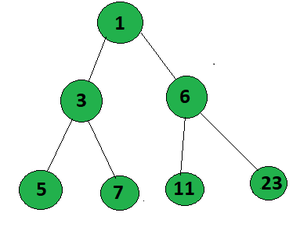
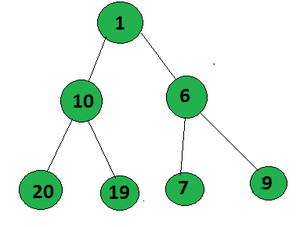
Dado un árbol binario, la tarea es contar todos los caminos desde la raíz hasta la hoja, lo que forma una progresión aritmética .
Ejemplos:
Aporte:
Salida: 2
Explicación:
Las rutas que forman un AP en el árbol dado desde la raíz hasta la hoja son:
- 1->3->5 (AP con diferencia común 2)
- 1->6->11 (AP con diferencia común 5)
Aporte:
Salida: 1
Explicación:
La ruta que forma un AP en el árbol dado desde la raíz hasta la hoja es 1->10->19 (AP con diferencia 9)
Enfoque: El problema se puede resolver usando Preorder Traversal . Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Realice Preorder Traversal en el árbol binario dado.
- Inicialice una array arr[] para almacenar la ruta.
- Inicialice el conteo = 0, para almacenar el conteo de rutas que forman un AP
- Después de llegar al Node hoja, verifique si los elementos actuales en la array (es decir, los valores del Node desde la raíz hasta la ruta hoja) forman un AP .
- Si es así, incremente el conteo
- Después del recorrido completo del árbol, imprima el conteo.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation to count
// the path which forms an A.P.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int count = 0;
// Node structure
struct Node {
int val;
// left and right child of the node
Node *left, *right;
// initialization constructor
Node(int x)
{
val = x;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
// Function to check if path
// format A.P. or not
bool check(vector<int> arr)
{
if (arr.size() == 1)
return true;
// if size of arr is greater than 2
int d = arr[1] - arr[0];
for (int i = 2; i < arr.size(); i++) {
if (arr[i] - arr[i - 1] != d)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Function to find the maximum
// setbits sum from root to leaf
int countAP(Node* root, vector<int> arr)
{
if (!root)
return 0;
arr.push_back(root->val);
// If the node is a leaf node
if (root->left == NULL
&& root->right == NULL) {
if (check(arr))
return 1;
return 0;
}
// Traverse left subtree
int x = countAP(root->left, arr);
// Traverse the right subtree
int y = countAP(root->right, arr);
return x + y;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(3);
root->right = new Node(6);
root->left->left = new Node(5);
root->left->right = new Node(7);
root->right->left = new Node(11);
root->right->right = new Node(23);
cout << countAP(root, {});
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation to count
// the path which forms an A.P.
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
int count = 0;
// Node structure
static class Node
{
int val;
// left and right child of the node
Node left, right;
// Initialization constructor
Node(int x)
{
val = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
};
// Function to check if path
// format A.P. or not
static boolean check(Vector<Integer> arr)
{
if (arr.size() == 1)
return true;
// If size of arr is greater than 2
int d = arr.get(1) - arr.get(0);
for(int i = 2; i < arr.size(); i++)
{
if (arr.get(i) - arr.get(i - 1) != d)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Function to find the maximum
// setbits sum from root to leaf
static int countAP(Node root,
Vector<Integer> arr)
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
arr.add(root.val);
// If the node is a leaf node
if (root.left == null &&
root.right == null)
{
if (check(arr))
return 1;
return 0;
}
// Traverse left subtree
int x = countAP(root.left, arr);
// Traverse the right subtree
int y = countAP(root.right, arr);
return x + y;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(6);
root.left.left = new Node(5);
root.left.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left = new Node(11);
root.right.right = new Node(23);
System.out.print(countAP(root, new Vector<Integer>()));
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Python3
# Python3 implementation to count # the path which forms an A.P. # Node structure class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.val = x self.left = None self.right = None # Function to check if path # format A.P. or not def check(arr): if len(arr) == 1: return True # If size of arr is greater than 2 d = arr[1] - arr[0] for i in range(2, len(arr)): if arr[i] - arr[i - 1] != d: return False return True # Function to find the maximum # setbits sum from root to leaf def countAP(root, arr): if not root: return 0 arr.append(root.val) # If the node is a leaf node if (root.left == None and root.right == None): if check(arr): return 1 return 0 # Traverse the left subtree x = countAP(root.left, arr) # Traverse the right subtree y = countAP(root.right, arr) return x + y # Driver code root = Node(1) root.left = Node(3) root.right = Node(6) root.left.left = Node(5) root.left.right = Node(7) root.right.left = Node(11) root.right.right = Node(23) print(countAP(root, [])) # This code is contributed by stutipathak31jan
C#
// C# implementation to count
// the path which forms an A.P.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
//int count = 0;
// Node structure
class Node
{
public int val;
// left and right child of the node
public Node left, right;
// Initialization constructor
public Node(int x)
{
val = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
};
// Function to check if path
// format A.P. or not
static bool check(List<int> arr)
{
if (arr.Count == 1)
return true;
// If size of arr is greater than 2
int d = arr[1] - arr[0];
for(int i = 2; i < arr.Count; i++)
{
if (arr[i] - arr[i - 1] != d)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Function to find the maximum
// setbits sum from root to leaf
static int countAP(Node root,
List<int> arr)
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
arr.Add(root.val);
// If the node is a leaf node
if (root.left == null &&
root.right == null)
{
if (check(arr))
return 1;
return 0;
}
// Traverse left subtree
int x = countAP(root.left, arr);
// Traverse the right subtree
int y = countAP(root.right, arr);
return x + y;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(6);
root.left.left = new Node(5);
root.left.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left = new Node(11);
root.right.right = new Node(23);
Console.Write(countAP(root, new List<int>()));
}
}
// This code is contributed by amal kumar choubey
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript implementation to count
// the path which forms an A.P.
let count = 0;
// Node structure
class Node
{
// Initialize constructor
constructor(x)
{
this.val = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
var root;
// Function to check if path
// format A.P. or not
function check(arr)
{
if (arr.length == 1)
return true;
// If size of arr is greater than 2
let d = arr[1] - arr[0];
for(let i = 2; i < arr.length; i++)
{
if (arr[i] - arr[i - 1] != d)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Function to find the maximum
// setbits sum from root to leaf
function countAP(root, arr)
{
if (!root)
return 0;
arr.push(root.val);
// If the node is a leaf node
if (root.left == null &&
root.right == null)
{
if (check(arr))
return 1;
return 0;
}
// Traverse left subtree
let x = countAP(root.left, arr);
// Traverse the right subtree
let y = countAP(root.right, arr);
return x + y;
}
// Driver Code
root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(6);
root.left.left = new Node(5);
root.left.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left = new Node(11);
root.right.right = new Node(23);
let arr = [];
document.write(countAP(root, arr));
// This code is contributed by Dharanendra L V.
</script>
Producción:
2
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(h), donde h es la altura del árbol binario.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por mohit kumar 29 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA