentStatus += 1;
else
{
currentStatus -= 1;
totalValue += 1;
}
}
return totalValue;
}
// Driver Code
static public void Main ()
{
int x = 4;
int []arr = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
Console.Write(countValue);
}
}
// This code is contributed by ajit.
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation of the approach
// Function to count number
// of students got selected
function increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x)
{
let currentStatus = 0;
let totalValue = 0;
let i;
let len = arr.length;
for (i = 0; i < len ; i++ )
{
// Adding currentStatus to the
// value of that index to get
// the original value
// if it is less than X
if (arr[i] + currentStatus < x)
currentStatus += 1;
else
{
currentStatus -= 1;
totalValue += 1;
}
}
return totalValue;
}
let x = 4;
let arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
let countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
document.write(countValue);
</script>
1
Complejidad del tiempo: ![]()